MSS User Guide
Technical Support
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
Sales Offices
Disclaimer & Revisions
Contents
Configuration
Using the MSS
Compliance and Warranty Information
MSS Family Features
Introduction to the MSS Family
Protocols
Terms
About The Documentation
MSS User Guide Introduction to the MSS Family
MSS-VIA Installation
Installation
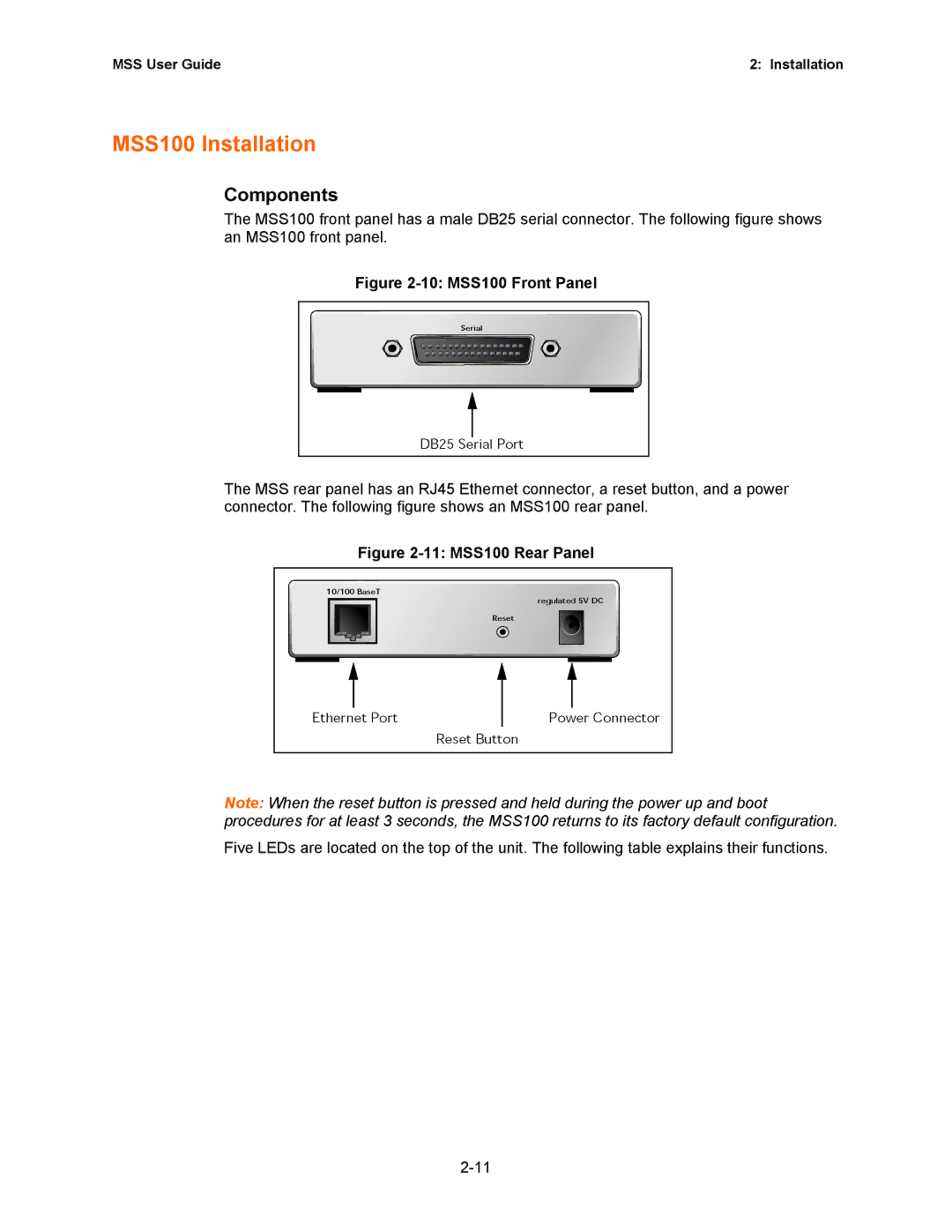
Components
MSS-VIA Rear Panel
MSS-VIA LEDs
Installation Procedure
Example Wired Network Layout
MSS User Guide Installation
Pinging the MSS
Temperature
MSS-VIA Specifications
Power power cube adaptor
Humidity
MSS4 Installation
MSS4 Components
MSS4 LEDs
MSS Connected to a Serial Device and Network
MSS User Guide Installation
MSS4 Specifications
MSS100 Installation
10 MSS100 Front Panel
MSS100 LEDs
12 MSS Network Layout
13 MSS Connected to Serial Device and Ethernet
MSS100 Specifications
14 Pinging the MSS
Getting Started
Privileged User Status
Using a Web Browser
IP Address Configuration
Using EZWebCon
From the Action menu, select Assign IP Address
Using ARP and Ping
Entering ARP and Ping Unix
Using a DHCP, BOOTP, or Rarp Reply
Using the Serial Console
Incoming TCP/IP Logins
Incoming Logins
Login Password
Web Browser Login and Configuration
Rlogin
Serial Port Logins
EZWebCon Login and Configuration
Telnet
Remote Console Logins
Changing the Login Password
Incoming LAT Logins
Outbound Connections
Logout
Normal Reboot
Configuration
Rebooting the MSS
Overview
Factory Defaults
Protocol Configuration
TCP/IP Configuration
Specifying a Gateway for MSS-VIA and MSS4
Name Server
IP Security
Supported Mibs
Snmp Trap Support
IPX NetWare Configuration
Configuring Snmp
Routing and Encapsulation
Internal Network Number
Loadhost
Circuit Timer
LAT Configuration
Service Groups
Server Identification
RS-485 Configuration
Two-Wire Mode
Four-Wire Mode
22 Enabling Two-Wire RS-485 Mode for MSS4
TXDrive
Termination
Access Mode
Serial Port Configuration
Autostart
36 Configuring an Autostart Character for MSS-VIA and MSS4
Serial Data
Baud Rate
Character Size, Parity, and Stop Bits
Modems and Modem Signaling
Flow Control
Modem Control
Signal Checking
DSRLogout
Logouts
DTRWait
Preferred Host
Configuration
Dedicated Host
Enabling 802.11 Networking
Region
Extended Service Set ID Essid
MAC Address
Setting the WEP Key and Index Number
Network Mode
Channel
Modem Cards
Formatting an ATA Flash Card
Encrypted Traffic
Incoming Calls
Outgoing Calls
Incoming Connections
Using the MSS
Socket Connections
Outbound Connections
Interactive Connections
TCP/IP Socket Connections
Backward, Forward, and Switches
Break Key and Local Switch
Session Control
Session Limits
Status Displays
Disconnect and Resume
Show
Serial Tunnel
TCP Configuration
UDP Configuration
Multihost Mode
Enabling Multihost Mode
Adding Hosts
Modem Emulation Mode
Removing Hosts
Modem Mode Commands
17. Enabling Modem Mode for MSS100
Wiring Requirements
Sequential Hostlist Mode
COM Port Redirector
Power-up Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Power-up Problems and Error Messages
Dhcp Troubleshooting
Dhcp Troubleshooting
Bootp Troubleshooting
Bootp Troubleshooting
Modem Configuration Checklist
Rarp Troubleshooting
Tftp Troubleshooting
Rarp Troubleshooting
Change Bootp Enabled, Disabled
Entering Commands at the Boot Prompt
Init
Change Ipaddress ipaddress
Change Dhcp Enabled, Disabled
Change Hardware
Change Loadhost ipaddress
Technical Support
Technical Support Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Serial Connectors
Ethernet Connector
MSS VIA Connectors
Pinouts
RS-232 DB9 Connector
MSS4 Connectors
RS-485 DB9 Connectors
DB25 Connector
MSS100 Connectors
RS-232 DB9 Connectors
DSR Data Signal Ready versus CD Carrier Detect
Modem Wiring
DTR Data Terminal Ready
Reloading Software
Updating Software
Obtaining Software
Via the Web Via FTP
FTP
Flash ROM Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Flash ROM Updates
NetWare
MSS User Guide Updating Software
Compliance and Warranty Information
Compliance Information
Warranty