Spanning Tree Protocol
The spanning tree protocol allows you to configure the STP parameters on network Ethernet interface.
To provide path redundancy to prevent undesirable loops,
STP is a technology that allows bridges to communicate with each other to discover physical loops in the network. The protocol then specifies an algorithm that bridges can use to create a
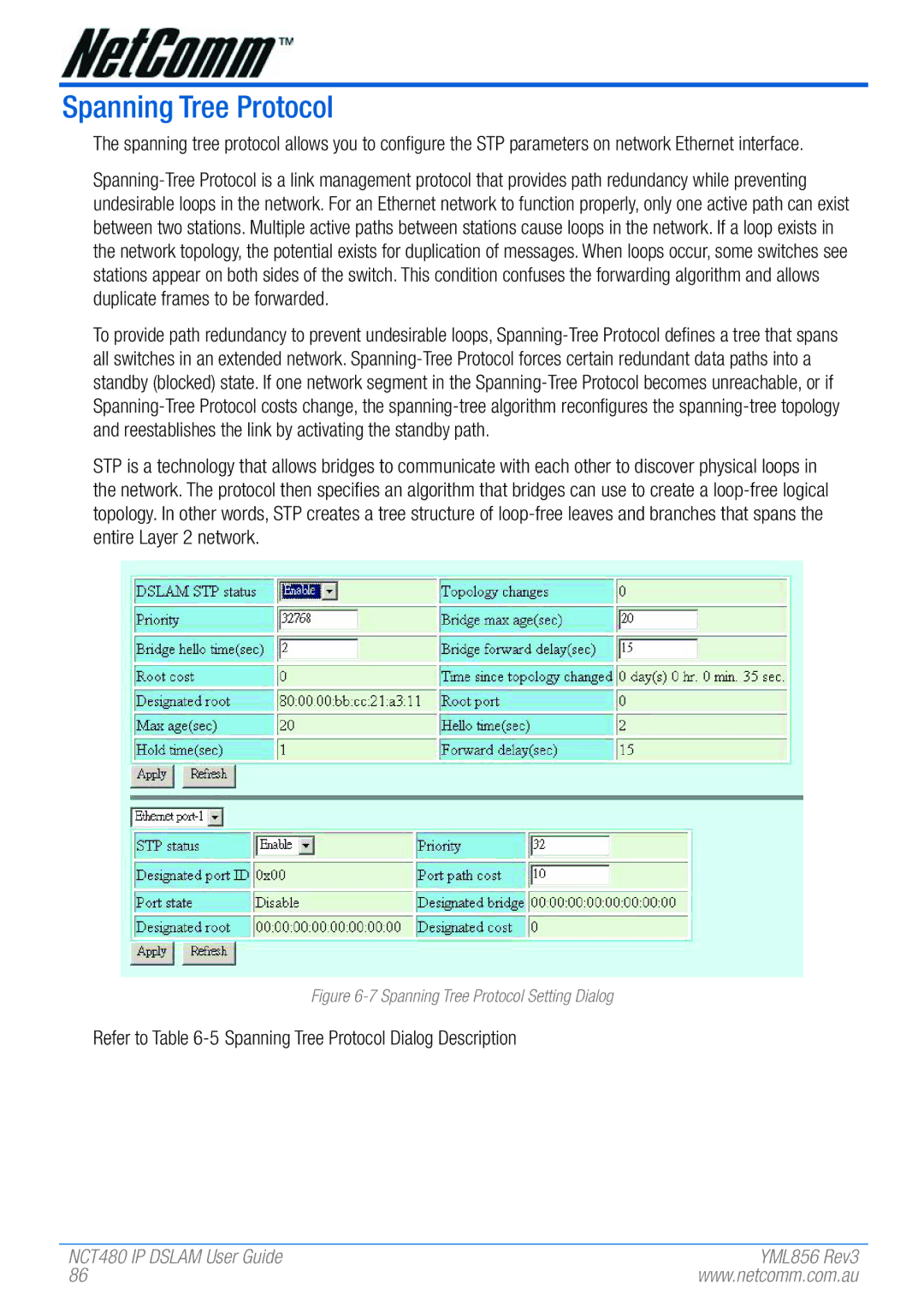
Figure 6-7 Spanning Tree Protocol Setting Dialog
Refer to Table
NCT480 IP DSLAM User Guide | YML856 Rev3 |
86 | www.netcomm.com.au |