11-168 User’s Reference Guide
Basic Firewall blocks undesirable traffic originating from the WAN (in most cases, the Internet), but forwards all traffic originating from the LAN. It follows the conservative “that which is not expressly permitted is prohibited” approach: unless an incoming packet expressly matches one of the constituent input filters, it will not be forwarded to the LAN.
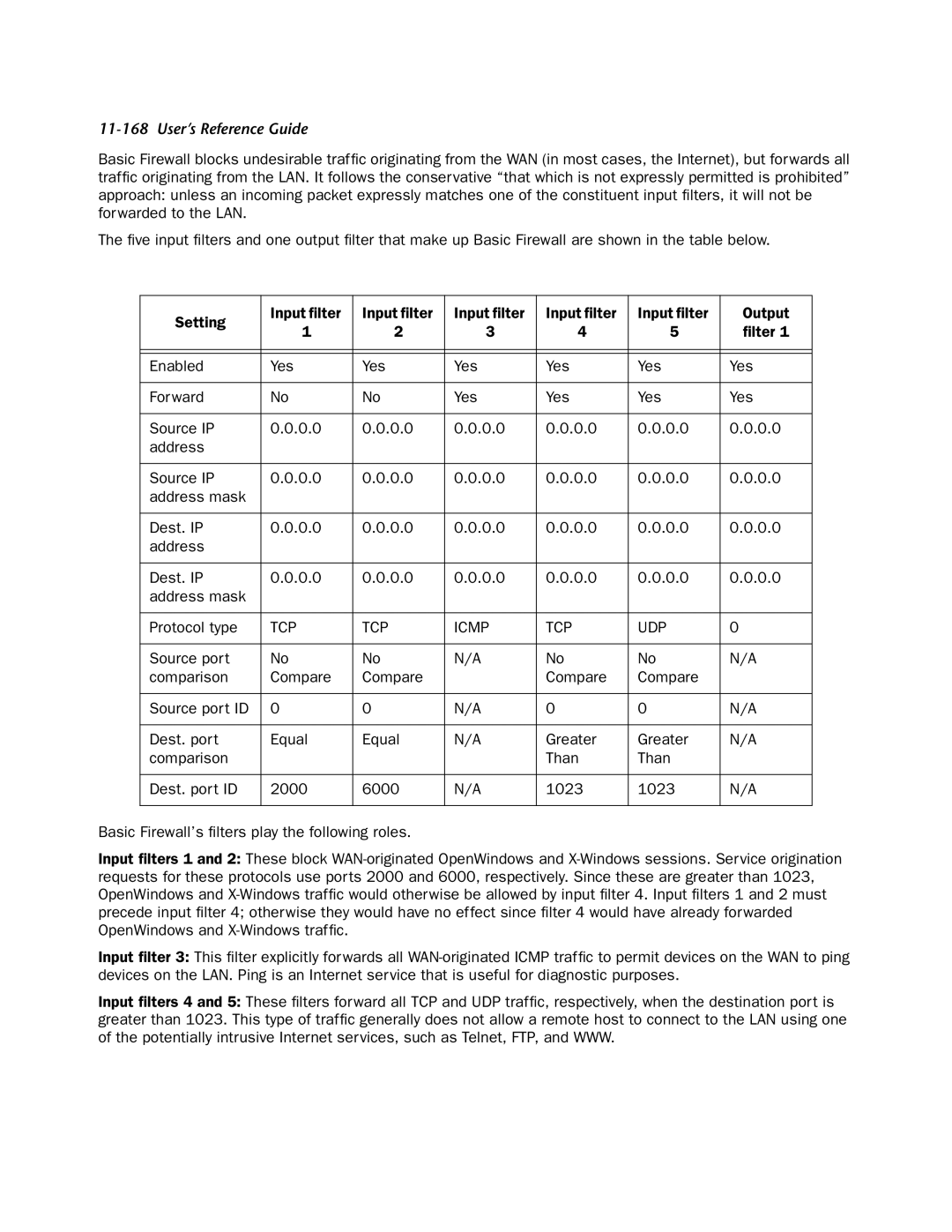
The five input filters and one output filter that make up Basic Firewall are shown in the table below.
Setting | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Input filter | Output | |
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | filter 1 | ||
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Enabled | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Forward | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address mask |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. IP | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0.0.0.0 | |
address mask |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Protocol type | TCP | TCP | ICMP | TCP | UDP | 0 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source port | No | No | N/A | No | No | N/A | |
comparison | Compare | Compare |
| Compare | Compare |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Source port ID | 0 | 0 | N/A | 0 | 0 | N/A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. port | Equal | Equal | N/A | Greater | Greater | N/A | |
comparison |
|
|
| Than | Than |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dest. port ID | 2000 | 6000 | N/A | 1023 | 1023 | N/A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Firewall’s filters play the following roles.
Input filters 1 and 2: These block
Input filter 3: This filter explicitly forwards all
Input filters 4 and 5: These filters forward all TCP and UDP traffic, respectively, when the destination port is greater than 1023. This type of traffic generally does not allow a remote host to connect to the LAN using one of the potentially intrusive Internet services, such as Telnet, FTP, and WWW.