Operating Instructions
Model Number SC-07 / SC-05 Responsible Party Name
Operating Environment
Federal Communications Commission Declaration of Conformity
Keep in a Secure AREA. this is for Your Security
Risk of Electric Shock Do not Open
Wash hands after handling
Contents
Other connections
Other Settings
Using other functions
Playback with Home Media Gallery inputs
Controlling the rest of your system
Additional information
Before you start Chapter
Installing the receiver
Before you start
Checking what’s in the box
Introduction to home theater
Simple Home Theater Guide
Simple Home Theater Guide Chapter
Listening to Surround Sound
Follow the instructions on-screen
1a.Full Auto Mcacc
Playing a source
Problems when using the Auto Mcacc Setup
Simple Home Theater Guide
Select the input source you want to play
Phase Control on
Using Phase Control
Phase Control OFF
Source.1
Phase Control indicator on the front panel lights
Using Full Band Phase Control
Full Band Phase Control OFF
Full Band Phase Control on
Fullband PHASE.1
Rear panel
Connecting your equipment
Connecting your equipment Chapter
Connecting your equipment
When making cable connections
If you have an Hdmi or DVI with Hdcp equipped
Connecting your equipment About the video converter
Connecting using Hdmi
About Hdmi
Be careful to connect the terminal in the proper direction
Connect using an Hdmi cable
SC-07
Connecting your equipment Connecting your TV and DVD player
STB
For a second recorder, use the DVR 2 in inputs
Connecting your equipment Using the component video jacks
Use a three-way component video cable
Use an optical cable for the connection
Connecting your equipment Connecting digital audio sources
About the WMA9 Pro decoder
Connecting your equipment Connecting analog audio sources
Connecting a component to the front panel inputs
Connecting your equipment Installing your speaker system
Connecting the speakers
Banana plug connections
Bare wire connections
Placing the speakers
Connecting antennas
THX speaker system setup
Plugging in the receiver
FM wire antenna
Connecting external antennas
AM loop antenna
Front panel
Controls and displays
Controls and displays Chapter
STANDBY/ON
Operating range of remote control unit
Controls and displays
Controls and displays Display
Multi Operation
Controls and displays Remote control
RECEIVER
Input Select
SOURCE
Mute
Listening in surround sound
Listening to your system
Listening to your system Chapter
Auto playback
Listening to your system
Using the Home THX modes
Using the Advanced surround effects
PRO LOGIC+THX Cinema
Tip
Using Front Stage Surround Advance
Listening in stereo
Choosing the input signal
Listening to your system Using Stream Direct
Selecting Mcacc presets
Hdmi Digital Analog
Hdmi Digital
Using surround back channel processing
Using the Virtual Surround Back mode
Auto
Pro Logic
Mode
Listening to the radio
Using the tuner
Using the tuner Chapter
Listening to station presets
Using the tuner Saving station presets
Naming station presets
Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
Advanced Mcacc menu
Making receiver settings from the Advanced Mcacc menu
Select the setting you want to adjust
Advanced Mcacc menu Chapter
Use / to select the item, then use / to set
Advanced Mcacc menu Automatic Mcacc Expert
Select the parameters you want to set
Advanced Mcacc 1b.Auto Mcacc
If necessary, confirm the speaker configuration in the OSD.2
Advanced Mcacc menu
1c.Manual Mcacc
Manual Mcacc setup
Mcacc Data Check
Fine Channel Level
Fine Speaker Distance
Adjust the parameters for the Standing Wave Control
Acoustic Calibration EQ Adjust
Select ‘Standing Wave’ from the Manual Mcacc setup menu
Standing Wave
Select ‘EQ Adjust’ from the Manual Mcacc setup menu
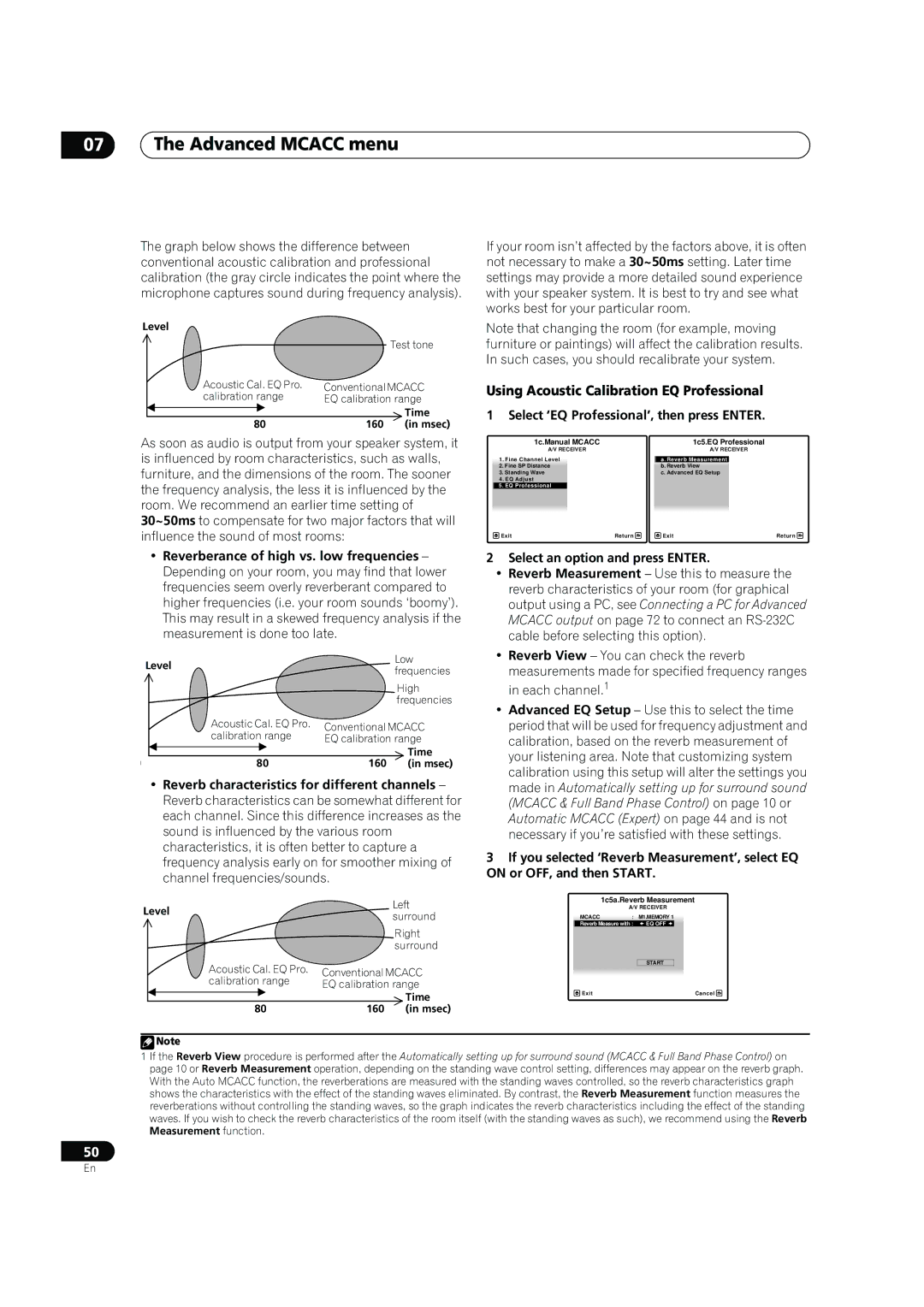
How to use Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
How to interpret the graphical output
Select the channels you want and adjust to your liking
Select an option and press Enter
Using Acoustic Calibration EQ Professional
Select ‘EQ Professional’, then press Enter
1c.Manual Mcacc 1c5.EQ Professional
Checking Mcacc Data
Set the operation selector switch to RCV, then press
Select the setting you want to check
Select ‘MCACC Data Check’ from the Home Menu
Speaker Distance
Speaker Setting
Channel Level
Standing Wave
Acoustic Cal EQ
Group Delay
Data Management
Copying Mcacc preset data
Renaming Mcacc presets
Clearing Mcacc presets
Making receiver settings from the System Setup menu
System Setup menu
System Setup menu Chapter
Manual speaker setup
Speaker Setting
System Setup menu
Surround back speaker setting
Confirm your selected setup option
Select ‘Channel Level’ from the Manual SP Setup menu
Select a setup option
Adjust the level of each channel using /
Curve
THX Audio Setting
Speaker Distance
4a.Manual SP Setup 4a6.THX Audio Setting
Other connections
Using XM Radio
Connecting your XM Radio receiver
Other connections Chapter
Saving channel presets
Using Sirius Radio
Using XM HD Surround
Using the XM Menu
Listening to Sirius Radio
Connecting your SiriusConnect Tuner
Press Sirius to switch to the Sirius input
Chuck Berry
Selecting the multichannel analog inputs
Connecting the multichannel analog inputs
Using the Sirius Menu
Use Input Select to select Multi CH
Speaker B setting only.1
Speaker B setup
Switching the speaker system
Bi-amping your speakers
Make sure that the + / connections are properly inserted
Connecting additional amplifiers
Bi-wiring your speakers
Large
MULTI-ZONE listening options
Other connections MULTI-ZONE listening
Making MULTI-ZONE connections
ZONE2
Audio
Basic MULTI-ZONE setup Zone
MULTI-ZONE setup using speaker terminals Zone
Digital Audio
Using the MULTI-ZONE controls
Secondary MULTI-ZONE setup Zone
Panel
Input Use to select the input source in the currently
Connecting an IR receiver
Button What it does
Select selected sub zone
Using this receiver with a Pioneer flat panel TV
Or off just by pressing the input functions you’ve set on
Using the SR+ mode with a Pioneer flat panel TV
DVD
System must have internet access
Other connections Connecting a PC for Advanced Mcacc output
Advanced Mcacc output using your PC
Mcacc Data Check 2g.Output PC
Steps to enjoy the Home Media Gallery
Playback with Home Media Gallery inputs
Playback with Home Media Gallery inputs Chapter
Specifications of a LAN terminal
Connecting to the network through LAN interface
Connecting an iPod
Playback with Home Media Gallery inputs
Windows Media Connect
Introduction
About network playback
Windows Media DRM
Playback with Home Media Gallery
Content playable over a network
Server without the mark cannot be accessed
Authorizing this receiver
Case of a USB memory device or a server
Enter
Item. To return to the list screen, press Return
Repeat to play back the desired song or photo
To return to the previous level any time, press
About the playback screen
Finding what you want to play
Use / to browse the selected category e.g., albums
Finding what you want to play
Switching the iPod controls1
Playing back audio files stored on a USB memory device
Basic playback controls
About Internet radio
Reconnect the USB device with the receiver switched
Listening to Internet radio stations
Off
Saving and retrieving Internet radio stations
Use / to select ‘Get access code’, then press
About list of Internet radio
Use / to select ‘Help’, then press Enter
About Neural Music Direct
Listening to Neural Music Direct
Playing back your favorite songs
About the Favorites folder
About playable file formats
Music files
Saving Internet radio stations
Setting up the network
Advanced operations for Internet radio
Retrieving saved Internet radio stations
Select ‘Change’ and press Enter to confirm your selection
Select ‘Setup’ and press Enter to confirm your selection
Proxy Hostname/Proxy Port
Enter the IP address
Enter the alternate DNS server address
Checking the network settings
Press Enter to complete the network setup procedure
Enter the address of your proxy server or Domain name
Dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server
Software update
Default Gateway
Glossary
Mass Storage Class devices
MAC Media Access Control address
IP Internet Protocol address
Neural Surround
Making the Hdmi Control connections
Hdmi Control
Hdmi Control Chapter
Setting the Hdmi Control mode
Hdmi Control Setting the Hdmi options
Before using synchronization
Setup
Canceling synchronized amp mode
Hdmi Control Synchronized amp mode
Synchronized amp mode operations
About Hdmi Control
Input Setup menu
Other Settings
Other Settings Chapter
Component
Changing the OSD display language OSD Language
Other Settings
Input function default and possible settings
Language used on the on-screen display can be changed
Select ‘Multi Ch In Setup’ from the Other Setup menu
Other Settings Other Setup menu
Multi Channel Input Setup
Select the ‘SW Input Gain’ setting you want
Flicker Reduction Setup
Zone Audio Setup
SR+ Setup for Pioneer flat panel TVs
Setting the Audio options
Using other functions
Using other functions Chapter
Press Return to confirm and exit the menu
Using other functions
Making an audio or a video recording
Using other functions Setting the Video options
Current source, setting and status of the receiver
Video Parameter menu, it is unavailable due to
Dimming the display
Using the sleep timer
Reducing the level of an analog signal
Resetting the system
Using other functions Switching the Hdmi output
Checking your system settings
Hdmi OUT
MULTI-ZONE
Default system settings
Setting Default
SR+
Controlling the rest of your system
Setting the remote to control other components
Selecting preset codes directly
Controlling the rest of your system Chapter
Press and hold the button to be erased for two seconds
Erasing one of the remote control button settings
Use / to select ERASE, then press Enter
Controlling the rest of your system
Resetting the remote control presets
Confirming preset codes
Renaming input source names
Programming a multi-operation or a shutdown sequence
Select the button for the command you want to input
Following remote control commands can be selected
Controls for TVs
Using multi operations
Using System off
Press Multi Operation
CLR
SOURCE
& Enter
Decide which component you want to use the remote sensor
Additional information Chapter
Speaker Setting Guide
Additional information
Positioning and adjusting the subwoofer
Additional information
Position of center speaker and monitor
Positional relationship between speakers and monitor
Position of front speakers and monitor
Symptom Remedy
Additional information Troubleshooting
Power
Digital Video Scaler
No sound
Other audio problems
Symptom
Settings
Video
SEL
Professional Calibration EQ graphical output
Display
Remote control
Hdcp Error shows
Configuration a
Configuration B
Important information regarding the Hdmi connection
Symptoms
Causes Remedies Refer to
Symptoms Causes Remedies Refer to
XM radio messages
Symptom Cause
About status messages
Status messages Descriptions
Hdmi C ERR 1B0
Sirius radio messages
Hdmi C ERR 1A0
Hdmi C ERR 1C0
Additional information Surround sound formats
Dolby
DTS Neo6
Windows Media Audio 9 Professional
DTS Digital Surround
DTS 96/24
Additional information About THX
THX Loudness Plus Description
About Neural THX Surround
THX Games
THX Ultra2/Select2 Cinema
About Flac
Additional information About XM
About Sirius
Flac Decoder
Auto Surround
Stereo 2 channel signal formats
Input signal format Standard
ON/AUTO
129
PRO LOGIC+THX
130
131
132
Multichannel signal formats
Input signal format
Additional information Specifications
Our philosophy
Additional information Cleaning the unit
Features
Home Media Gallery
Hdmi and digital video conversion
THX certified design In case of SC-07
THX certified design In case of SC-05
DCDi
Decibel Level Example
To establish a safe level
Once you have established a comfortable sound level
Pioneer Corporation