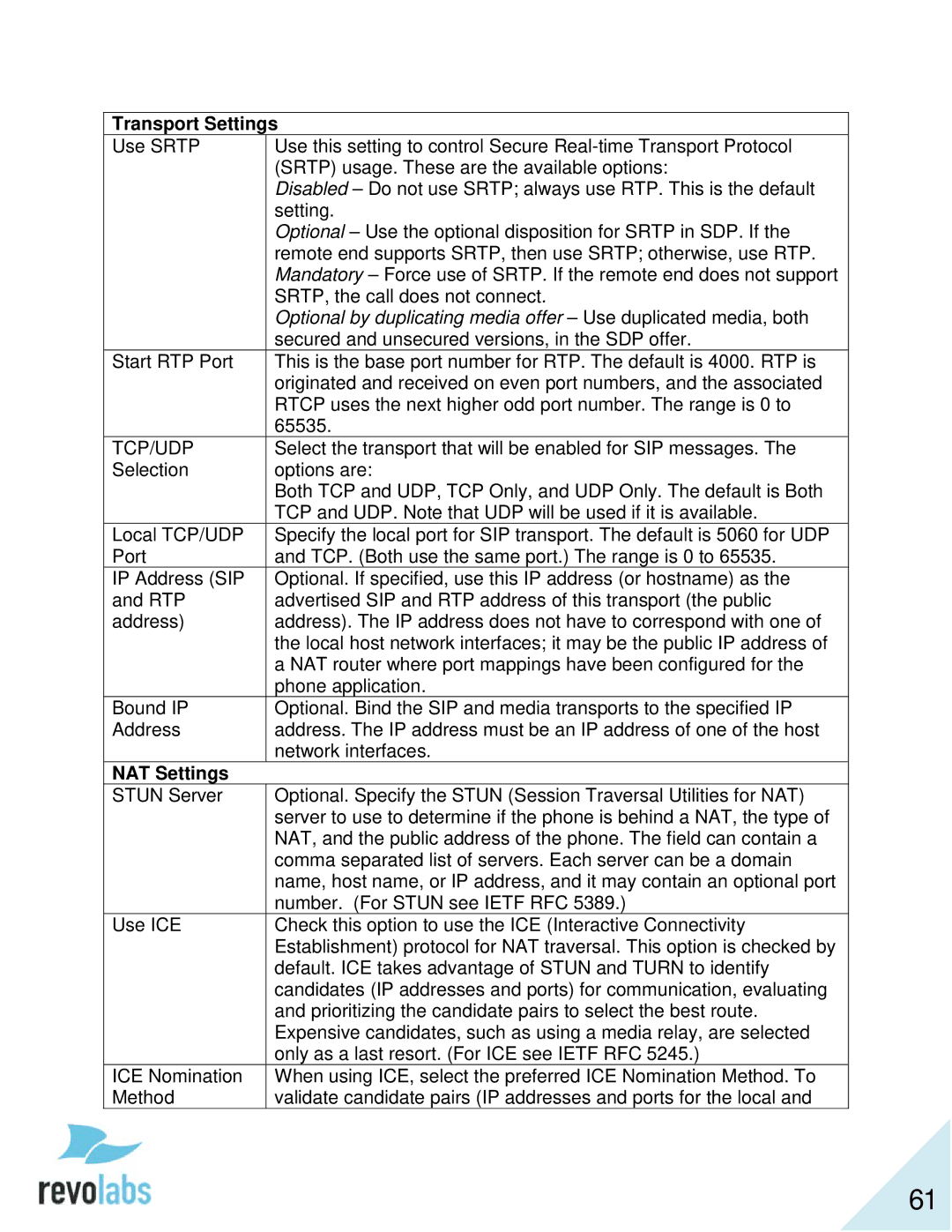
Transport Settings
Use SRTP | Use this setting to control Secure |
| (SRTP) usage. These are the available options: |
| Disabled – Do not use SRTP; always use RTP. This is the default |
| setting. |
| Optional – Use the optional disposition for SRTP in SDP. If the |
| remote end supports SRTP, then use SRTP; otherwise, use RTP. |
| Mandatory – Force use of SRTP. If the remote end does not support |
| SRTP, the call does not connect. |
| Optional by duplicating media offer – Use duplicated media, both |
| secured and unsecured versions, in the SDP offer. |
Start RTP Port | This is the base port number for RTP. The default is 4000. RTP is |
| originated and received on even port numbers, and the associated |
| RTCP uses the next higher odd port number. The range is 0 to |
| 65535. |
TCP/UDP | Select the transport that will be enabled for SIP messages. The |
Selection | options are: |
| Both TCP and UDP, TCP Only, and UDP Only. The default is Both |
| TCP and UDP. Note that UDP will be used if it is available. |
Local TCP/UDP | Specify the local port for SIP transport. The default is 5060 for UDP |
Port | and TCP. (Both use the same port.) The range is 0 to 65535. |
IP Address (SIP | Optional. If specified, use this IP address (or hostname) as the |
and RTP | advertised SIP and RTP address of this transport (the public |
address) | address). The IP address does not have to correspond with one of |
| the local host network interfaces; it may be the public IP address of |
| a NAT router where port mappings have been configured for the |
| phone application. |
Bound IP | Optional. Bind the SIP and media transports to the specified IP |
Address | address. The IP address must be an IP address of one of the host |
| network interfaces. |
NAT Settings |
|
STUN Server | Optional. Specify the STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) |
| server to use to determine if the phone is behind a NAT, the type of |
| NAT, and the public address of the phone. The field can contain a |
| comma separated list of servers. Each server can be a domain |
| name, host name, or IP address, and it may contain an optional port |
| number. (For STUN see IETF RFC 5389.) |
Use ICE | Check this option to use the ICE (Interactive Connectivity |
| Establishment) protocol for NAT traversal. This option is checked by |
| default. ICE takes advantage of STUN and TURN to identify |
| candidates (IP addresses and ports) for communication, evaluating |
| and prioritizing the candidate pairs to select the best route. |
| Expensive candidates, such as using a media relay, are selected |
| only as a last resort. (For ICE see IETF RFC 5245.) |
ICE Nomination | When using ICE, select the preferred ICE Nomination Method. To |
Method | validate candidate pairs (IP addresses and ports for the local and |
61