Chapter 3. Performance
■Adjusting the Sound to Achieve the Preferred
Tone Quality (Equalizer)
The
An equalizer boosts or cuts specific sound pitches (frequency ranges) to adjust the sound balance for the overall performance. For example, you can boost the highs to get a crisper sound, or boost the low end for a more powerful sound.
You can also adjust the sound to compensate for the acoustical characteristics of the performance space.
If raising the values for separate frequencies causes the sound to distort, you can use the “Master Level” (see below) to control such distortion.
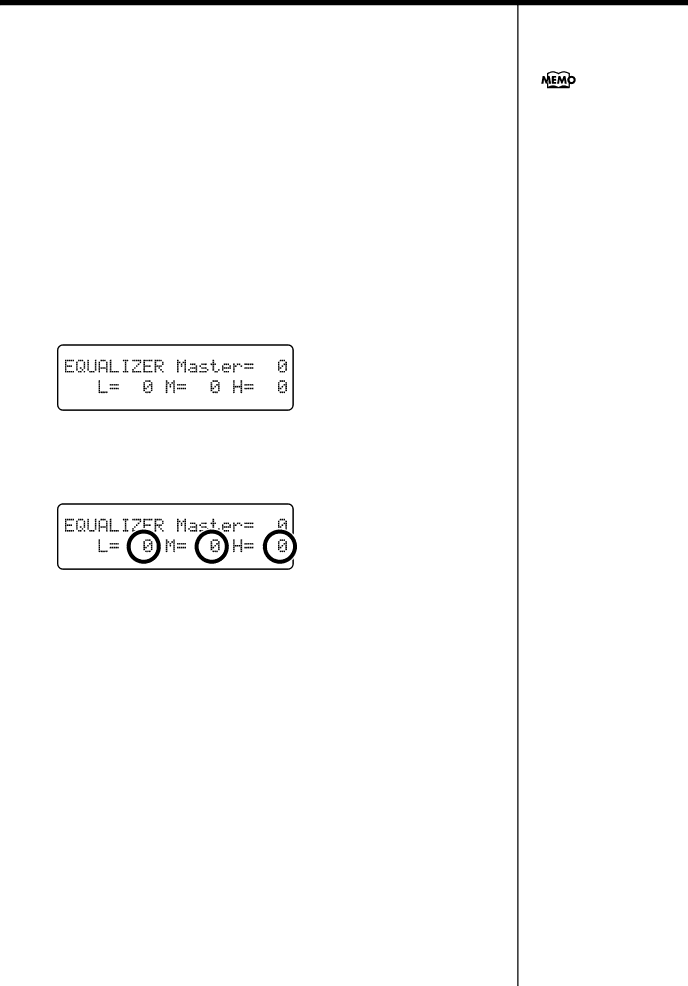
1 Press the [Function] (Exit) button, getting its indicator to light.
2 Press the [Song] (Select ![]()
![]() ] (Select +) button to display the EQUALIZER screen.
] (Select +) button to display the EQUALIZER screen.
fig.
3 Press the [Song] (Select ![]()
![]() ] (Select +) button so that the value for the range you want to set is flashing.
] (Select +) button so that the value for the range you want to set is flashing.
fig.
Value | Description | |
|
| |
|
| |
Master | You can temper the distortion in the sound by lowering | |
the level. Raising the level too much may cause the sound | ||
(Master Level) | ||
to become distorted. | ||
| ||
|
| |
L (Low) | ||
instruments like drums, bass, organ, guitar and strings. | ||
| ||
|
| |
M (Middle) | Midrange. This is the range of frequencies where most | |
instrument sounds are concentrated. | ||
| ||
|
| |
H (High) | ||
the sound. | ||
| ||
|
|
4 Press the [![]()
![]() ] (Value
] (Value ![]()
![]() ] (Value +) button to adjust the range and the overall level.
] (Value +) button to adjust the range and the overall level.
Value:
5 Press the [Function] (Exit) button so the indicator goes out.
You can save this setting in the
Memory Backup function (p.
72).
60
