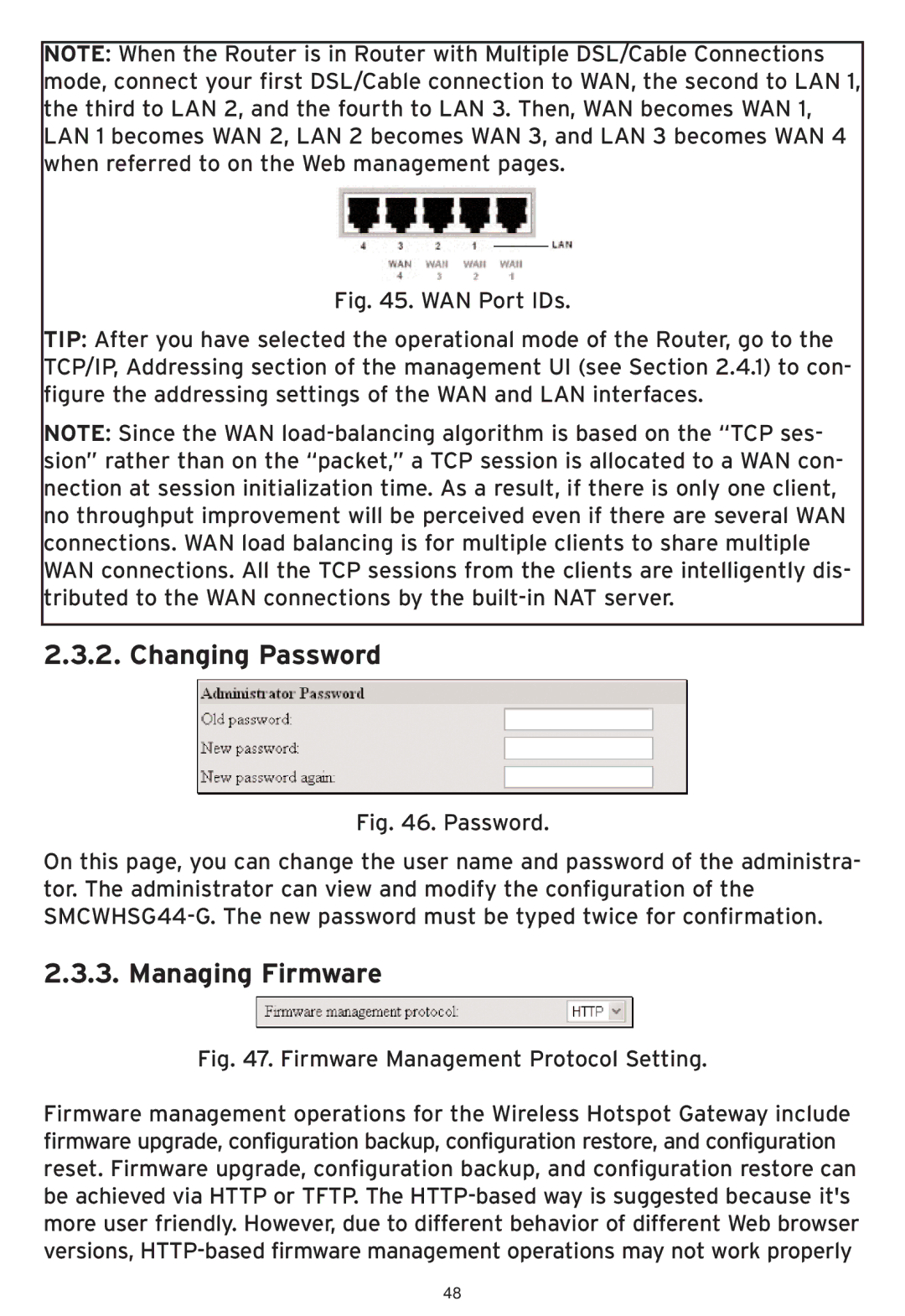
NOTE: When the Router is in Router with Multiple DSL/Cable Connections mode, connect your first DSL/Cable connection to WAN, the second to LAN 1, the third to LAN 2, and the fourth to LAN 3. Then, WAN becomes WAN 1, LAN 1 becomes WAN 2, LAN 2 becomes WAN 3, and LAN 3 becomes WAN 4 when referred to on the Web management pages.
Fig. 45. WAN Port IDs.
TIP: After you have selected the operational mode of the Router, go to the TCP/IP, Addressing section of the management UI (see Section 2.4.1) to con- figure the addressing settings of the WAN and LAN interfaces.
NOTE: Since the WAN
2.3.2. Changing Password
Fig. 46. Password.
On this page, you can change the user name and password of the administra- tor. The administrator can view and modify the configuration of the SMCWHSG44-G. The new password must be typed twice for confirmation.
2.3.3. Managing Firmware
Fig. 47. Firmware Management Protocol Setting.
Firmware management operations for the Wireless Hotspot Gateway include firmware upgrade, configuration backup, configuration restore, and configuration reset. Firmware upgrade, configuration backup, and configuration restore can be achieved via HTTP or TFTP. The HTTP-based way is suggested because it's more user friendly. However, due to different behavior of different Web browser versions, HTTP-based firmware management operations may not work properly
48