stored in the computer hard disk or a smart card for authentication. And after a successful
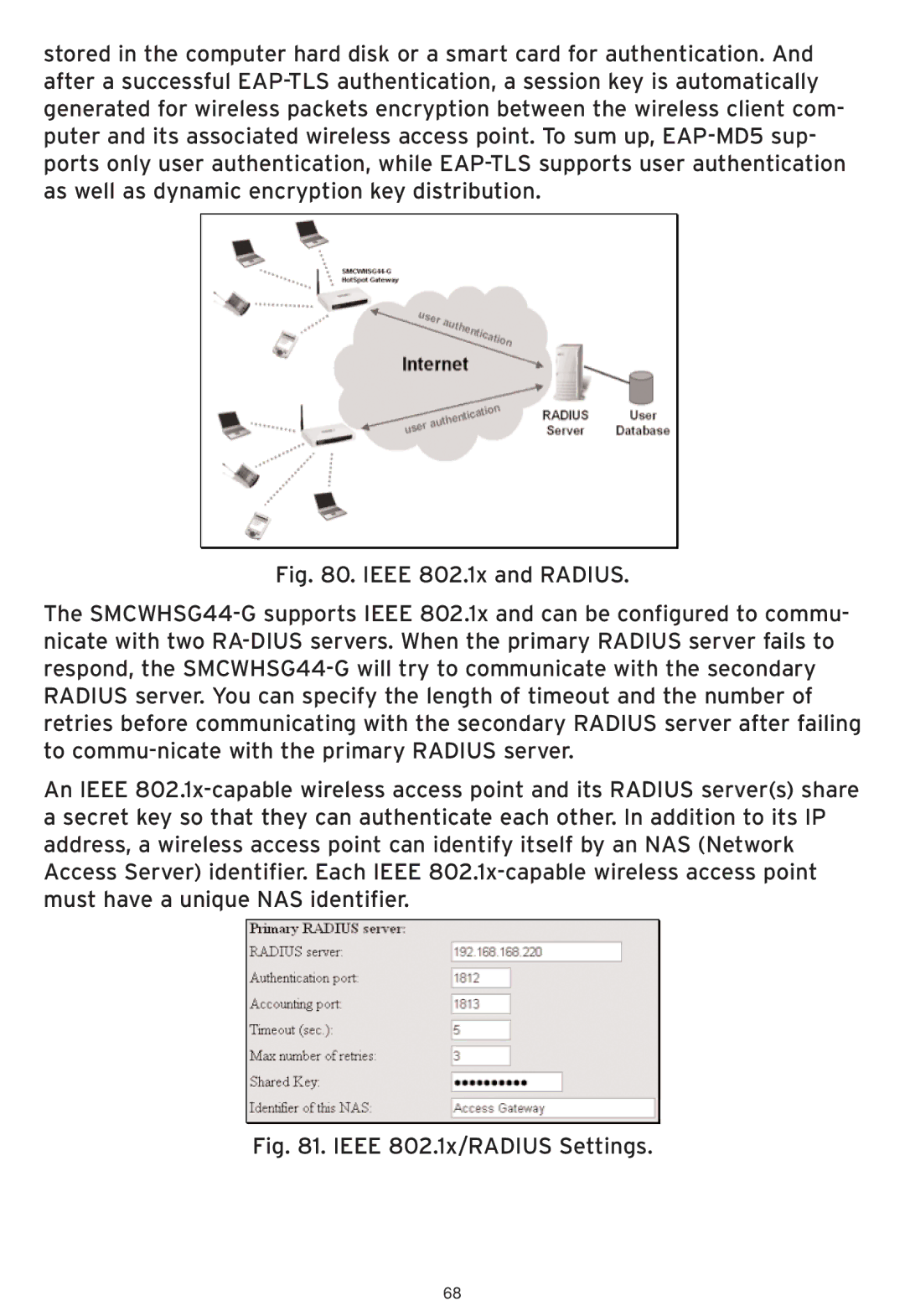
Fig. 80. IEEE 802.1x and RADIUS.
The SMCWHSG44-G supports IEEE 802.1x and can be configured to commu- nicate with two RA-DIUS servers. When the primary RADIUS server fails to respond, the SMCWHSG44-G will try to communicate with the secondary RADIUS server. You can specify the length of timeout and the number of retries before communicating with the secondary RADIUS server after failing to commu-nicate with the primary RADIUS server.
An IEEE 802.1x-capable wireless access point and its RADIUS server(s) share a secret key so that they can authenticate each other. In addition to its IP address, a wireless access point can identify itself by an NAS (Network Access Server) identifier. Each IEEE 802.1x-capable wireless access point must have a unique NAS identifier.
Fig. 81. IEEE 802.1x/RADIUS Settings.
68