B-1: TCP/IP Setting Problems
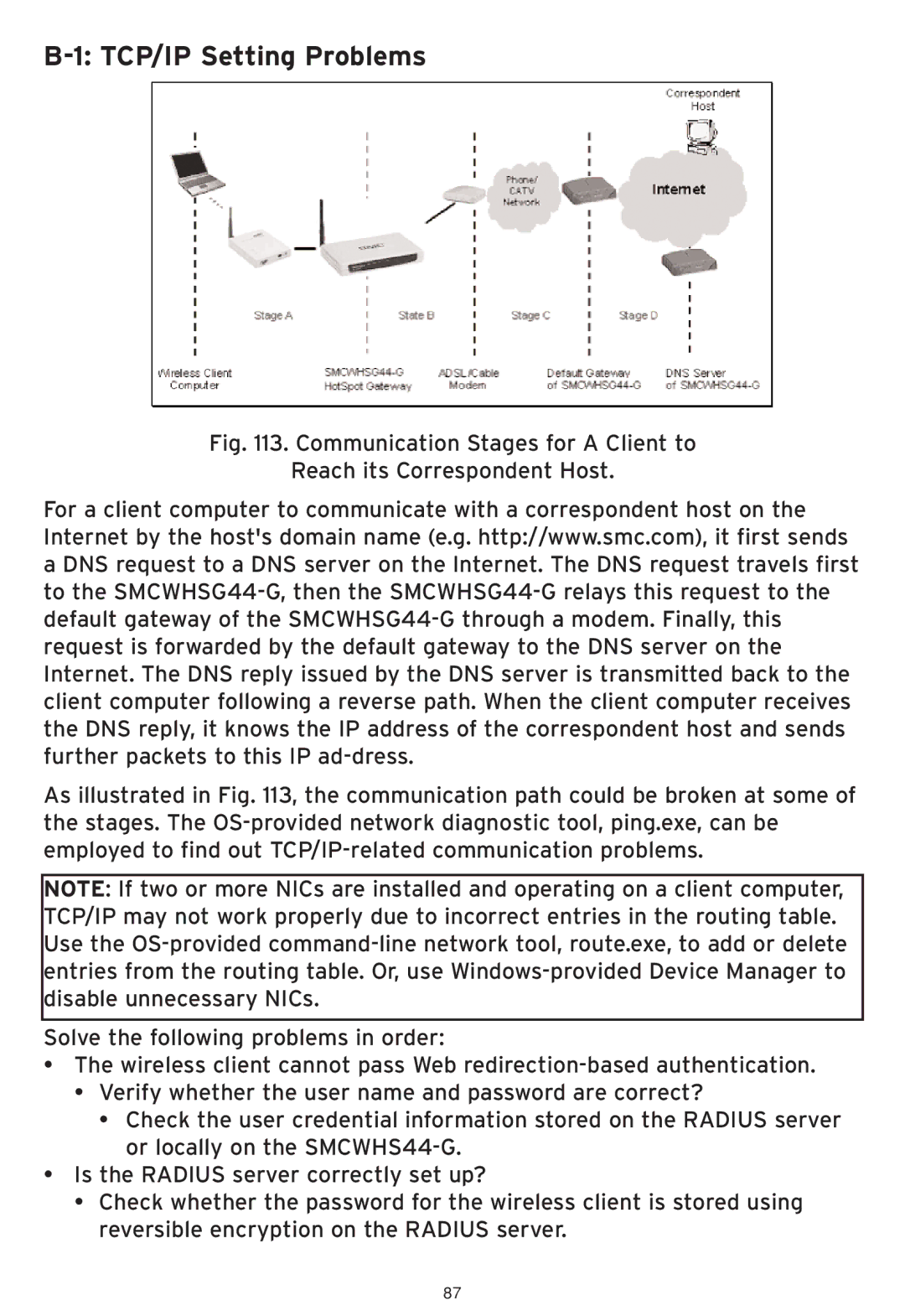
Fig. 113. Communication Stages for A Client to
Reach its Correspondent Host.
For a client computer to communicate with a correspondent host on the Internet by the host's domain name (e.g. http://www.smc.com), it first sends a DNS request to a DNS server on the Internet. The DNS request travels first to the
As illustrated in Fig. 113, the communication path could be broken at some of the stages. The OS-provided network diagnostic tool, ping.exe, can be employed to find out TCP/IP-related communication problems.
NOTE: If two or more NICs are installed and operating on a client computer, TCP/IP may not work properly due to incorrect entries in the routing table. Use the
Solve the following problems in order:
•The wireless client cannot pass Web redirection-based authentication.
•Verify whether the user name and password are correct?
•Check the user credential information stored on the RADIUS server or locally on the SMCWHS44-G.
•Is the RADIUS server correctly set up?
•Check whether the password for the wireless client is stored using reversible encryption on the RADIUS server.
87