32
CE4000 Cable Explorer TDR
User Manual
energy and a lower frequency and thus more energy is transmitted and less loss is present in the cable. This allows a longer range. The range is dependent on the VOP and pulse width used for the test. A table providing maximum ranges for each pulse width is provided in the Appendix.
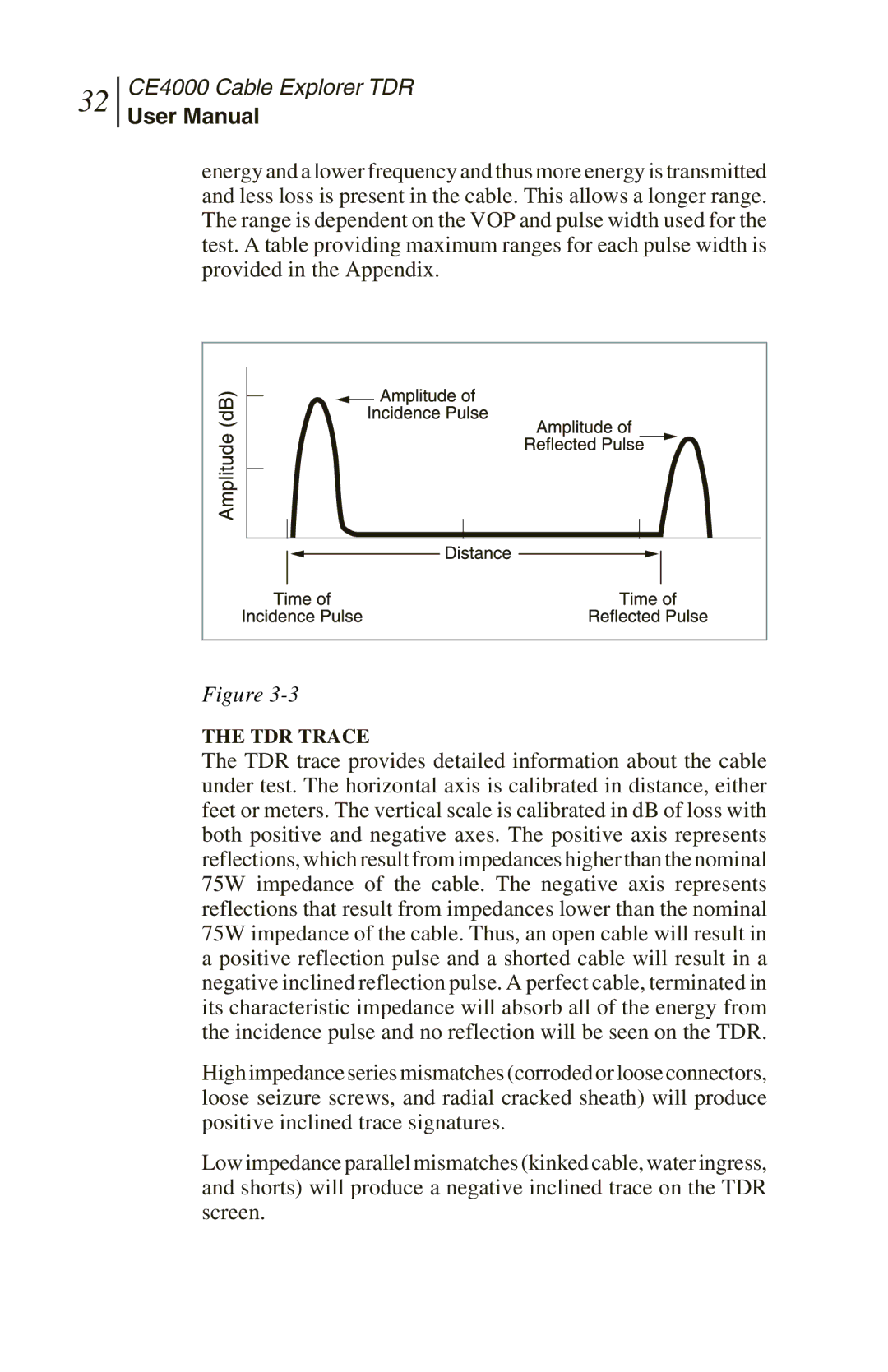
Figure
THE TDR TRACE
The TDR trace provides detailed information about the cable under test. The horizontal axis is calibrated in distance, either feet or meters. The vertical scale is calibrated in dB of loss with both positive and negative axes. The positive axis represents reflections, which result from impedances higher than the nominal 75W impedance of the cable. The negative axis represents reflections that result from impedances lower than the nominal 75W impedance of the cable. Thus, an open cable will result in a positive reflection pulse and a shorted cable will result in a negative inclined reflection pulse. A perfect cable, terminated in its characteristic impedance will absorb all of the energy from the incidence pulse and no reflection will be seen on the TDR.
High impedance series mismatches (corroded or loose connectors, loose seizure screws, and radial cracked sheath) will produce positive inclined trace signatures.
Low impedance parallel mismatches (kinked cable, water ingress, and shorts) will produce a negative inclined trace on the TDR screen.