www.ti.com
Scope of the Standard
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) are often programmed like "traditional" embedded microprocessors. That is, they are programmed in a mix of C and assembly language, they directly access hardware peripherals, and, for performance reasons, almost always have little or no standard operating system support. Thus, like traditional microprocessors, there is very little use of commercial
However, unlike
Such algorithms are often the result of many years of doctoral research. However, because of the lack of consistent standards, it is not possible to use an algorithm in more than one system without significant reengineering. Since few companies can afford a team of DSP PhDs, and the reuse of DSP algorithms is so labor intensive, the
This document defines a set of requirements for DSP algorithms that, if followed, allow system integrators to quickly assemble
1.1Scope of the Standard
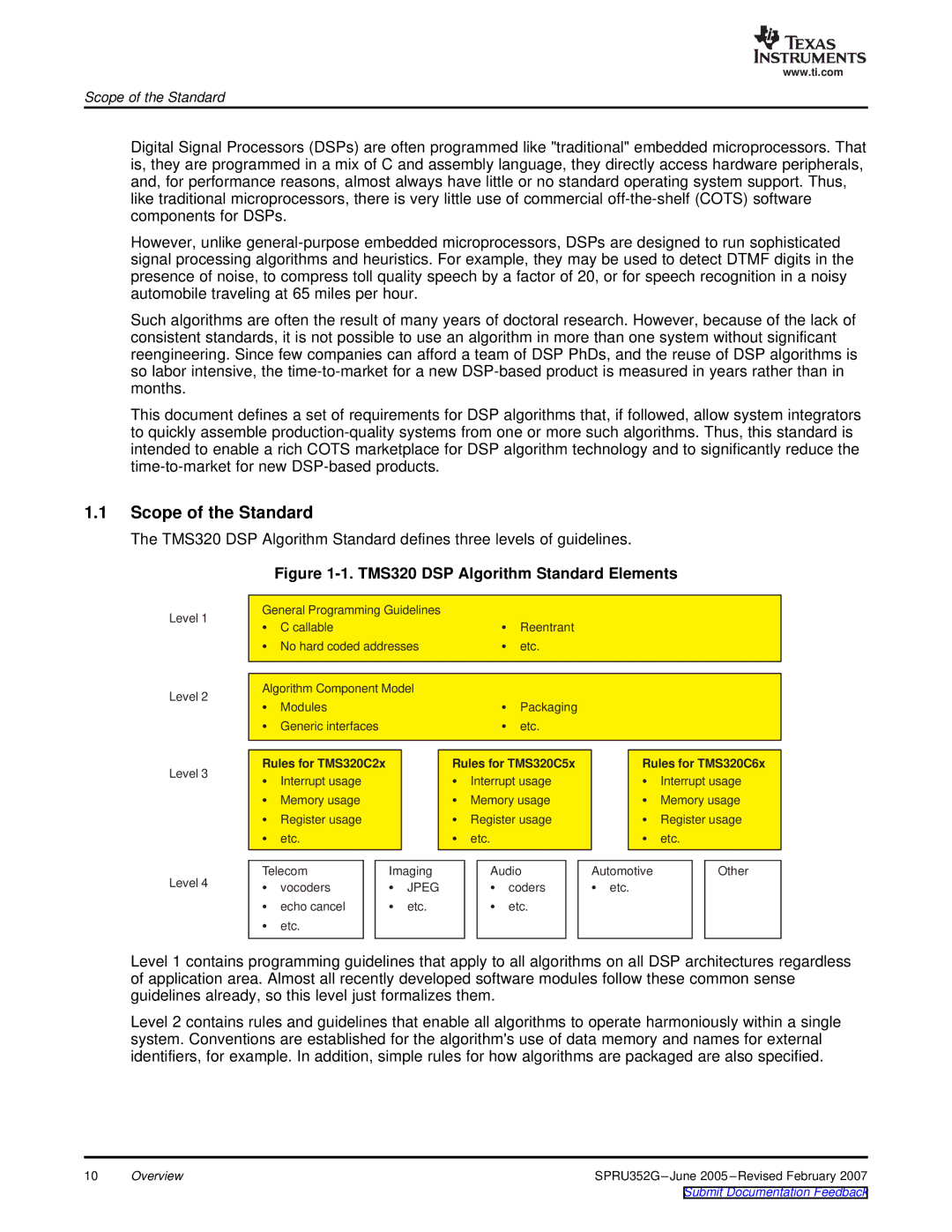
The TMS320 DSP Algorithm Standard defines three levels of guidelines.
Figure 1-1. TMS320 DSP Algorithm Standard Elements
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
General Programming Guidelines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
S | C callable |
|
|
|
|
| S | Reentrant |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
S No hard coded addresses |
|
| S | etc. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Algorithm Component Model |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
S | Modules |
|
|
|
|
| S | Packaging |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
S | Generic interfaces |
|
|
|
|
| S | etc. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rules for TMS320C2x |
|
|
| Rules for TMS320C5x |
| Rules for TMS320C6x | |||||||||||
S | Interrupt usage |
|
|
| S | Interrupt usage |
| S | Interrupt usage | ||||||||
S | Memory usage |
|
|
| S | Memory usage |
| S | Memory usage | ||||||||
S | Register usage |
|
|
| S | Register usage |
| S | Register usage | ||||||||
S | etc. |
|
|
| S | etc. |
|
|
|
| S | etc. | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
Telecom | Imaging |
|
| Audio | Automotive |
|
| Other | |||||||||
S | vocoders | S | JPEG |
|
| S | coders | S etc. |
|
|
| ||||||
S | echo cancel | S | etc. |
|
| S | etc. |
|
|
|
|
| |||||
Setc.
Level 1 contains programming guidelines that apply to all algorithms on all DSP architectures regardless of application area. Almost all recently developed software modules follow these common sense guidelines already, so this level just formalizes them.
Level 2 contains rules and guidelines that enable all algorithms to operate harmoniously within a single system. Conventions are established for the algorithm'suse of data memory and names for external identifiers, for example. In addition, simple rules for how algorithms are packaged are also specified.
10 | Overview | SPRU352G |