www.ti.com
|
|
| Algorithm A |
|
|
|
|
| Algorithm B | |||
CPU context |
|
| active |
|
|
|
|
| active |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
(timeline) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||||||
DMA context |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(timeline) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DMA/CPU idle
CPU context switch
CPU/DMA active
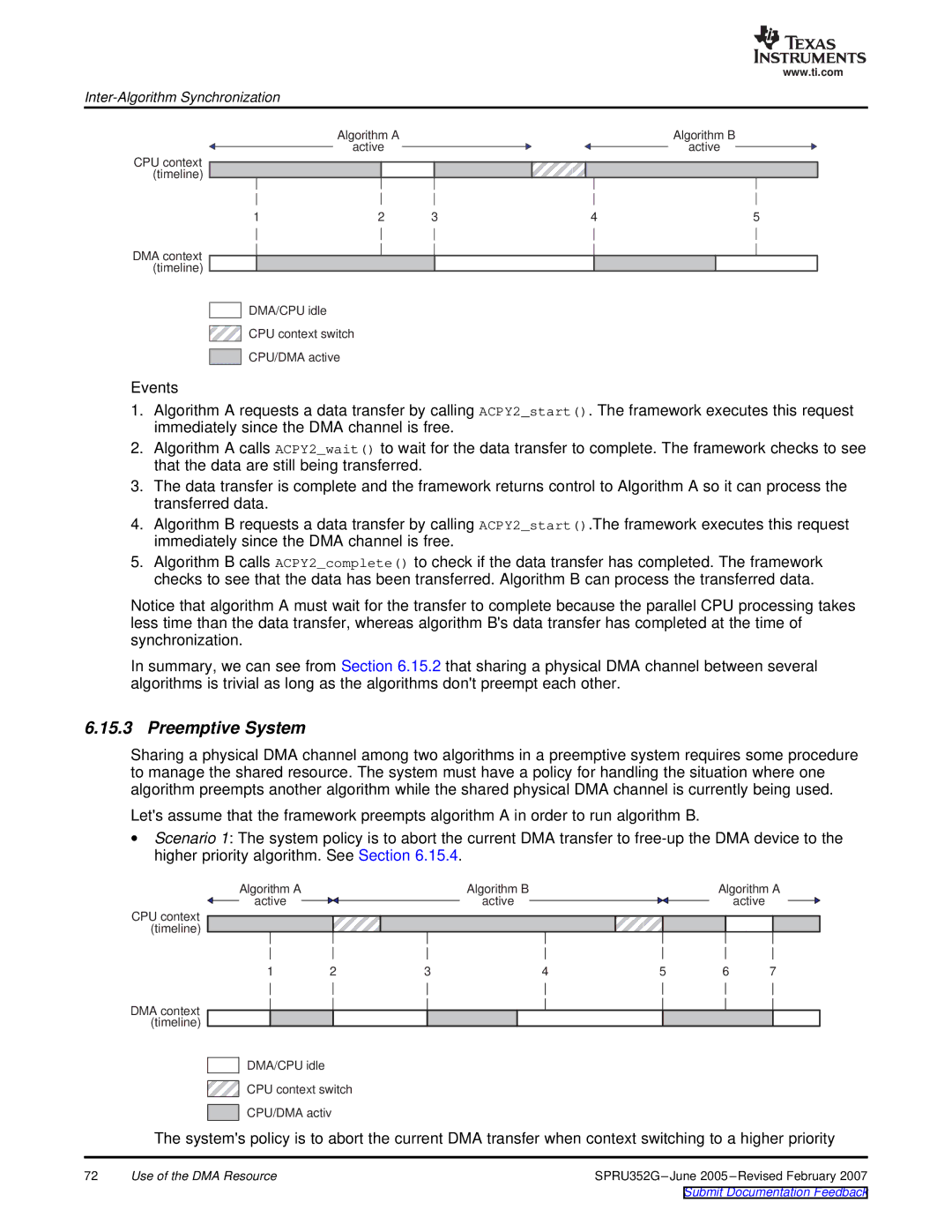
Events
1.Algorithm A requests a data transfer by calling ACPY2_start(). The framework executes this request immediately since the DMA channel is free.
2.Algorithm A calls ACPY2_wait() to wait for the data transfer to complete. The framework checks to see that the data are still being transferred.
3.The data transfer is complete and the framework returns control to Algorithm A so it can process the transferred data.
4.Algorithm B requests a data transfer by calling ACPY2_start().The framework executes this request immediately since the DMA channel is free.
5.Algorithm B calls ACPY2_complete() to check if the data transfer has completed. The framework checks to see that the data has been transferred. Algorithm B can process the transferred data.
Notice that algorithm A must wait for the transfer to complete because the parallel CPU processing takes less time than the data transfer, whereas algorithm B'sdata transfer has completed at the time of synchronization.
In summary, we can see from Section 6.15.2 that sharing a physical DMA channel between several algorithms is trivial as long as the algorithms don'tpreempt each other.
6.15.3 Preemptive System
Sharing a physical DMA channel among two algorithms in a preemptive system requires some procedure to manage the shared resource. The system must have a policy for handling the situation where one algorithm preempts another algorithm while the shared physical DMA channel is currently being used.
Let'sassume that the framework preempts algorithm A in order to run algorithm B.
∙Scenario 1: The system policy is to abort the current DMA transfer to
Algorithm A |
|
| Algorithm B |
| Algorithm A | |
active |
|
| active |
|
| active |
CPU context |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(timeline) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
DMA context |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(timeline) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DMA/CPU idle
CPU context switch
CPU/DMA activ
The system'spolicy is to abort the current DMA transfer when context switching to a higher priority
72 | Use of the DMA Resource | SPRU352G |