www.ti.com | Architecture |
2.8MDIO Module
The MDIO module is used to manage up to 32 physical layer (PHY) devices connected to the Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC). The DM36x device supports a single PHY being connected to the EMAC at any given time. The MDIO module is designed to allow almost transparent operation of the MDIO interface with little maintenance from the CPU.
The MDIO module continuously polls 32 MDIO addresses in order to enumerate all PHY devices in the system. Once a PHY device has been detected, the MDIO module reads the MDIO PHY link status register (LINK) to monitor the PHY link state. Link change events are stored in the MDIO module, which can interrupt the CPU. This storing of the events allows the CPU to poll the link status of the PHY device without continuously performing MDIO module accesses. However, when the CPU must access the MDIO module for configuration and negotiation, the MDIO module performs the MDIO read or write operation independent of the CPU. This independent operation allows the processor to poll for completion or interrupt the CPU once the operation has completed.
2.8.1MDIO Module Components
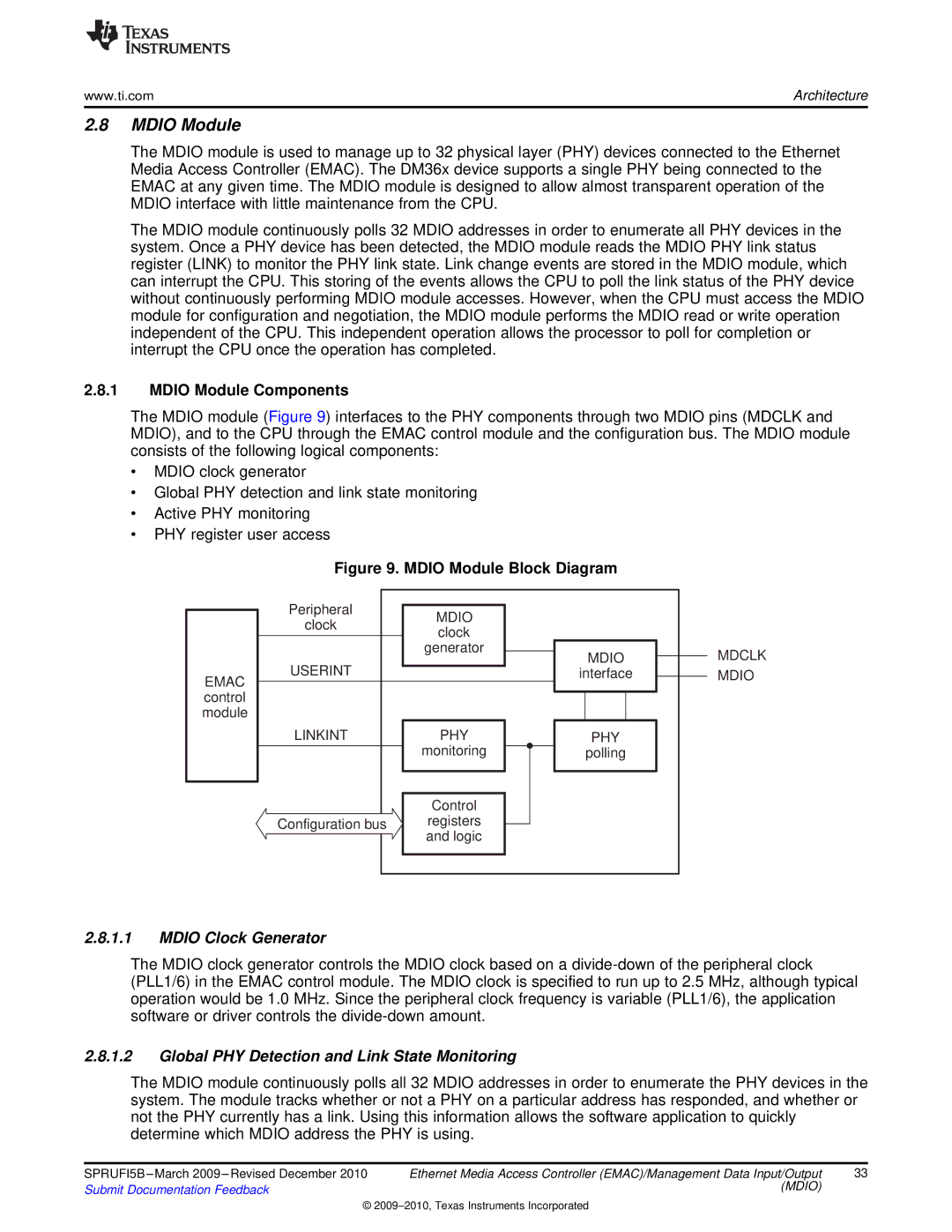
The MDIO module (Figure 9) interfaces to the PHY components through two MDIO pins (MDCLK and MDIO), and to the CPU through the EMAC control module and the configuration bus. The MDIO module consists of the following logical components:
•MDIO clock generator
•Global PHY detection and link state monitoring
•Active PHY monitoring
•PHY register user access
Figure 9. MDIO Module Block Diagram | ||
Peripheral | MDIO |
|
clock |
| |
clock |
| |
|
| |
| generator | MDIO |
USERINT |
| |
| interface | |
EMAC |
|
|
control |
|
|
module |
|
|
LINKINT | PHY | PHY |
| monitoring | polling |
| Control |
|
Configuration bus | registers |
|
| and logic |
|
MDCLK
MDIO
2.8.1.1MDIO Clock Generator
The MDIO clock generator controls the MDIO clock based on a
2.8.1.2Global PHY Detection and Link State Monitoring
The MDIO module continuously polls all 32 MDIO addresses in order to enumerate the PHY devices in the system. The module tracks whether or not a PHY on a particular address has responded, and whether or not the PHY currently has a link. Using this information allows the software application to quickly determine which MDIO address the PHY is using.
SPRUFI5B
Submit Documentation Feedback | (MDIO) |
|
©