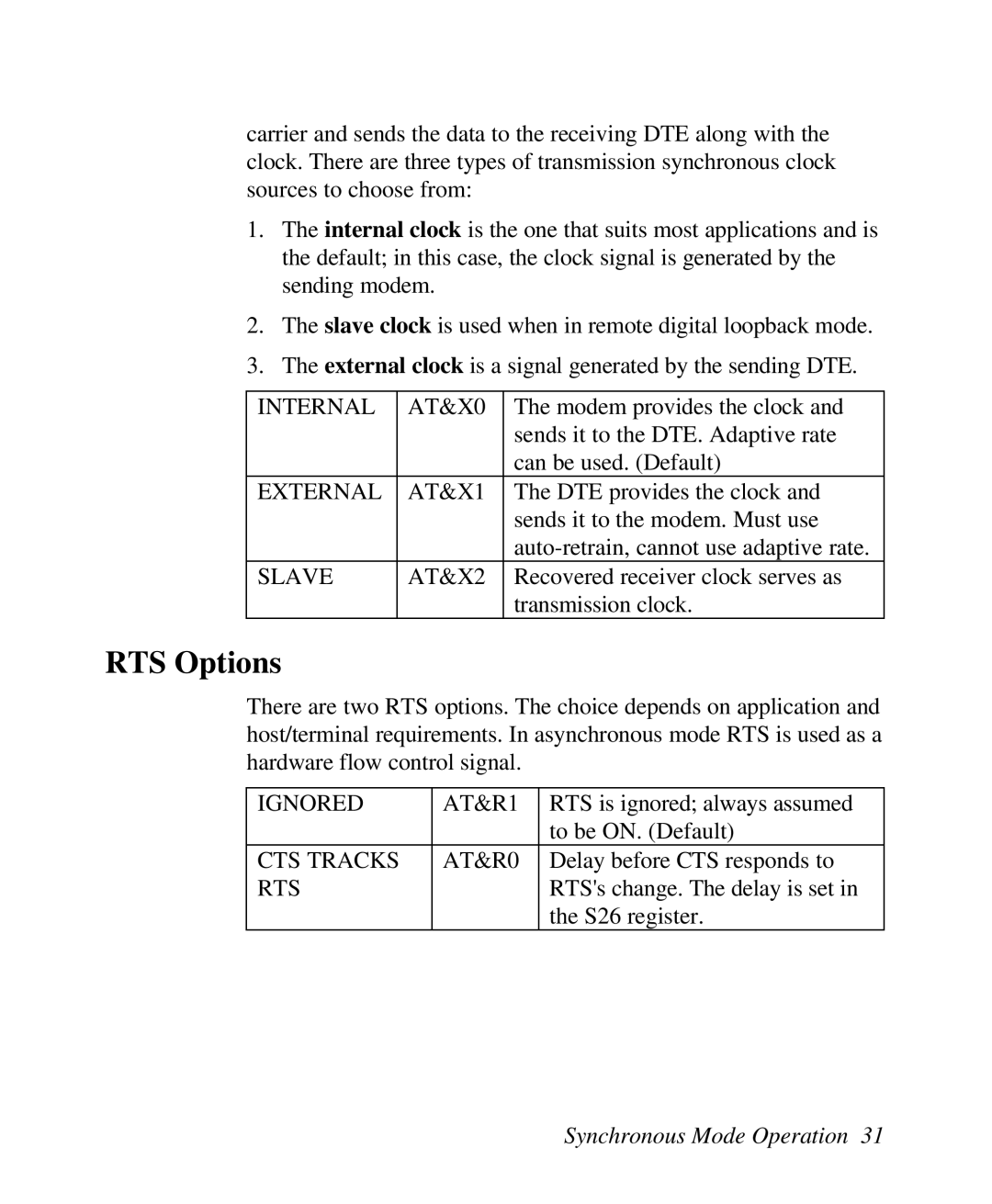
carrier and sends the data to the receiving DTE along with the clock. There are three types of transmission synchronous clock sources to choose from:
1.The internal clock is the one that suits most applications and is the default; in this case, the clock signal is generated by the sending modem.
2.The slave clock is used when in remote digital loopback mode.
3.The external clock is a signal generated by the sending DTE.
INTERNAL | AT&X0 | The modem provides the clock and |
|
| sends it to the DTE. Adaptive rate |
|
| can be used. (Default) |
EXTERNAL | AT&X1 | The DTE provides the clock and |
|
| sends it to the modem. Must use |
|
| |
SLAVE | AT&X2 | Recovered receiver clock serves as |
|
| transmission clock. |
RTS Options
There are two RTS options. The choice depends on application and host/terminal requirements. In asynchronous mode RTS is used as a hardware flow control signal.
IGNORED | AT&R1 | RTS is ignored; always assumed |
|
| to be ON. (Default) |
CTS TRACKS | AT&R0 | Delay before CTS responds to |
RTS |
| RTS's change. The delay is set in |
|
| the S26 register. |