Testing | |
|
|
LOOPBACK OPERATION
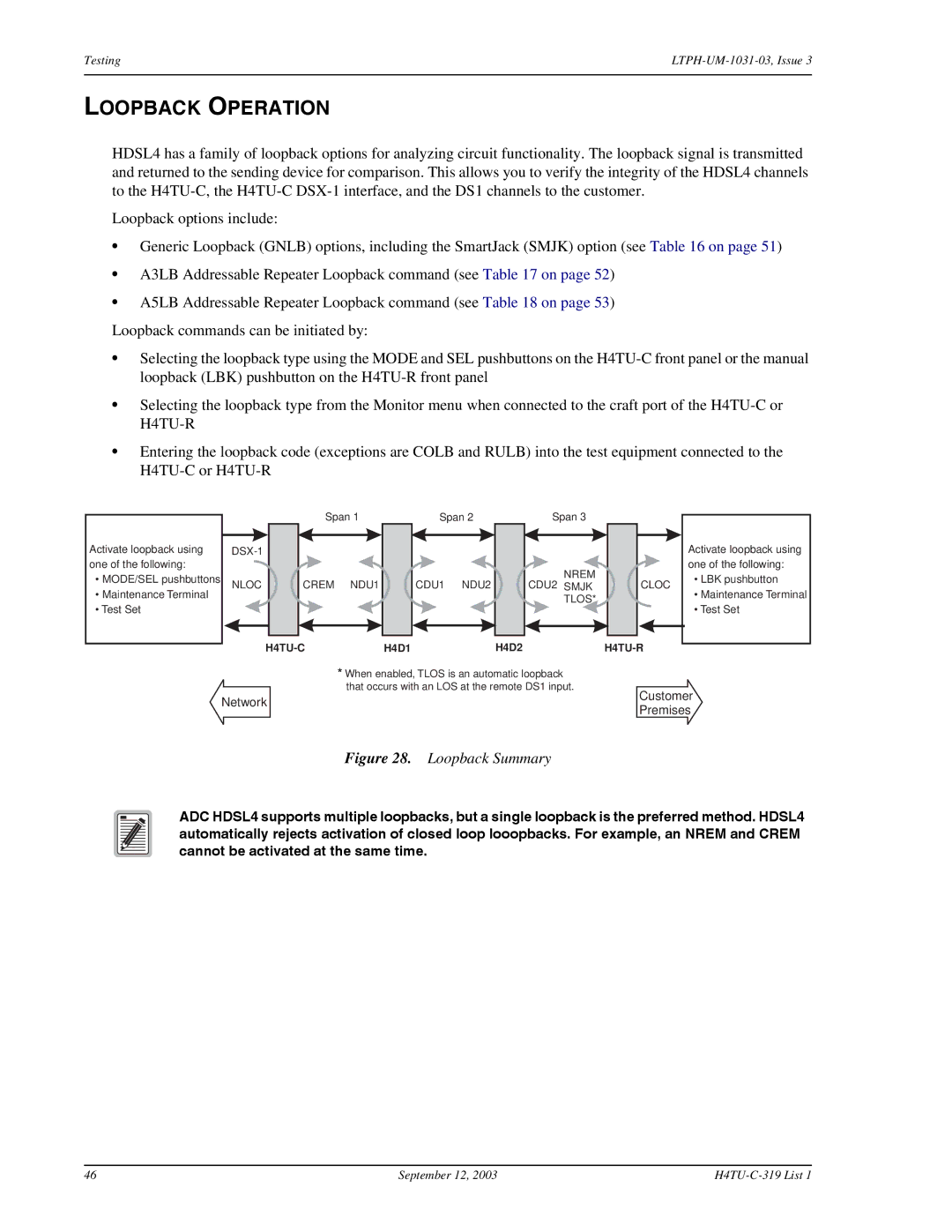
HDSL4 has a family of loopback options for analyzing circuit functionality. The loopback signal is transmitted and returned to the sending device for comparison. This allows you to verify the integrity of the HDSL4 channels to the
Loopback options include:
•Generic Loopback (GNLB) options, including the SmartJack (SMJK) option (see Table 16 on page 51)
•A3LB Addressable Repeater Loopback command (see Table 17 on page 52)
•A5LB Addressable Repeater Loopback command (see Table 18 on page 53)
Loopback commands can be initiated by:
•Selecting the loopback type using the MODE and SEL pushbuttons on the
•Selecting the loopback type from the Monitor menu when connected to the craft port of the
•Entering the loopback code (exceptions are COLB and RULB) into the test equipment connected to the
Activate loopback using one of the following:
•MODE/SEL pushbuttons
•Maintenance Terminal
•Test Set
| Span 1 | |
|
| |
NLOC | CREM | NDU1 |
| H4D1 | |
Span 2
CDU1 NDU2
Span 3
NREM
CDU2 SMJK
TLOS*
H4D2
CLOC |
|
Activate loopback using one of the following:
•LBK pushbutton
•Maintenance Terminal
•Test Set
* When enabled, TLOS is an automatic loopback that occurs with an LOS at the remote DS1 input.
Network | Customer | |
Premises | ||
|
Figure 28. Loopback Summary
ADC HDSL4 supports multiple loopbacks, but a single loopback is the preferred method. HDSL4 automatically rejects activation of closed loop looopbacks. For example, an NREM and CREM cannot be activated at the same time.
46 | September 12, 2003 |