DMC-13X8
Using This Manual
Contents
Connecting Hardware
Programming Motion
Hardware & Software Protection 149
ZOH
DAC
Index 207
Introduction
Overview of Motor Types
Overview
Brushless Servo Motor with Sinusoidal Commutation
Standard Servo Motor with +/- 10 Volt Command Signal
Stepper Motor with Step and Direction Signals
DMC-13X8 Functional Elements
General I/O
Microcomputer Section
Motor Interface
Communication
System Elements
Motor
Amplifier Driver
Encoder
Watch Dog Timer
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Getting Started
DMC-13X8 Motion Controller
JP9
Elements You Need
Sinusoidal Commutation
Installing the DMC-13X8
Determine Overall Motor Configuration
Standard Servo Motor Operation
Install Jumpers on the DMC-13X8
Optional Motor Off Jumpers
Install the DMC-13X8 in the VME Host
Establish Communication with the Galil controller
Determine the Axes to be Used for Sinusoidal Commutation
Baxz
Make Connections to Amplifier and Encoder
Getting Started
Check the Polarity of the Feedback Loop
Connect Standard Servo Motors
Inverting the Loop Polarity
BGX CR
TTX CR
DC Power Supply
DC Brush
Connect Sinusoidal Commutation Motors
If Hall Sensors are Not Available
If Hall Sensors are Available
BCX
SHX
BGX
AMX
Tune the Servo System
Connect Step Motors
InstructionInterpretation
Design Examples
Example 1 System Set-up
TE X CR
Example 5 Position Interrogation
Example 2 Profiled Move
Example 3 Multiple Axes
Example 4 Independent Moves
Example 7 Velocity Control
Example 6 Absolute Position
Example 9 Interrogation
Example 10 Operation in the Buffer Mode
Example 11 Using the On-Board Editor
Example 8 Operation Under Torque Limit
Example 13 Motion Programs with Trippoints
Example 12 Motion Programs with Loops
Example 14 Control Variables
Example 15 Linear Interpolation
Example 16 Circular Interpolation
Motion Path for Example
VM XY
Overview
Using Optoisolated Inputs
Limit Switch Input
Connecting Hardware
Abort Input
Home Switch Input
Wiring the Optoisolated Inputs
Group Controllers with 1- 4 Axes Common Signal
Uncommitted Digital Inputs
Optoisolated Inputs
Using an Isolated Power Supply
Analog Inputs
Amplifier Interface
Bypassing the Opto-Isolation
ICM-1900/2900
TTL Inputs
TTL Outputs
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Register Description Address Read/Write
Communication with Controller
Communication Registers
AM5 AM4 AM3 AM2 AM1 AM0
Advanced Communication Techniques
Simplified Communication Procedure
Polling Mode Read Procedure
Communication with Controller Secondary Fifo channel
Polling Fifo
Addr Type
Overview of Secondary Fifo Procedure
DMA / Secondary Fifo Memory Map
Operation Register address Value
Error code
BIT
Axis Switch Information 1 Byte
General Status Information 1 Byte
Axis Status Information 2 Byte
Setting up Interrupts
Configuring Interrupts
Interrupts
Bit number n Input
Bit Number m Condition
Hex Data Condition
Servicing Interrupts
Example Interrupts
BGY
UI1
Controller Response to Data
Command Basics
Command Syntax Ascii
BG TW
Coordinated Motion with more than 1 axis
BG Xyzw
BG S
Datafields Format
Command Syntax Binary
Binary Command Format
Header Format
LE, VE
Binary command table
Command
Example
Interrogating the Controller
Interrogation Commands
=TPX
Summary of Interrogation Commands
Interrogating Current Commanded Values
Operands
Command Summary
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Programming Motion
Example Application Mode of Motion Commands
Independent Axis Positioning
Example Multiple Move Sequence
Command Summary Independent Axis
Operand Summary Independent Axis
Example Absolute Position Movement
Axis velocity profile
Velocity COUNTS/SEC
Command Summary Jogging
Independent Jogging
Example Jog in X only
Linear Interpolation Mode
Specifying Linear Segments
Example Joystick Jogging
#LMOVE
Additional Commands
An Example of Linear Interpolation Motion
Specifying Vector Speed for Each Segment
LM?
Command Summary Linear Interpolation
Changing Feedrate
#ALT
Operand Summary Linear Interpolation
Example Linear Move
LM ZW
Example Multiple Moves
#LOAD
COUNT=0
Vector Mode Linear and Circular Interpolation Motion
Specifying the Coordinate Plane
Specifying Vector Segments
Additional commands
Compensating for Differences in Encoder Resolution
Trippoints
Tangent Motion
Operand Summary Coordinated Motion Sequence
Command Summary Coordinated Motion Sequence
Required Path
Electronic Gearing
Example Electronic Gearing
Command Summary Electronic Gearing
Command Description
Example Simple Master Slave
Electronic Cam
Example Gantry Mode
EAp where p = X,Y,Z,W Is the selected master axis
Programming Motion
3000 2250 1500 2000 4000 6000 Master
Instruction Interpretation
Command Summary Electronic CAM
Operand Summary Electronic CAM
Example Electronic CAM
Operand Description
Specifying Contour Segments
Contour Mode
DT0CD0
CMX
Generating an Array An Example
Command Summary Contour Mode
Operand Summary Contour Mode
General Velocity Profiles
POSC=V4
Contour Mode Example
Instruction Interpretation
#POINTS
Record and Playback Example
Teach Record and Play-Back
Virtual Axis
AC, DC, JG, SP, PR, PA, BG, IT, GA, VM, VP, CR, ST, DP, RP
BGN
Stepper Motor Smoothing
Monitoring Generated Pulses vs Commanded Pulses
Stepper Motor Operation
Specifying Stepper Motor Operation
Motion Complete Trippoint
Using an Encoder with Stepper Motors
Stepper Position Maintenance Mode SPM
Command Summary Stepper Motor Operation
Operand Summary Stepper Motor Operation
Error Limit
Example SPM Mode Setup
Correction
Half-Stepping Drive, X axis
Example Error Correction
#MOTION
#LOOP
Example Friction Correction
= Main Encoder Second Encoder
Using the CE Command
Additional Commands for the Auxiliary Encoder
Dual Loop Auxiliary Encoder
#DUALOOP
Backlash Compensation
Continuous Dual Loop Example
Sampled Dual Loop Example
Using the IT and VT Commands
Motion Smoothing
Example Smoothing
Trapezoidal velocity and smooth velocity profiles
Using the KS Command Step Motor Smoothing
Homing
Motion intervals in the Home sequence
FE Xyzw FI Xyzw HM Xyzw SC Xyzw TS Xyzw
Command Summary Homing Operation
High Speed Position Capture The Latch Function
Operand Summary Homing Operation
AL Y
Fast Update Rate Mode
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Using the DMC-13X8 Editor to Enter Programs
ED #BEGIN
Application Programming
Edit Mode Commands
Program Format
Return
#BEGIN1
Using Labels in Programs
Special Labels
#BEGIN #SQUARE
No Bottom Line
Using the command, no
Executing Programs Multitasking
Commenting Programs
Debugging Programs
Trace Commands
Operands
Error Code Command
Stop Code Command
RAM Memory Interrogation Commands
Event Triggers & Trippoints
Program Flow Commands
Function
DMC-13X8 and DMC-13X8 Event Triggers
Event Trigger Repetitive Position Trigger
Event Trigger Examples
Event Trigger Multiple Move Sequence
Event Trigger Set Output after Distance
Event Trigger Set output when At speed
Event Trigger Start Motion on Input
Event Trigger Change Speed along Vector Path
Define Output Waveform Using AT
Conditional Jumps
Event Trigger Multiple Move with Wait
Multiple Conditional Statements
Command Format JP and JS
Logical operators
Conditional Statements
Using the if and Endif Commands
Using If, Else, and Endif Commands
Using the JP Command
Example Using JP command
Nesting if Conditional Statements
Using the Else Command
Command Format IF, Else and Endif
Example using IF, Else and Endif
Subroutines
Stack Manipulation
Auto-Start Routine
Subroutine Description
Example Limit Switch
Example Position Error
Automatic Subroutines for Monitoring Conditions
Example Input Interrupt
Example Motion Complete Timeout
Example Command Error
Example Command Error w/Multitasking
Operand Function
Operator Function
Mathematical and Functional Expressions
Mathematical Operators
Bit-Wise Operators
LEN1=FLEN&$00FF
Functions
ENTER,LENS6
FLEN=@FRACLEN
Reallongname
Variables
Programmable Variables
Posx POS1 Speedz
Displaying the value of variables at the terminal
Example Using Variables for Joystick
Assigning Values to Variables
Assigning Variable Values to Controller Parameters
Examples of Keywords
Operands
Special Operands Keywords
Examples of Internal Variables
Assignment of Array Entries
Using a Variable to Address Array Elements
Arrays
Defining Arrays
Command Summary Automatic Data Capture
Automatic Data Capture into Arrays
Uploading and Downloading Arrays to On Board Memory
Data Type Description
Data Types for Recording
Operand Summary Automatic Data Capture
Example Recording into An Array
An Example for Inputting Numeric Data
Input of Data Numeric and String
Deallocating Array Space
Input of Data
Formatting Messages
Output of Data Numeric and String
Sending Messages
Inputting String Variables
Using the MG Command to Configure Terminals
Displaying Variables and Arrays
Summary of Message Functions
BL ? LE ? DE ? PA ? DP ? PR ? EM ?
LZ0
Local Formatting of Response of Interrogation Commands
Formatting Variables and Array Elements
Local Formatting of Variables
Hardware I/O
Converting to User Units
Digital Outputs
Instruction Function
Digital Inputs
Example Start Motion on Switch
Input Interrupt Function
Examples Input Interrupt
Analog Inputs
Example Position Follower Point-to-Point
Example Position Follower Continuous Move
Wire Cutter
Example Applications
JP #A
Table Controller
Motor Velocity and the Associated Input/Output signals
BGS AMS
BGZ
AMZ
BGZ AMZ
Speed Control by Joystick
DP0
Position Control by Joystick
Backlash Compensation by Sampled Dual-Loop
JG VEL JP #B
PR ER
LINPOS=0
LIN POS = DEX
ER=1000-LINPOS-TEX
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Hardware Protection
Output Protection Lines
Hardware & Software Protection
Programmable Position Limits
Signal or Function State if Error Occurs
Software Protection
Input Protection Lines
#AJP #AEN
Off-On-Error
Automatic Error Routine
Limit Switch Routine
Stxamx
V2=LRX
JP#END
#LF
Remedy
Installation
Symptom Diagnosis Cause
Troubleshooting
Communication
Operation
Stability
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Theory of Operation
Theory of Operation
Level
Velocity and Position Profiles
Operation of Closed-Loop Systems
System Modeling
Voltage Drive
Motor-Amplifier
Velocity Loop
Current Drive
Voltage Source
Digital Filter
DAC
ZOH
System Analysis
Ms = P/I = Kt/Js2 = 500/s2 rad/A Amp Ka = 4 Amp/V
Analytical Method
System Design and Compensation
Kd = 10/32768 = Encoder Kf = 4N/2π =
Theory of Operation
Equivalent Filter Form
KP, KD, KI, PL
PID, T
Input/Output
Electrical Specifications
Servo Control
Stepper Control
Power
Performance Specifications
Connectors for DMC-13X8 Main Board
J1 DMC-13X8 A-D Axes Main J5-DMC-13X8 A-D Axes
PIN High Density Auxiliary Encoders 26-PIN IDC
PWM/STEP OUT
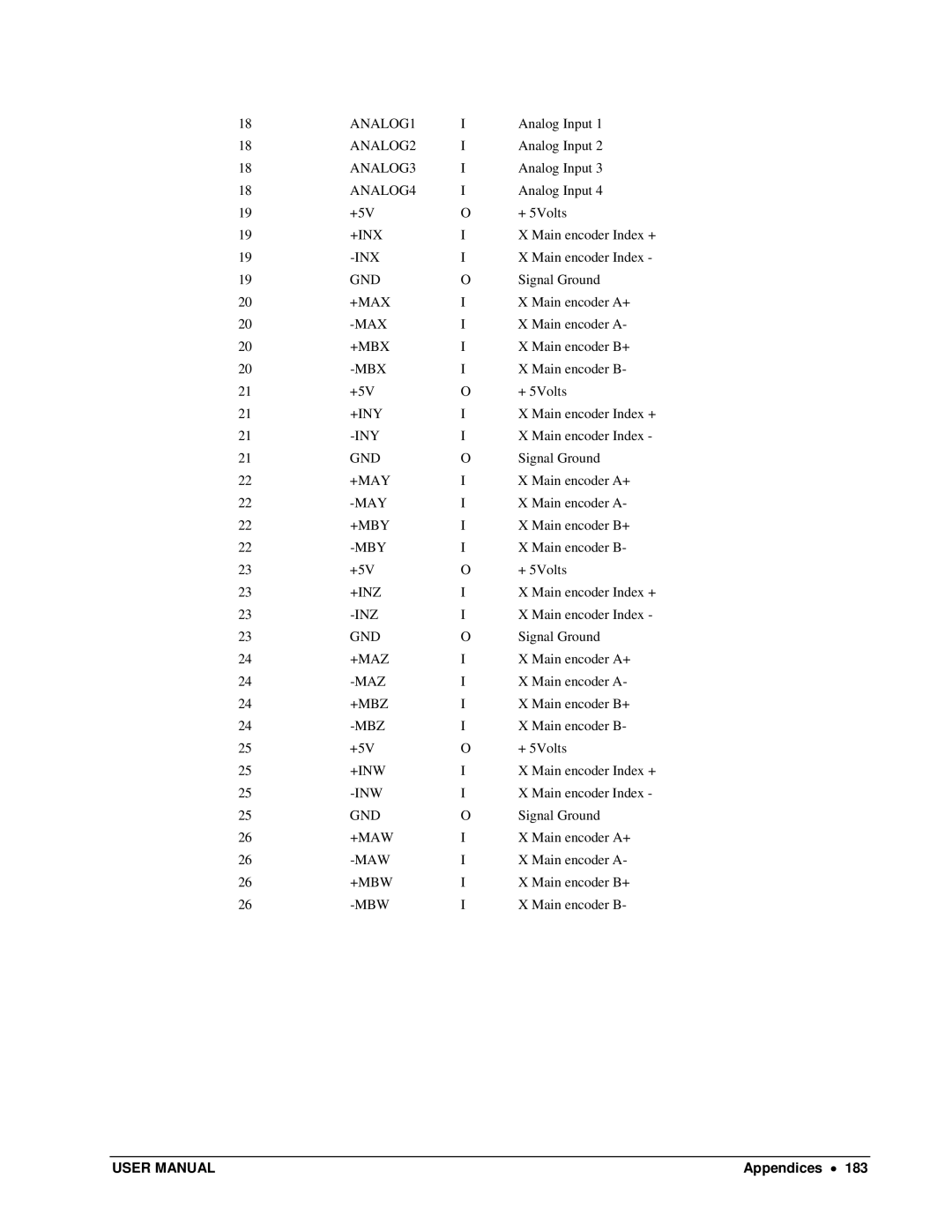
Pin-Out Description for DMC-13X8
Accessories and Options
Terminal # Label Description
ICM-1900 Interconnect Module
ABY
Error
Reset
+ABY
Ylatch
Rlsx
Flsx
Xlatch
+MBZ
INY
+MAZ
MAZ
ICM-1900 Drawing
AMP-19X0 Mating Power Amplifiers
ICM-2900 Interconnect Module
OUT PWR
OUT GND
ANALOG7
ANA GND
ANALOG5
ANALOG6
ANALOG4
ANALOG1
ANALOG2
ANALOG3
Opto-Isolated Outputs ICM-1900 / ICM-2900 -Opto option
Extended I/O of the DMC-13X8 Controller
Standard Opto-isolation and High Current Opto-isolation
BIT I/O Block Binary Representation Decimal Value for Block
Configuring the I/O of the DMC-13X8
Accessing extended I/O
Saving the State of the Outputs in Non-Volatile Memory
BIT #
Connector Description
PIN Signal Block
BIT @INn
GND
@OUTn
Description
IOM-1964 Opto-Isolation Module for Extended I/O Controllers
Overview
Configuring Hardware Banks
For example, here is the layout of bank
Sinking Sourcing
Input Circuit
High Power Digital Outputs
Internal Pullup
Standard Digital Outputs
Standard Digital Outputs
Electrical Specifications
High Power Digital Outputs
Digital Inputs
Relevant DMC Commands
Screw Terminal Listing
Terminal Label Description
Appendices
Coordinated Motion Mathematical Analysis
Vs = Vx 2 + Vy
Velocity
Tt = VSD + Ta = 0.407s
DMC-13X8
DMC-13X8/DMC-1300 Comparison
List of Other Publications
Benefit
WHO should Attend
Training Seminars
Galil Motion Control
Contacting Us
Warranty
206
Limswi
Poserr
Index
Address ... Error! Not a valid bookmark in entry on
Interrupt...Error! Not a valid bookmark in entry on
Stop