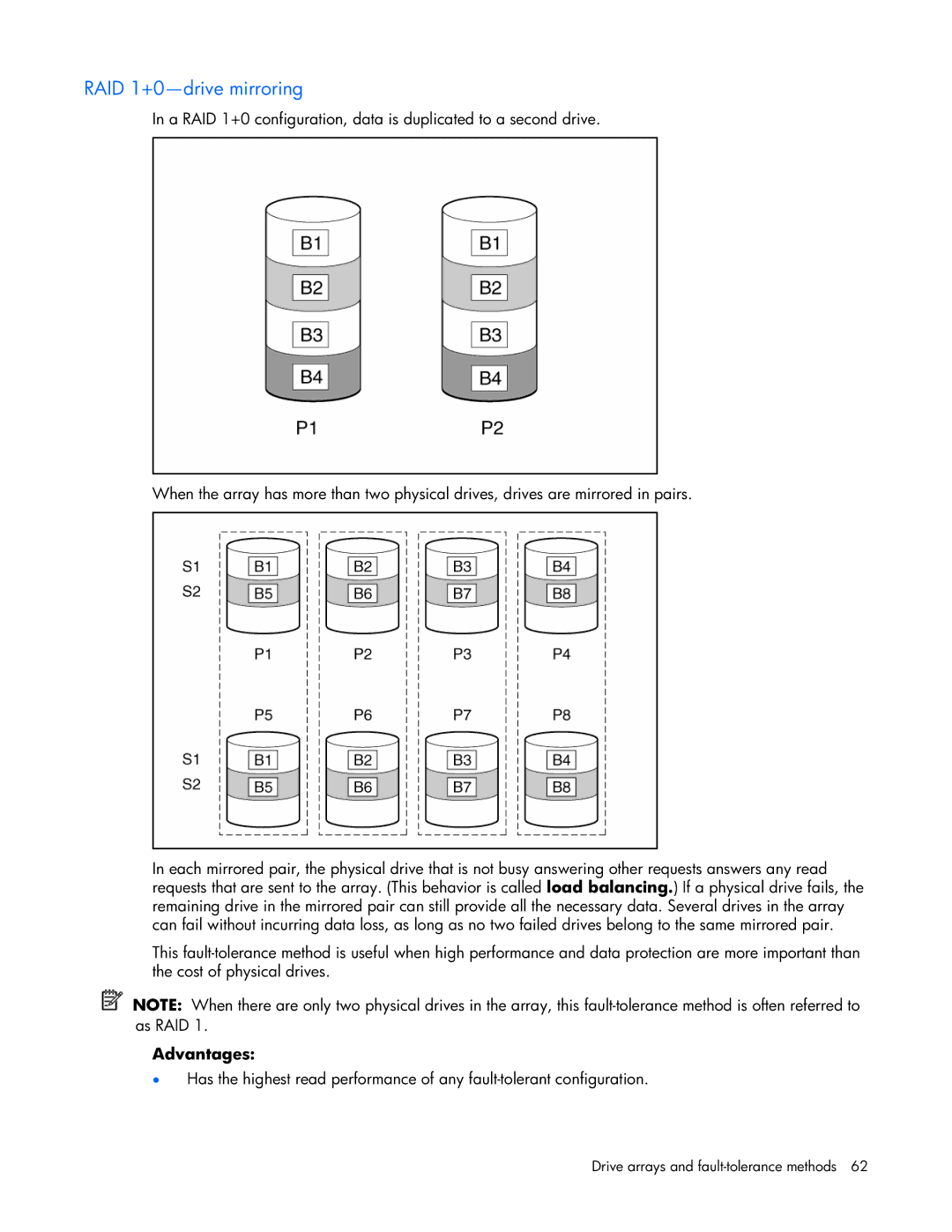
RAID 1+0—drive mirroring
In a RAID 1+0 configuration, data is duplicated to a second drive.
When the array has more than two physical drives, drives are mirrored in pairs.
In each mirrored pair, the physical drive that is not busy answering other requests answers any read requests that are sent to the array. (This behavior is called load balancing.) If a physical drive fails, the remaining drive in the mirrored pair can still provide all the necessary data. Several drives in the array can fail without incurring data loss, as long as no two failed drives belong to the same mirrored pair.
This
NOTE: When there are only two physical drives in the array, this
Advantages:
•Has the highest read performance of any