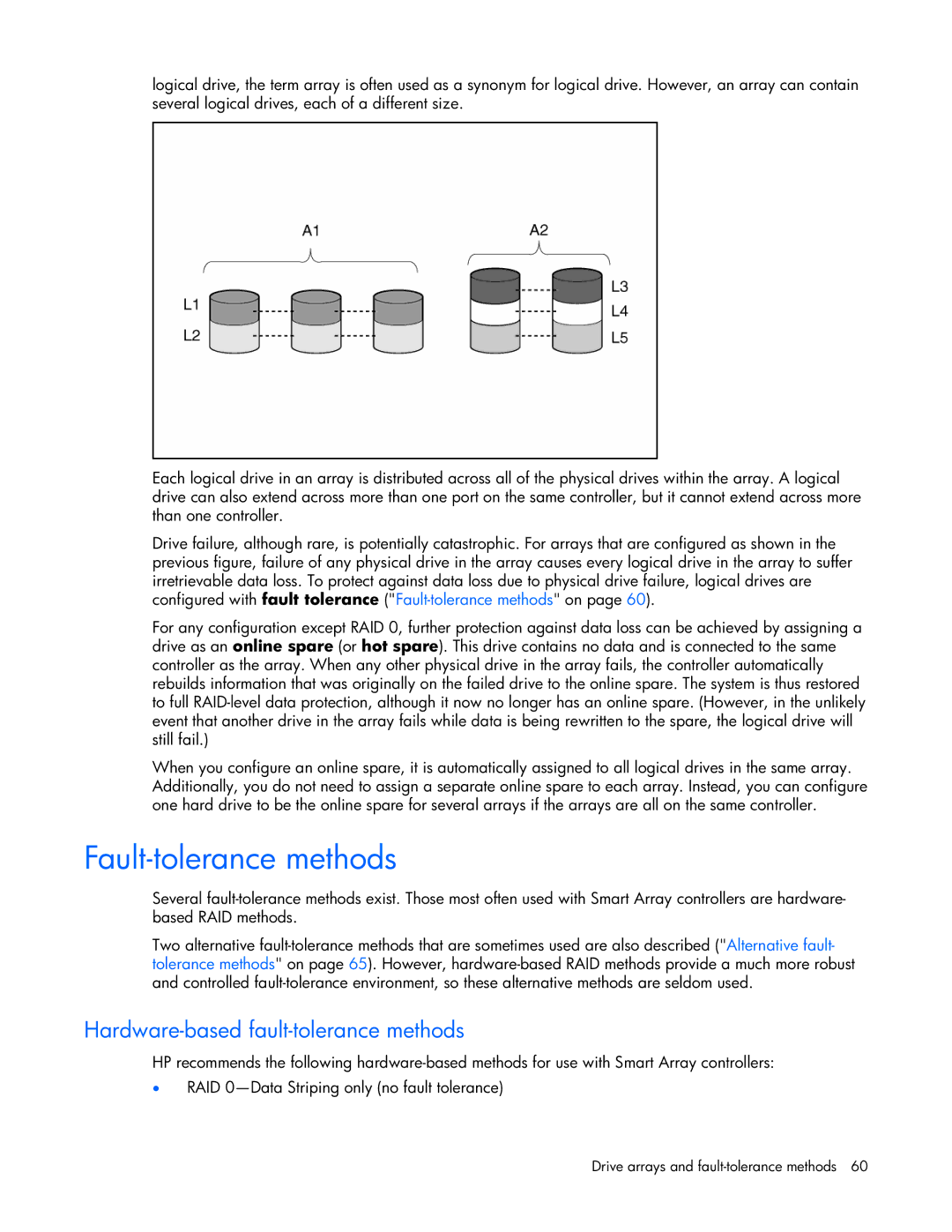
logical drive, the term array is often used as a synonym for logical drive. However, an array can contain several logical drives, each of a different size.
Each logical drive in an array is distributed across all of the physical drives within the array. A logical drive can also extend across more than one port on the same controller, but it cannot extend across more than one controller.
Drive failure, although rare, is potentially catastrophic. For arrays that are configured as shown in the previous figure, failure of any physical drive in the array causes every logical drive in the array to suffer irretrievable data loss. To protect against data loss due to physical drive failure, logical drives are configured with fault tolerance
For any configuration except RAID 0, further protection against data loss can be achieved by assigning a drive as an online spare (or hot spare). This drive contains no data and is connected to the same controller as the array. When any other physical drive in the array fails, the controller automatically rebuilds information that was originally on the failed drive to the online spare. The system is thus restored to full
When you configure an online spare, it is automatically assigned to all logical drives in the same array. Additionally, you do not need to assign a separate online spare to each array. Instead, you can configure one hard drive to be the online spare for several arrays if the arrays are all on the same controller.
Fault-tolerance methods
Several
Two alternative
Hardware-based fault-tolerance methods
HP recommends the following
•RAID