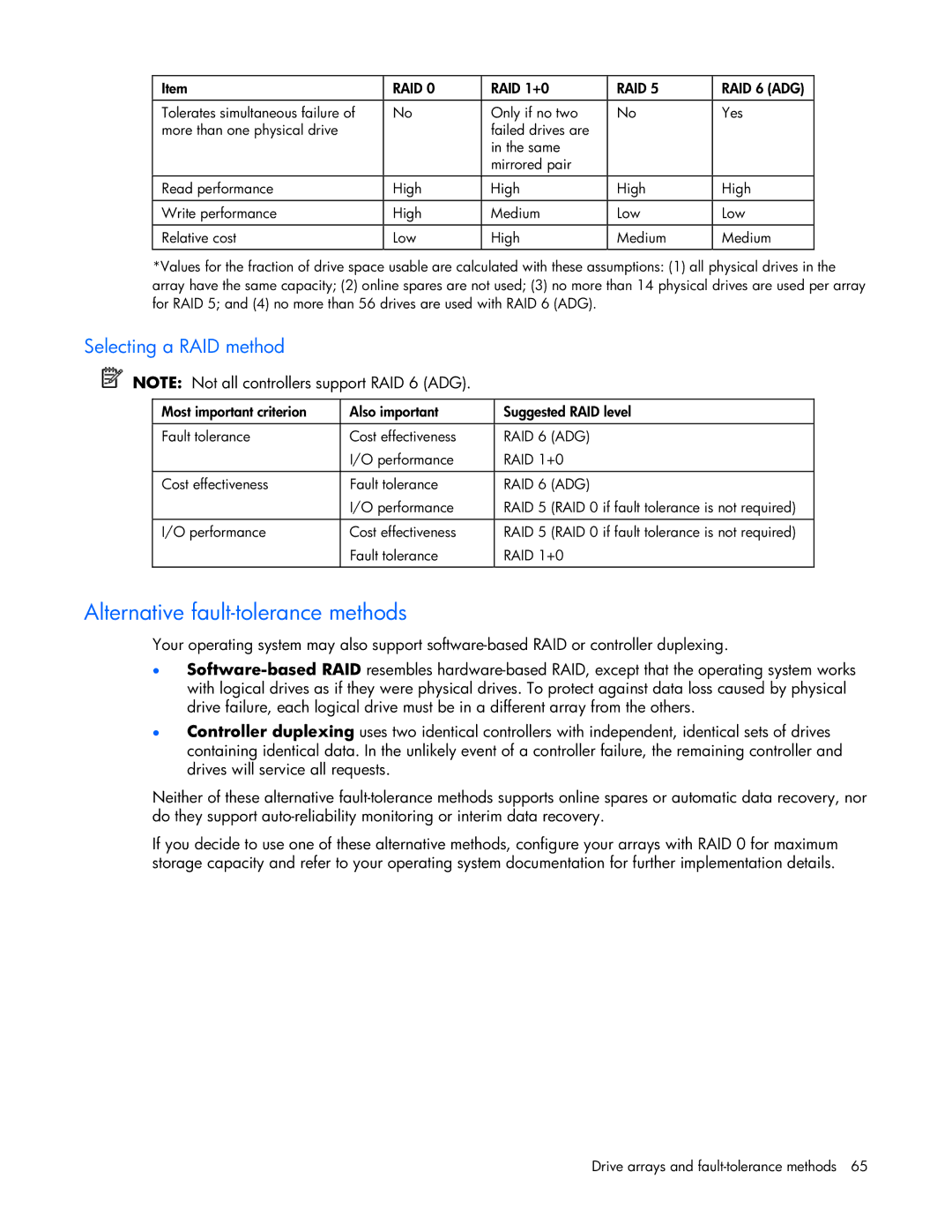
Item | RAID 0 | RAID 1+0 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 (ADG) |
|
|
|
|
|
Tolerates simultaneous failure of | No | Only if no two | No | Yes |
more than one physical drive |
| failed drives are |
|
|
|
| in the same |
|
|
|
| mirrored pair |
|
|
Read performance | High | High | High | High |
|
|
|
|
|
Write performance | High | Medium | Low | Low |
|
|
|
|
|
Relative cost | Low | High | Medium | Medium |
|
|
|
|
|
*Values for the fraction of drive space usable are calculated with these assumptions: (1) all physical drives in the array have the same capacity; (2) online spares are not used; (3) no more than 14 physical drives are used per array for RAID 5; and (4) no more than 56 drives are used with RAID 6 (ADG).
Selecting a RAID method
NOTE: Not all controllers support RAID 6 (ADG).
Most important criterion | Also important | Suggested RAID level | |
|
|
|
|
Fault tolerance | Cost effectiveness | RAID 6 | (ADG) |
| I/O performance | RAID 1+0 | |
|
|
|
|
Cost effectiveness | Fault tolerance | RAID 6 | (ADG) |
| I/O performance | RAID 5 | (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required) |
|
|
|
|
I/O performance | Cost effectiveness | RAID 5 | (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required) |
| Fault tolerance | RAID 1+0 | |
|
|
|
|
Alternative fault-tolerance methods
Your operating system may also support
•
•Controller duplexing uses two identical controllers with independent, identical sets of drives containing identical data. In the unlikely event of a controller failure, the remaining controller and drives will service all requests.
Neither of these alternative
If you decide to use one of these alternative methods, configure your arrays with RAID 0 for maximum storage capacity and refer to your operating system documentation for further implementation details.