Intel Server Board SDS2
Order Number A85874-002
Revision History Intel Server Board SDS2
Revision
Date Revision Modifications Number
Iii
Intel Server Board SDS2 Disclaimers
Table of Contents
Intel Server Board SDS2 Table of Contents
Revision Order Number A85874-002
Table of Contents Intel Server Board SDS2
106
101
102
Revision Vii Order Number A85874-002
124
Viii Revision Order Number A85874-002
Index
Reference Documents
Glossary
SDS2 Server Board Block Diagram
List of Figures Intel Server Board SDS2
List of Tables
Intel Server Board SDS2 List of Tables
List of Tables Intel Server Board SDS2
Xii Revision Order Number A85874-002
Revision Xiii Order Number A85874-002
This page intentionally left blank
Xiv Revision Order Number A85874-002
Introduction
Intel Server Board SDS2 Introduction
Architecture
Architecture Intel Server Board SDS2
Revision Order Number A85874-002
Processor and Chipset Intel Server Board SDS2
Processor and Chipset
Processors
SDS2 Intel Pentium III Processor Support Matrix
Intel Server Board SDS2 Processor and Chipset
SL5XL
Memory Subsystem
Memory Configuration
Processor Voltage Regulator Module VRM
Row
Dimm Pair
Memory Dimm
DIMM1A, DIMM1B DIMM2A, DIMM2B DIMM3A, DIMM3B
I2C Addresses for Dimm Slots
Chipset
2 I2C Bus
Device Address
1 CNB20HE-SL Champion North Bridge
PCI Bus P32-A I/O Subsystem
PCI Bus P64-B I/O Subsystem
CIOB20 Champion I/O Bridge
3 CSB5 South Bridge
PCI Bus P64-C I/O Subsystem
1 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI Subsystem
O Subsystem
PCI Subsystem
Device IDs Idsel
1.2 P32-A Arbitration
Subsystem Intel Server Board SDS2 P32-A Configuration IDs
2 64-bit, 66-MHz PCI Subsystem
P32-A Arbitration Connections
2.2 P64-B Arbitration
Intel Server Board SDS2 Subsystem P64-B Configuration IDs
P64-C Configuration IDs
2.3 P64-C Arbitration
Video Modes
Ultra160 Scsi
Video Controller
Zero Channel RAID ZCR Capable PCI Slot
Network Interface Controller NIC
Intel Server Board SDS2 Subsystem Video Modes
PCI Bus Interface
NIC Connector and Status LEDs
CSB5 South Bridge PCI-to-LPC Bridge, IDE, USB
PCI Bus Master IDE Interface
USB Interface
Power Management
General Purpose Input and Output Pins
Compatibility Interrupt Control
Super I/O
Pin # Signal Name Description
Chipset Support Components
General Purpose Input and Output Gpio
Keyboard and Mouse
Serial Ports
Floppy
Parallel Port
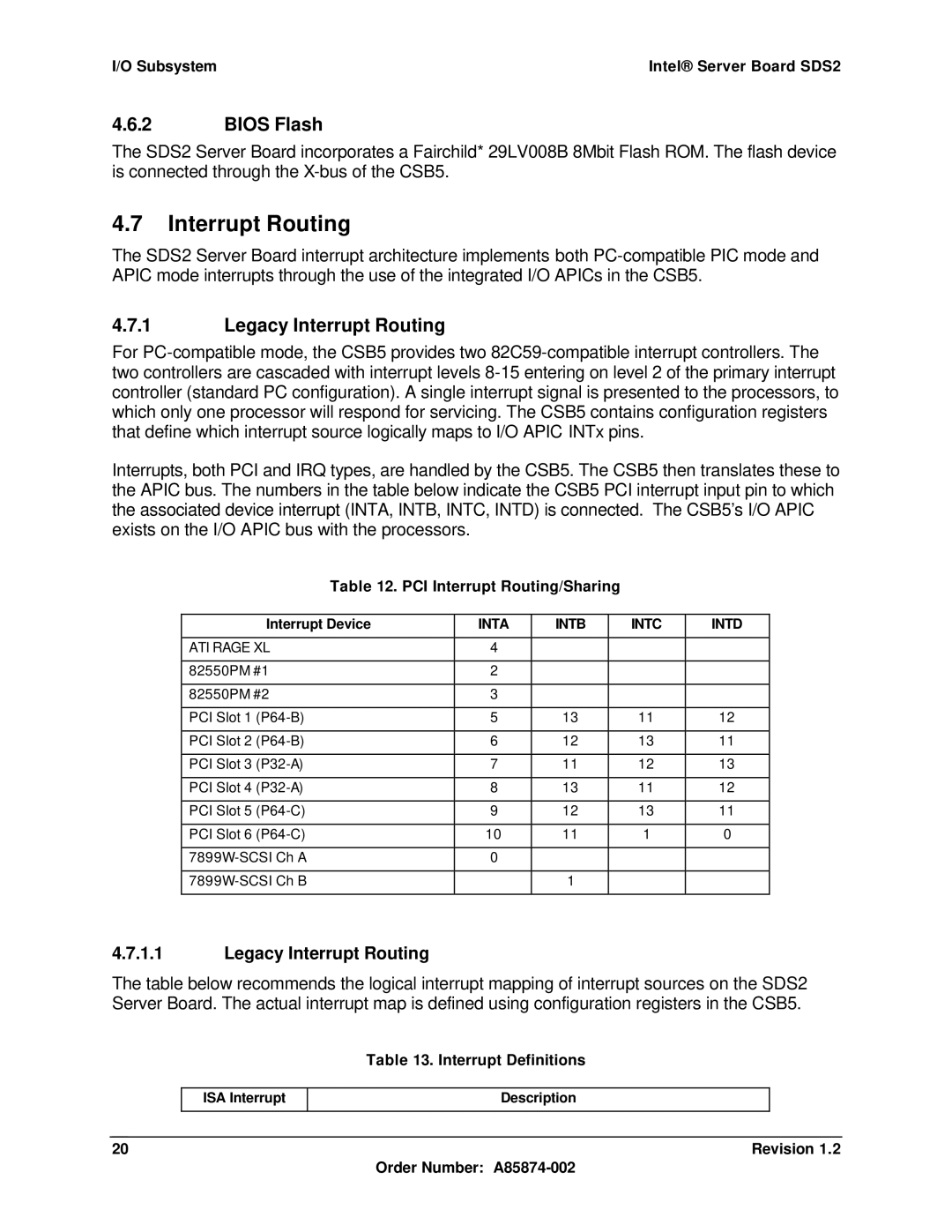
Legacy Interrupt Routing
Bios Flash
Interrupt Routing
Legacy Interrupt Routing
Serialized IRQ Support
Apic Interrupt Routing
IRQ Scan for Pciirq
SCAN0 Ioapic
Ioapic
SCAN2 INT
PCIIRQ0
CSB5 Interrupt Routing
Serialized IRQ Interface PCI IRQ Serializer
Super I/O
Slot
Server Management
Intel Server Board SDS2 Server Management
Server Management Intel Server Board SDS2
Baseboard
Sahalee Baseboard Management Controller
Pin Signal Name Description
ADM1026 Input Definition
Temperature Sensor Description Resolution Accuracy
Temperature Sensors
Sahalee Input Definition
Nmemalertl
Fault Resilient Booting
NFAN6SENSEP
Nbmcsecuremode
Hard Reset
System Reset Control
Power-up Reset
Soft Reset
Private I2C Bus 2 Devices
Intel Server Board SDS2 Server Management Ipmb Bus Devices
Private I2C Bus 1 Devices
Private I2C Bus 3 Devices
PCI Bus Errors
Error Reporting
Error Sources and Types
Intel Pentium III Processor Bus Errors
Acpi
AC Link Mode
Memory Bus Errors
ID LED
Setup Utility F2 can change the AC link mode settings
Bios
System Bios
Handling and Logging System Errors
Bios Error Handling
Logging Format Conventions
PCI Serr
Bios Generated SEL Errors
Sensor Sensor Type Number Specific Event Code Offset
PCI Perr
Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents
PCI Bus Error
Intel Pentium III Processor Bus Error
SMI Handler
Firmware BMC
Name
Sensor Type Triggers Event Reading Offset
BB Vbat
Lvds Scsi
OEM C7h 01h Temp Tach Fan 48h Fan 04h Threshold 49h
Ierr FRB1
FRB2 FRB3
Timestamp Clock
Post Codes
Error Messages and Error Codes
ASF Progress Codes
Port-80h Code Definition
Standard Bios Post Codes
Bios
Bios
Recovery Bios Post Codes
Beeps Reason
Code Error Message Failure Description
Post Error Codes and Messages
Post Error Messages and Codes
Cmos
BMC Beep Codes
Baseboard Management Controller BMC Beep Code Generation
Reason for Beep
Setup Utility Operation
Setup Utility
Configuration Utilities Overview
Setup Utility Screen
Entering Setup Utility
Keyboard Command Bar
Key Option Description
ESC
Menu Selection Bar
Main Menu Selections
Auto
Primary Master and Slave IDE Submenu Selections
Cdrom
Not Installed
Processor Settings Submenu Selections
Standard
Memory Configuration Menu Selections
Advanced Menu Selections
On-board VGA Submenu Selections
PCI Configuration Menu Selections
On-board Scsi and LAN Submenu Selections
PCI slot Submenu Selections
Bios
2F8h
O Device/Peripheral Configuration Submenu Selections
3F8h
EPP
PCI Device Submenu Selections
Advanced Chipset Controller Submenu Selections
Security Menu Selections
Normal
Server Menu Selections
Hours
BMC IRQ
Disable Immediately
System Management Submenu Selections
IRQ5 IRQ10
Console Redirection Submenu Selections
Boot Device Priority Selections
Boot Priority Device Description
9600
Exit Menu Selections
Hard Drive Selections
Removable Drive Selections
Option Description
Cmos Memory Definition
Flash Update Utility
Loading the System Bios
Clearing Cmos
User Binary Area
Recovery Mode
Performing Bios Recovery
Language Area
Bios
Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution
Clock
CPU HE-SL
Voltage
Supply
Power Distribution Board Connector
Connections
Intel Server Board SDS2 Connections
Memory Module Connector
Dimm Connector Pin-out
Pin Front Back
Scsi Hsbp Ipmb Connector
Icmb Connector
OEM Ipmb Connector
System Management Headers
KEY
Front Panel Header
Front Panel 34-Pin Header Pin-out
I2C SDA
64-bit 3.3V PCI Slot Pin-out
PCI Slot Connector
Bit 5 V PCI Slot Pin-out
Pin Side B Side a
M66EN
TDO TDI INTA# INTB# INTC# INTD# PRSNT1# RSV
PRSNT2# RSV
PAR64
Scsi Connector
I/O Connectors
VGA Connector
VGA Connector Pin-out
RJ-45 Connector Pin-out
NIC Connectors
Signal Name Connector Contact Number
IDE 40-pin Connector Pin-out
IDE Connector
Universal Serial Bus USB Connectors
Txdp Rxdp Txdm Rxdm
Floppy Connector
Pin USB Connection Header 2 x 5 Pin-out
Serial Port Connector
DB9 Serial Port Pin-out
Parallel Port
Keyboard and Mouse Connector
DB25 Parallel Port Pin-out
Fan Headers
External Scsi Activity LED Input Signal Connector
Miscellaneous Headers
Chassis Intrusion
Rear I/O Panel
Connector Manufacturers and Part Numbers
Server Board Connector Manufacturer Part Numbers
CN Numbers Qty Manufacturer Mfg Functional Description
Jumpers
System Configuration Jumpers
Jumpers Intel Server Board SDS2
SDS2 Configuration Jumpers
Intel Server Board SDS2 Jumpers
RSV
CN59 CPU Frequency Select Jumper Settings
System Configuration Jumper Options
Bios
CPU Frequency Select Jumper Options
Jumper Pins Default Operation
Performing Cmos Clear, Bios Recovery, and BMC Force Update
Performing Bios Recovery Boot
Performing Cmos Clear
Performing BMC Force Update
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Electrical and Thermal Specifications
Power Consumption
Absolute Maximum Ratings
SDS2 Power Supply Specification
Power Supply Specification
Power Timing
Voltage Timing Parameters
Page
Estimated SDS2 Server Board Mtbf Turn On/Off Timing
Estimateded Server Board Mtbf
100 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Mechanical Specifications
Intel Server Board SDS2 Mechanical Specifications
Regulatory Compliance
Safety Regulations
Regulatory and Integration Information
EMC Regulations
Ensure EMC
Installation Instructions
Revision 103 Order Number A85874-002
Prevent Power Supply Overload
Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications
Place Battery Marking on Computer
Use Only for Intended Applications
Installation Precautions
Icmb External Cable Connectors
External Icmb Cable Information
Errata Listing Intel Server Board SDS2
Errata Listing
Summary Errata Table
Errata Summary
Intel Server Board SDS2 Errata Listing
Revision 107 Order Number A85874-002
108 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Revision 109 Order Number A85874-002
Intel Server Board SDS2 CD-ROM issues
110 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Revision 111 Order Number A85874-002
Mode Support Comments
High resolution video modes do not work correctly
112 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Lower performance with CAS Latency 2 memory
Revision 113 Order Number A85874-002
Novell NetWare* v .0 does not install on SDS2
114 Revision Order Number A85874-002
SDS2 0B71 System Temperature out of the range Post message
Revision 115 Order Number A85874-002
SDS2 0B75 System Voltage out of the range Post message
116 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Recommendation for SDS2 rubber bumper installation
Revision 117 Order Number A85874-002
118 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Placing the Rubber Bumper in the Chassis
Revision 119 Order Number A85874-002
Secondary IDE References Added To Documentation for FAB
Boot to service partition via modem fails
120 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Bootable CD will not boot if inserted during Option ROM scan
Revision 121 Order Number A85874-002
122 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Status Will Not Fix
Can Not Change Bios Setup IDE Options Using Enter Key
Revision 123 Order Number A85874-002
124 Revision Order Number A85874-002
SDS2 PCI slot current levels supported by the 5V rail
Revision 125 Order Number A85874-002
126 Revision Order Number A85874-002
Term Definition
Glossary Intel Server Board SDS2
Reference Documents
Index
Index Intel Server Board SDS2
Get SDR Time command, 43 Get SEL Time command, 43 GPI pin
NPWRGD+00
RevisionIII Order Number A85874-002
Index Intel Server Board SDS2
RevisionV Order Number A85874-002