User Guide
Technical Support Sales Offices
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
Disclaimer
Table of Contents
Configuration via Telnet or Serial Port Setup Mode
Setup Mode Advanced Settings
Gpio Interface
List of Figures
List of Tables
Chapter Summary
Using This Guide
Purpose and Audience
XPico Integration Guide
Additional Documentation
Applications
Introduction
Capabilities
Hardware Address
Configuration Methods
Protocol Support
Addresses and Port Numbers
Port Numbers
Product Information Label
IP Address
Assigning an IP Address
Using DeviceInstaller
Installing DeviceInstaller
To install DeviceInstaller
Name
Accessing the xPico Using DeviceInstaller
To view the units current settings
Select Assign a specific IP address and click Next
Device Family
Dhcp Device Name
Group
Comments
Supports Http Setup
Firmware Upgradeable
Supports Configurable
Pins
Accessing Web-Manager Using DeviceInstaller
Configuration Using Web Manager
Web-Manager Login Window
Network Configuration
Select Obtain IP address automatically
Network Mode
To assign an IP address automatically
To assign an IP address manually
Static IP Address Configuration
Ethernet Configuration
Select Use the following IP configuration
Auto Negotiate
To configure the xPico’s device server settings
Advanced
Host List Configuration
Server Configuration
Host Information
Channel 1 and 2 Configuration
Retry Settings
To configure the xPico’s host list
Channel
Serial Settings
Port Settings
To configure the channel’s serial settings
Flush Input Buffer Serial to Network
Pack Control
At Time of Disconnect
Connection Settings TCP
To configure a channel’s TCP settings
Flush Output Buffer Network to Serial
TCP Connection Settings
Connect Protocol
Connect Mode Passive Connection
Connect Mode Active Connection
Endpoint Configuration
To configure a channel’s UDP settings
Connection Settings UDP
Disconnect Mode
Device Address Table
Datagram Mode
Datagram Type
Use Broadcast
To configure the xPico’s Configurable Pins
Configurable Pin Settings
Configurable Pin Functions
Serial Channel 2 Status LED
Apply Settings
Apply Defaults
Serial Channel 1 Status LED
Telnet Connection
Configuration via Telnet or Serial Port Setup Mode
Accessing Setup Mode
To establish a Telnet connection
Serial Port Connection
To exit setup mode
Exiting Setup Mode
IP Address
Setup Mode Server Configuration
Server Configuration Option
BootP/DHCP/AutoIP Options
Set DNS Server IP Address
Change Telnet/Web-Manager Password
Set Gateway IP Address
Netmask Number of Bits for Host Part
Dhcp Name
Baudrate
Setup Mode Channel Configuration
Channel 1 Option 1 or Channel 2 Option
Flow
Interface Mode
Interface Mode Options
RS232 Interface Mode Settings
Reserved Port Numbers
Connect Mode
Port Number
Flow Control Options
Response
Connect Mode Options
Incoming Connection
Incoming Connection
Active Startup
Response
Manual Connection Address Example
Manual Connection
Hostlist Option
To enable the hostlist
Directed UDP
Modem Mode
Datagram Type
Numeric Response
Modem Mode Commands
Auto Increment Source Port
Send the Escape Sequence +++ in Modem Mode
Show IP addr after Ring
Remote IP Address
Disconnect Mode Options
Pack Control
Flush Mode Buffer Flushing
Send Characters
Packing Interval
Trailing Characters
Telnet Terminal Type
DisConnTime Inactivity Timeout
Channel Port Password
Send Characters
TCP Keepalive time in seconds
Setup Mode Advanced Settings
Expert Settings Option
Http Port Number
ARP Cache timeout in seconds
Disable Monitor Mode at bootup
CPU Performance
Ethernet Connection Type
Security Settings Option
TCP Re-Transmission Timeout
Enable alternate MAC
Snmp Community Name
Disable Snmp
Disable Telnet Setup
Disable Web Setup
Disable Tftp Firmware Upgrade
Disable Port 77FE Hex
Disable Web Server
To configure AES encryption on the xPico
Enable Encryption
Channel 1 and Channel 2 Configuration Defaults
Default Settings Option
Enable Enhanced Password
Disable Port 77F0 Hex
Start character for serial channel
Expert Settings Defaults
Security Settings Defaults
Hostlist retry timeout
Gpio Interface
Configurable Pins
Features
Guidelines
Commands
Byte 0 Command Types
Control Protocol
Command 13h, Get Current States
Command 10h, Get Functions
Command 11h, Get Directions
Command 12h, Get Active Levels
Command details
Command 19h, Set Directions
Command 1Ah, Set Active Levels
Command 1Bh, Set States
Response details
To download new firmware from a computer
Firmware Upgrades
Using Tftp Graphical User Interface
Obtaining Firmware Reloading Firmware
Tftp Window
Using Tftp Command Line Interface
To recover firmware
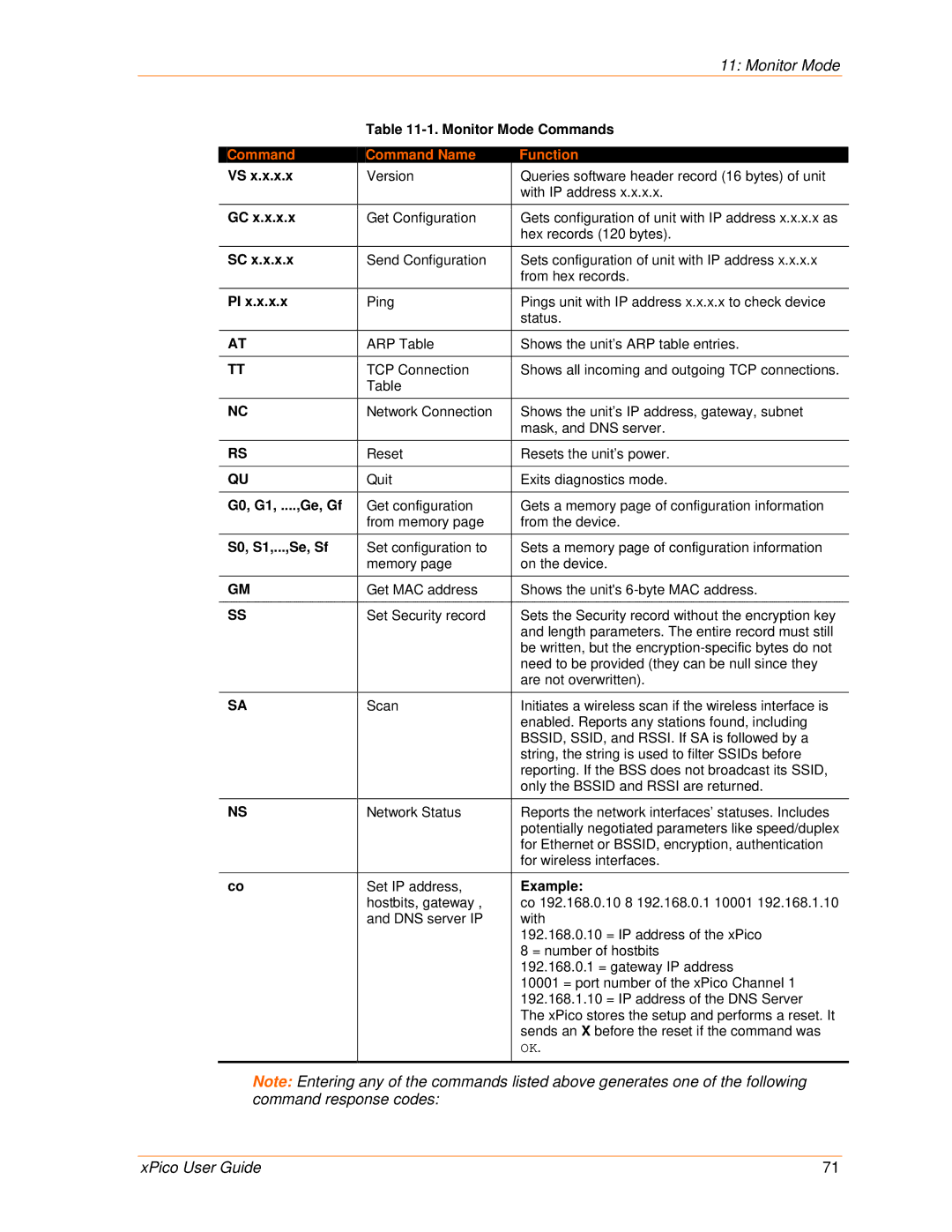
Monitor Mode Commands
Monitor Mode
Entering Monitor Mode Using the Serial Port
Entering Monitor Mode Using the Network Port
Example
Monitor Mode Commands
G0, G1, ....,Ge, Gf
S0, S1,...,Se, Sf
Response Meaning
Command Response Codes
Problems and Error Messages
Troubleshooting
Lock on
Caps Lock is not on
Troubleshooting
Technical Support Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Technical Support
Technical Support US
Scientific Calculator
Binary to Hexadecimal Conversions
Converting Binary to Hexadecimal
Conversion Table
Binary to Hexadecimal Conversions
RoHS Notice
Compliance