Automation and Drives - SCE
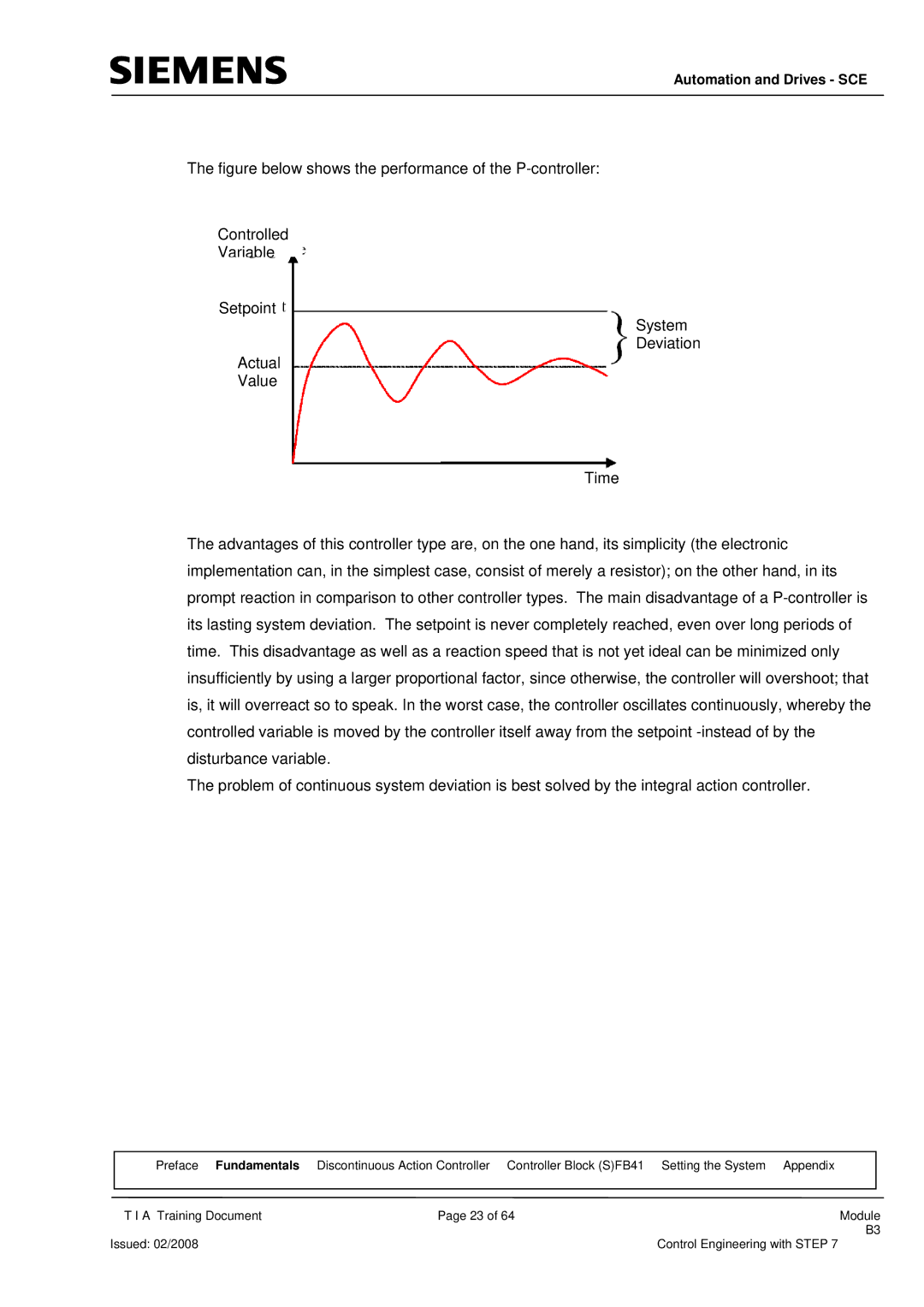
The figure below shows the performance of the P-controller:
Controlled
Variable
Setpoint
System
Deviation
Actual
Value
Time
The advantages of this controller type are, on the one hand, its simplicity (the electronic implementation can, in the simplest case, consist of merely a resistor); on the other hand, in its prompt reaction in comparison to other controller types. The main disadvantage of a P-controller is its lasting system deviation. The setpoint is never completely reached, even over long periods of time. This disadvantage as well as a reaction speed that is not yet ideal can be minimized only insufficiently by using a larger proportional factor, since otherwise, the controller will overshoot; that is, it will overreact so to speak. In the worst case, the controller oscillates continuously, whereby the controlled variable is moved by the controller itself away from the setpoint -instead of by the disturbance variable.
The problem of continuous system deviation is best solved by the integral action controller.
| Preface | Fundamentals | Discontinuous Action Controller Controller Block (S)FB41 | Setting the System Appendix |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| T I A Training Document | Page 23 of 64 | Module | ||
|
|
|
| B3 | |
Issued: 02/2008 |
|
| Control Engineering with STEP 7 | ||