Automation and Drives - SCE
2.7.3.2 Integral Action Controllers (I- Controller)
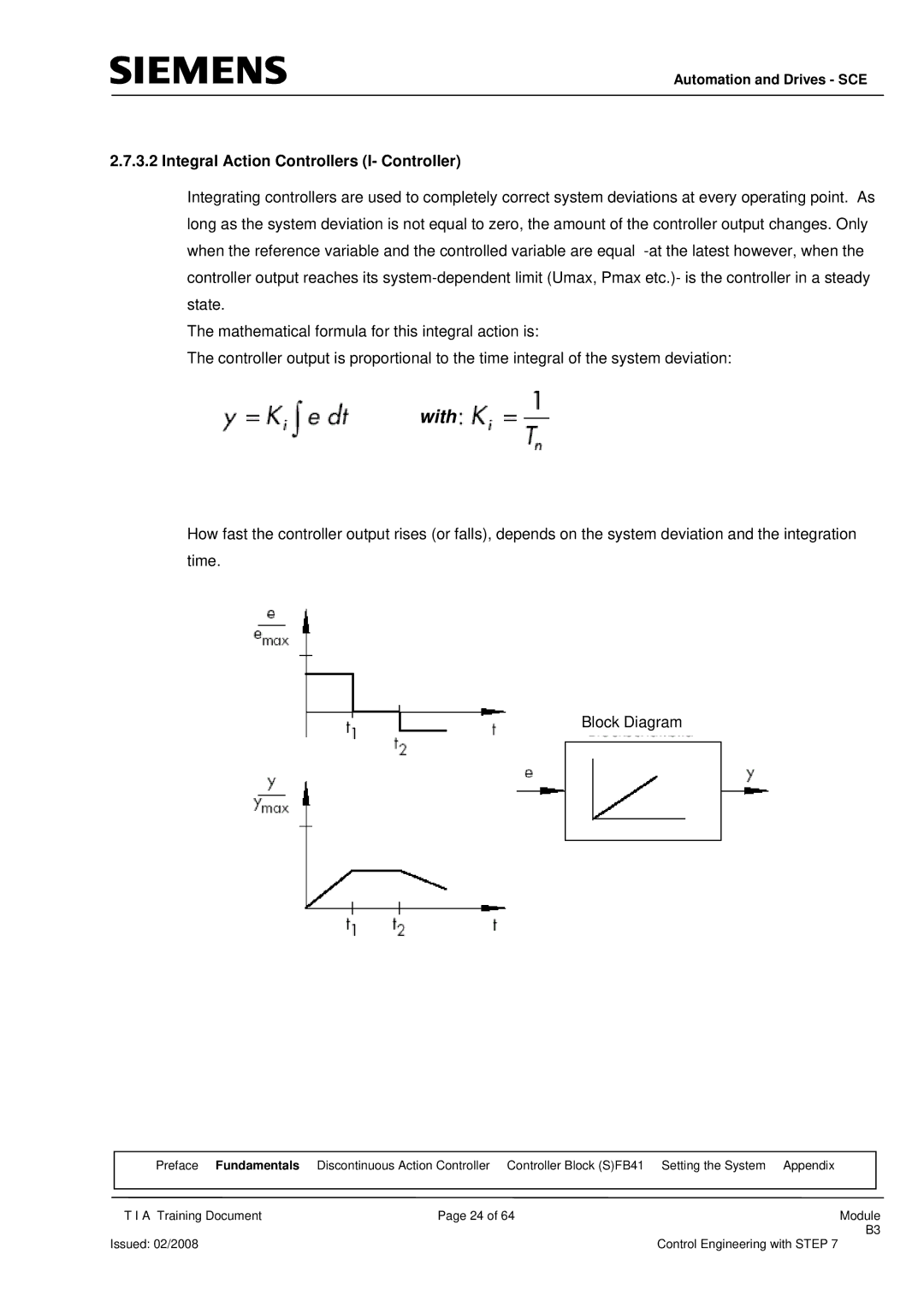
Integrating controllers are used to completely correct system deviations at every operating point. As long as the system deviation is not equal to zero, the amount of the controller output changes. Only when the reference variable and the controlled variable are equal
The mathematical formula for this integral action is:
The controller output is proportional to the time integral of the system deviation:
with
How fast the controller output rises (or falls), depends on the system deviation and the integration time.
Block Diagram
| Preface | Fundamentals | Discontinuous Action Controller Controller Block (S)FB41 | Setting the System Appendix |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| T I A Training Document | Page 24 of 64 | Module | ||
|
|
|
| B3 | |
Issued: 02/2008 |
|
| Control Engineering with STEP 7 | ||