Automation and Drives - SCE
2.2 Components of a Control Loop
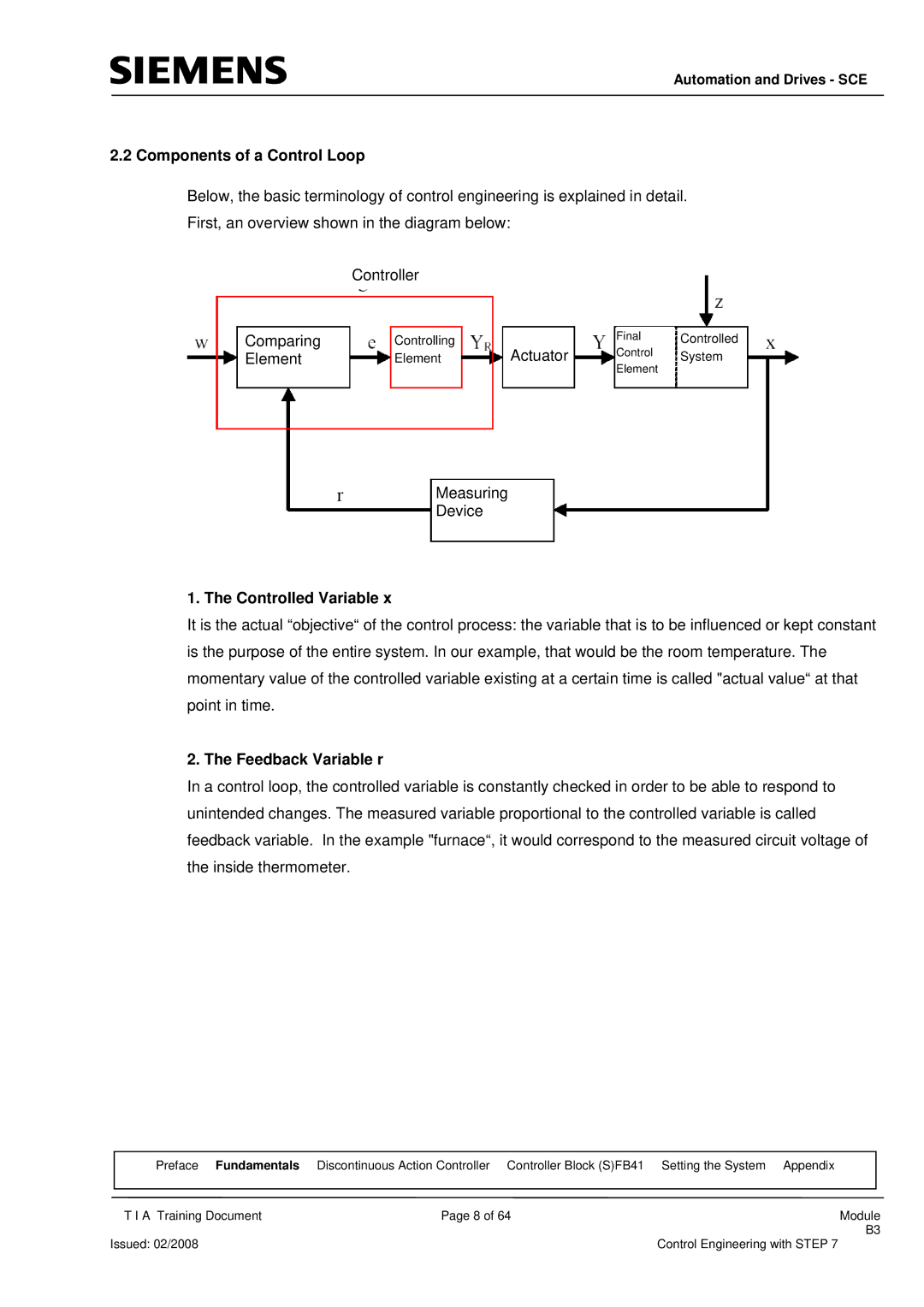
Below, the basic terminology of control engineering is explained in detail.
First, an overview shown in the diagram below:
|
| Controller |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Final | Controlled | ||
|
| Controlling |
|
|
|
| ||||
Comparing |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Element |
| Element |
|
| Actuator |
| Control |
| System | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Element |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measuring
Device
1. The Controlled Variable x
It is the actual “objective“ of the control process: the variable that is to be influenced or kept constant is the purpose of the entire system. In our example, that would be the room temperature. The momentary value of the controlled variable existing at a certain time is called "actual value“ at that point in time.
2. The Feedback Variable r
In a control loop, the controlled variable is constantly checked in order to be able to respond to unintended changes. The measured variable proportional to the controlled variable is called feedback variable. In the example "furnace“, it would correspond to the measured circuit voltage of the inside thermometer.
| Preface | Fundamentals | Discontinuous Action Controller Controller Block (S)FB41 | Setting the System Appendix |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| T I A Training Document | Page 8 of 64 | Module | ||
|
|
|
| B3 | |
Issued: 02/2008 |
|
| Control Engineering with STEP 7 | ||