KHM-220A DVD Optical Block
Sony DVD players had two independent laser assemblies. One was used to play DVD and the other used to play CDs. In 1999, a single DVD laser in the
By examining disc focusing, we can see why the lens was altered to play- back a CD with a DVD laser.
DVD Focus
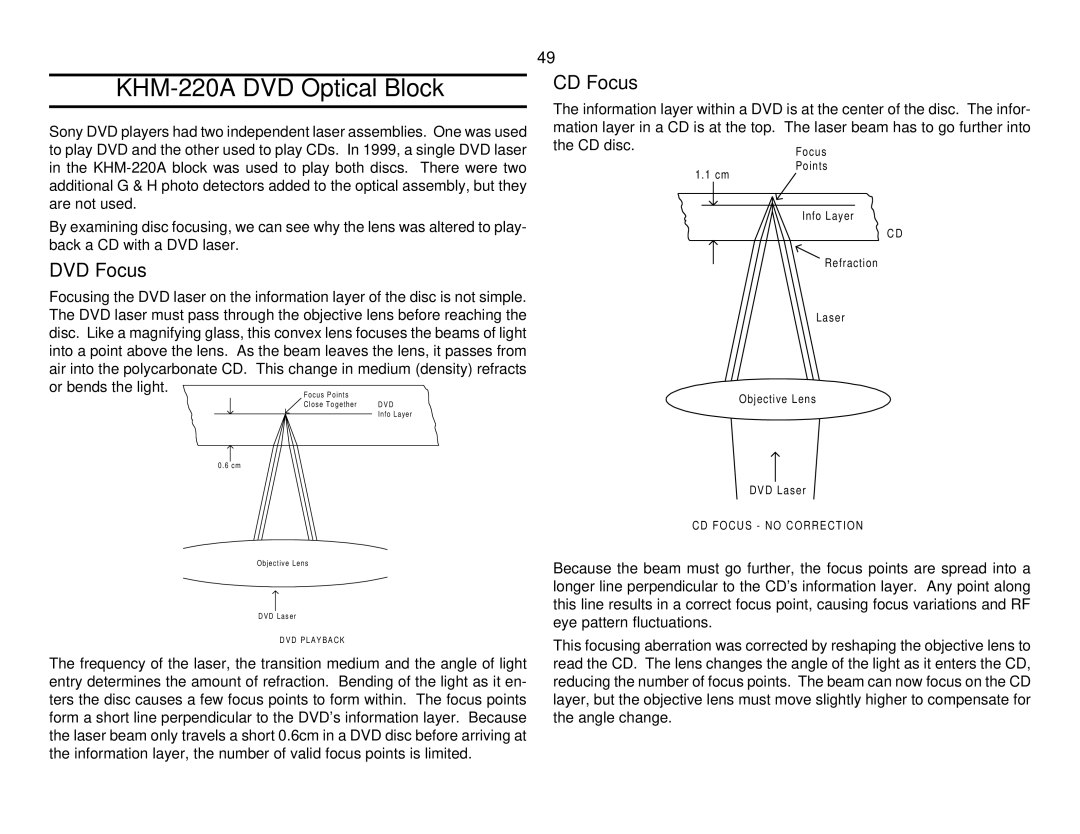
Focusing the DVD laser on the information layer of the disc is not simple. The DVD laser must pass through the objective lens before reaching the disc. Like a magnifying glass, this convex lens focuses the beams of light into a point above the lens. As the beam leaves the lens, it passes from air into the polycarbonate CD. This change in medium (density) refracts or bends the light.
D V D
Info Layer
0.6 cm
49
CD Focus
The information layer within a DVD is at the center of the disc. The infor- mation layer in a CD is at the top. The laser beam has to go further into the CD disc.
1.1 cm
Info Layer
CD
Refraction
Laser
Objective Lens
DVD Laser
CD FOCUS - NO CORRECTION
Objective Lens
DVD Laser
DVD PLAYBACK
The frequency of the laser, the transition medium and the angle of light entry determines the amount of refraction. Bending of the light as it en- ters the disc causes a few focus points to form within. The focus points form a short line perpendicular to the DVD’s information layer. Because the laser beam only travels a short 0.6cm in a DVD disc before arriving at the information layer, the number of valid focus points is limited.
Because the beam must go further, the focus points are spread into a longer line perpendicular to the CD’s information layer. Any point along this line results in a correct focus point, causing focus variations and RF eye pattern fluctuations.
This focusing aberration was corrected by reshaping the objective lens to read the CD. The lens changes the angle of the light as it enters the CD, reducing the number of focus points. The beam can now focus on the CD layer, but the objective lens must move slightly higher to compensate for the angle change.