Registers | www.ti.com |
4.3Asynchronous n Configuration Registers (A1CR-A4CR)
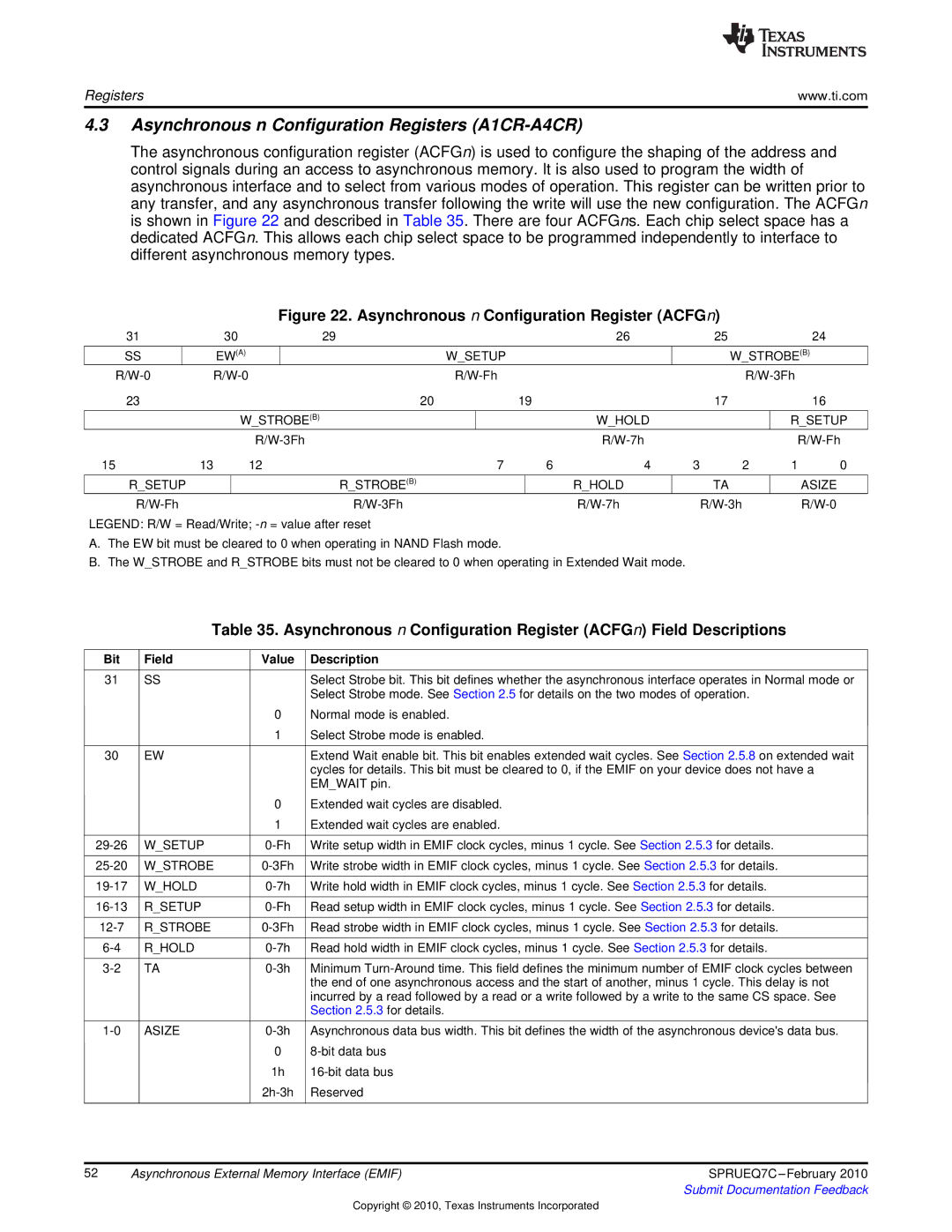
The asynchronous configuration register (ACFGn) is used to configure the shaping of the address and control signals during an access to asynchronous memory. It is also used to program the width of asynchronous interface and to select from various modes of operation. This register can be written prior to any transfer, and any asynchronous transfer following the write will use the new configuration. The ACFGn is shown in Figure 22 and described in Table 35. There are four ACFGns. Each chip select space has a dedicated ACFGn. This allows each chip select space to be programmed independently to interface to different asynchronous memory types.
Figure 22. Asynchronous n Configuration Register (ACFGn)
31 |
| 30 | 29 |
|
|
|
| 26 | 25 |
| 24 |
| ||
SS |
| EW(A) |
|
| W_SETUP |
|
|
| W_STROBE(B) |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
| 19 |
| 17 |
| 16 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| W_STROBE(B) |
|
|
|
| W_HOLD |
|
| R_SETUP | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
15 |
| 13 |
| 12 |
| 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R_SETUP |
|
|
| R_STROBE(B) |
|
|
|
| R_HOLD | TA |
| ASIZE |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write;
A.The EW bit must be cleared to 0 when operating in NAND Flash mode.
B.The W_STROBE and R_STROBE bits must not be cleared to 0 when operating in Extended Wait mode.
Table 35. Asynchronous n Configuration Register (ACFGn) Field Descriptions
Bit | Field | Value | Description |
|
|
|
|
31 | SS |
| Select Strobe bit. This bit defines whether the asynchronous interface operates in Normal mode or |
|
|
| Select Strobe mode. See Section 2.5 for details on the two modes of operation. |
|
| 0 | Normal mode is enabled. |
|
| 1 | Select Strobe mode is enabled. |
|
|
|
|
30 | EW |
| Extend Wait enable bit. This bit enables extended wait cycles. See Section 2.5.8 on extended wait |
|
|
| cycles for details. This bit must be cleared to 0, if the EMIF on your device does not have a |
|
|
| EM_WAIT pin. |
|
| 0 | Extended wait cycles are disabled. |
|
| 1 | Extended wait cycles are enabled. |
|
|
|
|
W_SETUP | Write setup width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
W_STROBE | Write strobe width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
W_HOLD | Write hold width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
R_SETUP | Read setup width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
R_STROBE | Read strobe width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
R_HOLD | Read hold width in EMIF clock cycles, minus 1 cycle. See Section 2.5.3 for details. | ||
|
|
|
|
TA | Minimum | ||
|
|
| the end of one asynchronous access and the start of another, minus 1 cycle. This delay is not |
|
|
| incurred by a read followed by a read or a write followed by a write to the same CS space. See |
|
|
| Section 2.5.3 for details. |
|
|
|
|
ASIZE | Asynchronous data bus width. This bit defines the width of the asynchronous device's data bus. | ||
|
| 0 | |
|
| 1h | |
|
| Reserved | |
|
|
|
|
52 | Asynchronous External Memory Interface (EMIF) | SPRUEQ7C |
|
| Submit Documentation Feedback |
Copyright © 2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated