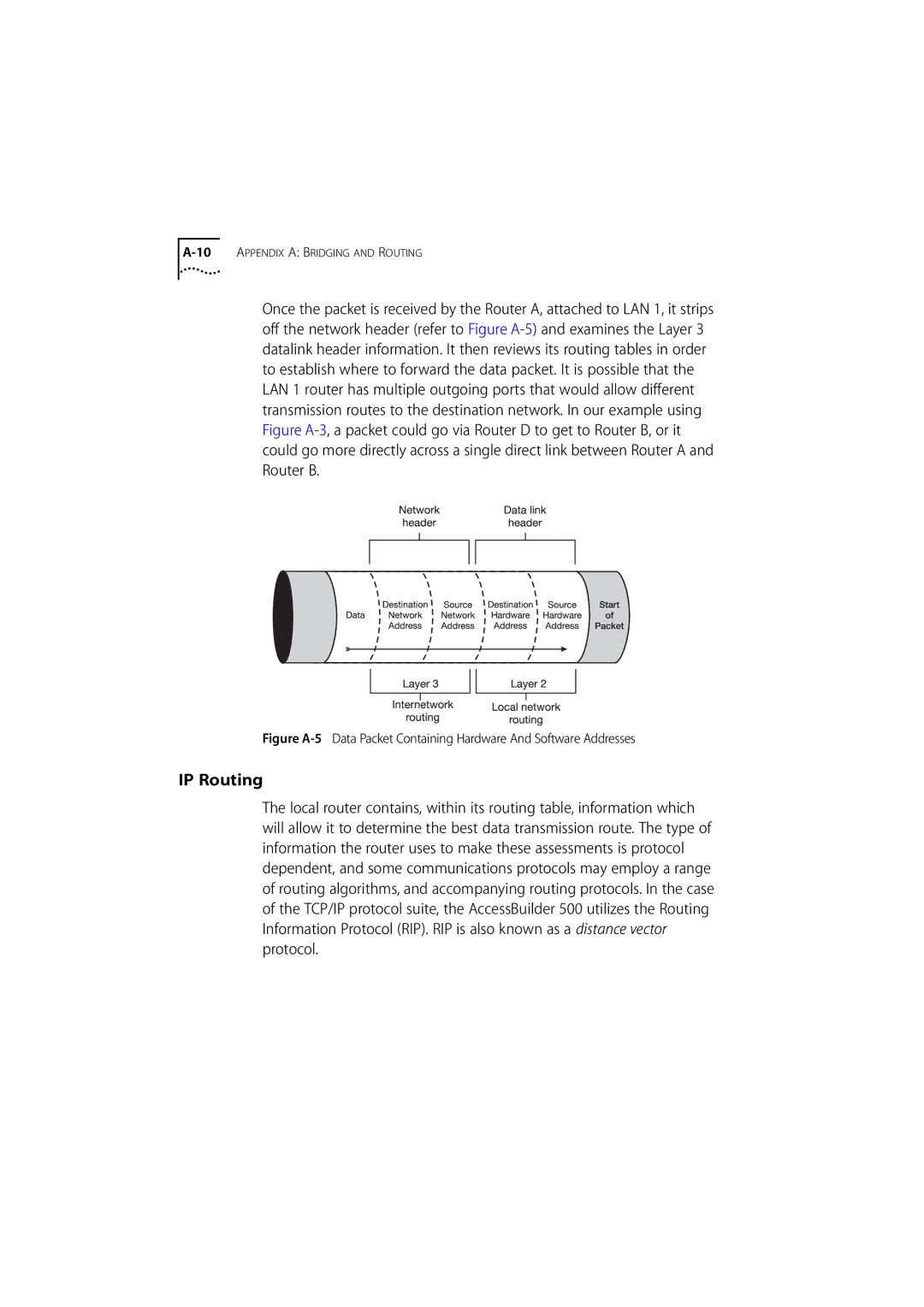
Once the packet is received by the Router A, attached to LAN 1, it strips off the network header (refer to Figure
Figure A-5 Data Packet Containing Hardware And Software Addresses
IP Routing
The local router contains, within its routing table, information which will allow it to determine the best data transmission route. The type of information the router uses to make these assessments is protocol dependent, and some communications protocols may employ a range of routing algorithms, and accompanying routing protocols. In the case of the TCP/IP protocol suite, the AccessBuilder 500 utilizes the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP is also known as a distance vector protocol.