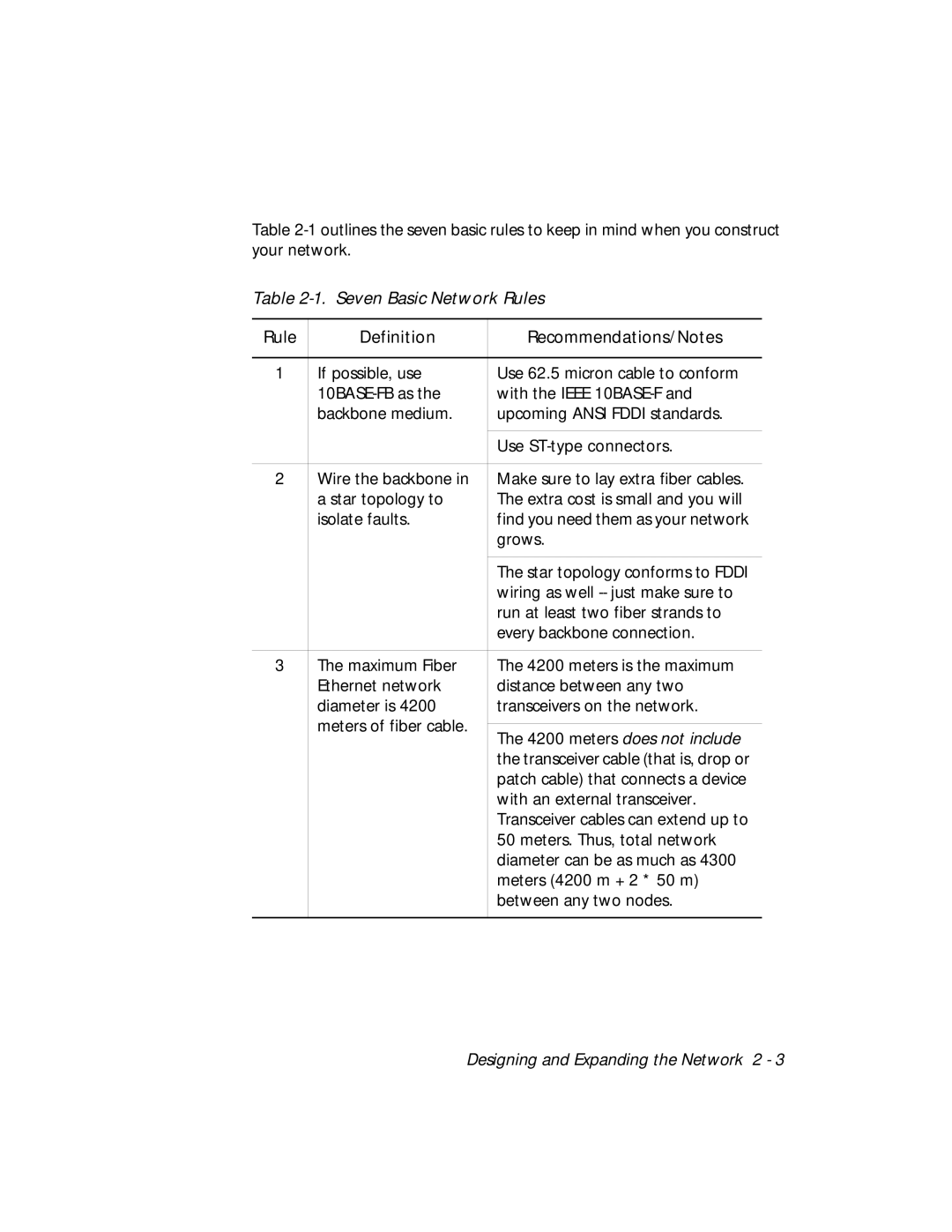
Table
Table 2-1. Seven Basic Network Rules
Rule | Definition | Recommendations/Notes |
|
|
|
1 | If possible, use | Use 62.5 micron cable to conform |
| with the IEEE | |
| backbone medium. | upcoming ANSI FDDI standards. |
|
|
|
|
| Use |
|
|
|
2 | Wire the backbone in | Make sure to lay extra fiber cables. |
| a star topology to | The extra cost is small and you will |
| isolate faults. | find you need them as your network |
|
| grows. |
|
|
|
|
| The star topology conforms to FDDI |
|
| wiring as well |
|
| run at least two fiber strands to |
|
| every backbone connection. |
|
|
|
3 | The maximum Fiber | The 4200 meters is the maximum |
| Ethernet network | distance between any two |
| diameter is 4200 | transceivers on the network. |
| meters of fiber cable. |
|
| The 4200 meters does not include | |
|
| |
|
| the transceiver cable (that is, drop or |
|
| patch cable) that connects a device |
|
| with an external transceiver. |
|
| Transceiver cables can extend up to |
|
| 50 meters. Thus, total network |
|
| diameter can be as much as 4300 |
|
| meters (4200 m + 2 * 50 m) |
|
| between any two nodes. |
|
|
|
Designing and Expanding the Network 2 - 3