Chapter 12 Avaya P330 Layer 3 Features
the next hop and transmits the packet.
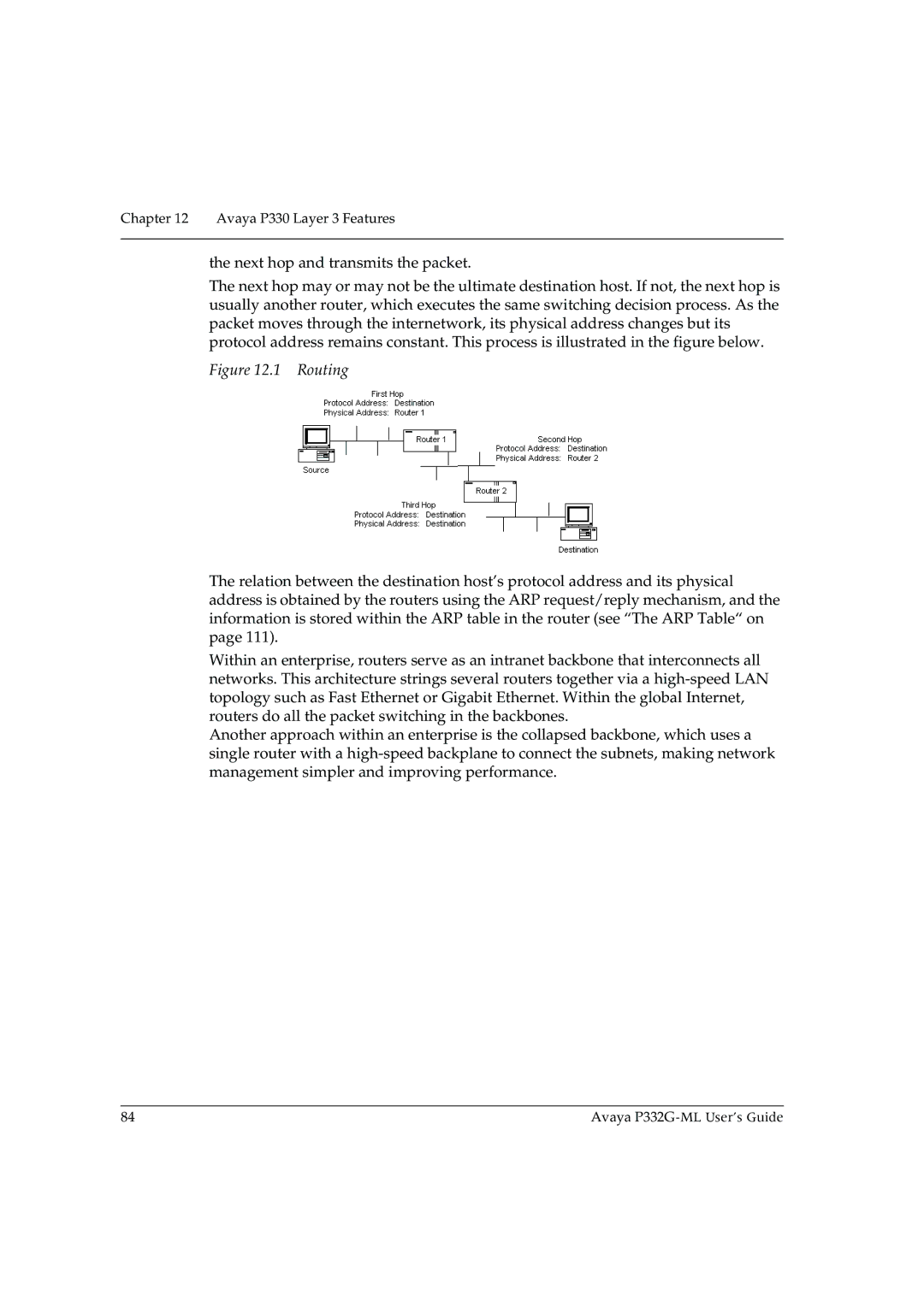
The next hop may or may not be the ultimate destination host. If not, the next hop is usually another router, which executes the same switching decision process. As the packet moves through the internetwork, its physical address changes but its protocol address remains constant. This process is illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 12.1 Routing
The relation between the destination host’s protocol address and its physical address is obtained by the routers using the ARP request/reply mechanism, and the information is stored within the ARP table in the router (see “The ARP Table“ on page 111).
Within an enterprise, routers serve as an intranet backbone that interconnects all networks. This architecture strings several routers together via a
Another approach within an enterprise is the collapsed backbone, which uses a single router with a
84 | Avaya |