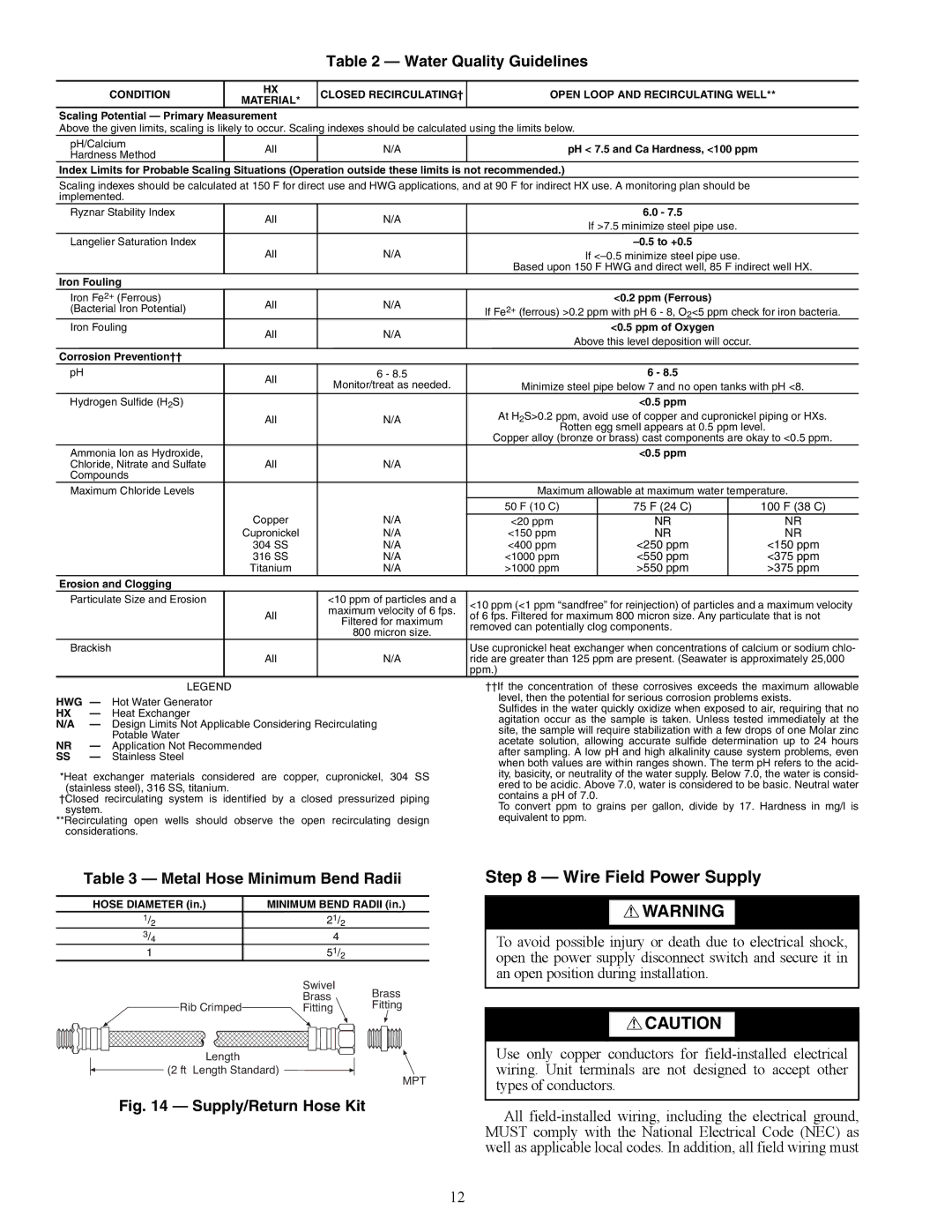
Table 2 — Water Quality Guidelines
CONDITION | HX | CLOSED RECIRCULATING† | OPEN LOOP AND RECIRCULATING WELL** | |||||
MATERIAL* | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Scaling Potential — Primary Measurement |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Above the given limits, scaling is likely to occur. Scaling indexes should be calculated using the limits below. |
| |||||||
pH/Calcium | All | N/A |
| pH < 7.5 and Ca Hardness, <100 ppm |
| |||
Hardness Method |
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Index Limits for Probable Scaling Situations (Operation outside these limits is not recommended.) |
| |||||||
Scaling indexes should be calculated at 150 F for direct use and HWG applications, and at 90 F for indirect HX use. A monitoring plan should be |
| |||||||
implemented. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Ryznar Stability Index | All | N/A |
| 6.0 - 7.5 |
|
| ||
|
| If >7.5 minimize steel pipe use. |
| |||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Langelier Saturation Index |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| All | N/A |
| If |
| |||
|
|
| Based upon 150 F HWG and direct well, 85 F indirect well HX. | |||||
Iron Fouling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Iron Fe2+ (Ferrous) | All | N/A |
|
| <0.2 ppm (Ferrous) |
| ||
(Bacterial Iron Potential) | If Fe2+ (ferrous) >0.2 ppm with pH 6 - 8, O2<5 ppm check for iron bacteria. | |||||||
|
| |||||||
Iron Fouling | All | N/A |
|
| <0.5 ppm of Oxygen |
| ||
|
| Above this level deposition will occur. |
| |||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Corrosion Prevention†† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
pH | All | 6 - 8.5 |
| 6 - 8.5 |
|
| ||
| Monitor/treat as needed. | Minimize steel pipe below 7 and no open tanks with pH <8. | ||||||
|
| |||||||
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) |
|
|
|
| <0.5 ppm |
| ||
| All | N/A | At H2S>0.2 ppm, avoid use of copper and cupronickel piping or HXs. | |||||
|
|
|
| Rotten egg smell appears at 0.5 ppm level. | ||||
|
|
| Copper alloy (bronze or brass) cast components are okay to <0.5 ppm. | |||||
Ammonia Ion as Hydroxide, |
|
|
|
| <0.5 ppm |
| ||
Chloride, Nitrate and Sulfate | All | N/A |
|
|
|
|
| |
Compounds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Maximum Chloride Levels |
|
| Maximum allowable at maximum water temperature. | |||||
|
|
| 50 F (10 C) |
| 75 F (24 C) |
| 100 F (38 C) | |
| Copper | N/A | <20 ppm |
| NR |
| NR | |
| Cupronickel | N/A | <150 ppm |
| NR |
| NR | |
| 304 SS | N/A | <400 ppm |
| <250 ppm |
| <150 ppm | |
| 316 SS | N/A | <1000 ppm |
| <550 ppm |
| <375 ppm | |
| Titanium | N/A | >1000 ppm |
| >550 ppm |
| >375 ppm | |
Erosion and Clogging |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Particulate Size and Erosion |
| <10 ppm of particles and a | <10 ppm (<1 ppm “sandfree” for reinjection) of particles and a maximum velocity | |||||
|
| maximum velocity of 6 fps. | ||||||
| All | of 6 fps. Filtered for maximum 800 micron size. Any particulate that is not | ||||||
| Filtered for maximum | |||||||
|
| removed can potentially clog components. |
| |||||
|
| 800 micron size. |
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Brackish |
|
| Use cupronickel heat exchanger when concentrations of calcium or sodium chlo- | |||||
| All | N/A | ride are greater than 125 ppm are present. (Seawater is approximately 25,000 | |||||
|
|
| ppm.) |
|
|
|
| |
|
| LEGEND |
HWG — | Hot Water Generator | |
HX | — | Heat Exchanger |
N/A | — | Design Limits Not Applicable Considering Recirculating |
NR | — | Potable Water |
Application Not Recommended | ||
SS— Stainless Steel
*Heat exchanger materials considered are copper, cupronickel, 304 SS (stainless steel), 316 SS, titanium.
†Closed recirculating system is identified by a closed pressurized piping system.
**Recirculating open wells should observe the open recirculating design considerations.
††If the concentration of these corrosives exceeds the maximum allowable level, then the potential for serious corrosion problems exists.
Sulfides in the water quickly oxidize when exposed to air, requiring that no agitation occur as the sample is taken. Unless tested immediately at the site, the sample will require stabilization with a few drops of one Molar zinc acetate solution, allowing accurate sulfide determination up to 24 hours after sampling. A low pH and high alkalinity cause system problems, even when both values are within ranges shown. The term pH refers to the acid- ity, basicity, or neutrality of the water supply. Below 7.0, the water is consid- ered to be acidic. Above 7.0, water is considered to be basic. Neutral water contains a pH of 7.0.
To convert ppm to grains per gallon, divide by 17. Hardness in mg/l is equivalent to ppm.
Table 3 — Metal Hose Minimum Bend Radii
|
|
|
| HOSE DIAMETER (in.) | MINIMUM BEND RADII (in.) | ||||||
1/ | 21/ | 2 |
|
|
| ||||||
2 |
|
|
|
| |||||||
3/ | 4 |
|
|
|
| ||||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
1 | 51/2 |
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Swivel |
| Brass | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Brass |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| Rib Crimped | Fitting |
| Fitting | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Length
![]() (2 ft Length Standard)
(2 ft Length Standard) ![]()
MPT
Fig. 14 — Supply/Return Hose Kit
Step 8 — Wire Field Power Supply
![]() WARNING
WARNING
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock, open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in an open position during installation.
![]() CAUTION
CAUTION
Use only copper conductors for
All
12