2635A
Limited Warranty & Limitation of Liability
Table of Contents
Front Panel Operations
2635A
Memory Card Operations
Printer Operations
Index
2635A
List of Tables
Viii
List of Figures
Overall PC-to-Instrument Modem Connection
Interference Information
Symbols Marked on Equipment
Safety Terms in this Manual
DC Power Source
AC Power Source
Use the Proper Power Cord
Use the Proper Fuse
Introduction
Ten Minute Tour
SET Func
Power Func
OFF VAC
Ten Minute Tour
Selecting a Measurement Scale. Select
Scan MON
Scan
Review
SET
Mx+B SET Mx+B
Alrm
SLO
YEAR TotAL
OFF
DESt
LISt
Mode
ALL
Xxiii
Xxiv
Preparation for Use
2635A
Preparation for Use 1 Introduction
Hydra
Operating Modes
Introduction
Data Bucket Features
Alarm Outputs Connector Digital I/O Connector RS-232C
Ground Terminal AC Power Connector Universal Input Module
Front Panel Operation
Memory Card Operation
Printer Operation
Computer Operation
Modem Operation
Applications Software
Measurement Capabilities
Connector Set, 2620A-100
Options and Accessories
Hydra Starter Package
Hydra Logger
Options and Accessories
Setting Up the Instrument
Unpacking and Inspecting the Instrument
Model
Connecting the Instrument to a Power Source
Adjusting the Handle
DC Operation
AC Operation
Input Channels
Measurement Connections
Using Shielded Wiring
Crosstalk
Universal Input Module Connections
Measurement Connections
Wire 4T Connection Source
Wire 2T Connection Source
Sense
Resistance
DC Power
Alarm Outputs Connections
Alarm Outputs
External Trigger Input
Digital I/O
Digital I/O Connections
Totalizer Input
Digital I/O
Front Panel Indicators
Controls and Indicators
Front Panel Controls
Auto MON
12. Annunciator Display
11. Secondary Display
Key
Rate K J Clock K I Mode K P
Front Panel Keys Description
Clear Local K Comm K L Zero Single K Q
Func Alarm
Annunciator Descriptions
MON Scan SET
OFF Auto Limit HI, LO Review MIN, MAX Last PRN EXT REM CAL
Annunciator Annunciator Descriptions
2635A
Front Panel Operations
Using the Monitor Mode Using the Review Mode
Front Panel Operations
Hydra Data Bucket
Summary of Front Panel Operations
How to use the Control/Annunciator Diagrams
Turning the Power on
Configuring the Instrument for Operation
Default Setting
Configuration Reset Default Settings Parameter
Selftest Error Codes Description
Code
Selecting a Channel
Configuring a Measurement Channel
Restrictions
Func SET Func
Configuring a Channel to Measure DC Volts
Configuring a Channel to Measure AC Volts
Configuring a Channel to Measure AC Volts
Configuring a Channel to Measure Resistance
Configuring a Channel to Measure Resistance
Configuring a Channel to Measure Frequency
Configuring a Channel to Measure Frequency
Resistance-Temperature Detectors
Configuring a Channel to Measure Temperature
Resistance Temperature Detectors Restrictions
Thermocouples
Positive Lead Color
Thermocouple Ranges Type Material
ANSI* IEC
Negative Lead Material
Configuring a Channel to Measure Temperature RTDs
Configuring a Channel Off
Setting Operating Conditions
11. Setting the Scan Interval
Setting the Scan Interval
Setting the Alarms
Setting the Measurement Rate
Alarm Indications While Scanning
RAtE
Alarm Indications While Reviewing
Alarm Indications While Monitoring
Clearing Alarm Parameters from a Channel
Alarms and Monitor-Alarm Triggering
Alarms and Autoprinting
Alarms and Mx+B Scaling
TLL Alarm Outputs Channels 0 to Decimal
Channels
TTL Alarm Outputs Channels 4 to
Alrm Limit
13. Setting the Alarms
Examples
Setting the Mx+B Scaling
Clearing Mx+B Scaling from a Channel
14. Setting the Mx+B Scaling
Required From the previous
Using the Scan Mode
Path to OPEn DAtxx Menu
Memory Card Data Extraction
16. Memory Card Error Messages
Memory Card Error Messages
17. Using the Monitor Mode
Using the Monitor Mode
18. Using the Review Mode
Using the Review Mode
Monitor-Alarm Trigger
Additional Features
Scan Triggering Options
External Trigger
19. Scan Triggering Options
Totalizer Operation
Xxxxx
Digital Input/output Lines
Year
Setting Date and Time
Mn.dY
Reading Instrument Software Versions
Returning to the Local Mode
Returning to the Local Mode. Press
Instrument Interfaces
REM Monitor Mode Review
Front Panel Key Lockout Options
Memory Card Interface
Using the RS-232 Computer Interface With a Modem
Using the RS-232 Computer Interface With a Printer
RS-232 Computer Interface
2635A
Recording Measurement Results During Scanning
Memory Card Operations
256KB
WRITE-PROTECT Switch
Insertion Direction PIN Connector
Lithium Battery 3 Volts
Summary of Memory Card Operations
Data Files
Setup Files
Memory Card Capacity
Inserting and Removing the Memory Card
Installing or Replacing the Memory Card Battery
Memory Card Error Codes Probable Cause
Error
Files
Initializing a Memory Card
Init
SUrE
MOdE
Recording Measurement Results During Scanning
Using Setup Store
Setup File Procedures
SEtUP
StorE
Using Setup Load to Load Configuration Files
Using Setup Load
ErASE
Using Setup Erase
Using Data Open
Data File Procedures
DAtA
Using Data Erase to Delete a Measurement Data File
Using Data Erase
NnnnK
Setup and Data Files Directory
USEd
Setup and Data File Current Status
Memory Card File Operations to and from a PC
Computer Operations
Op82f.eps
Summary of Computer Operations
Connecting the Instrument to a PC
PC Connection With DB-9
Connector
PC Connection With DB-25
PAR
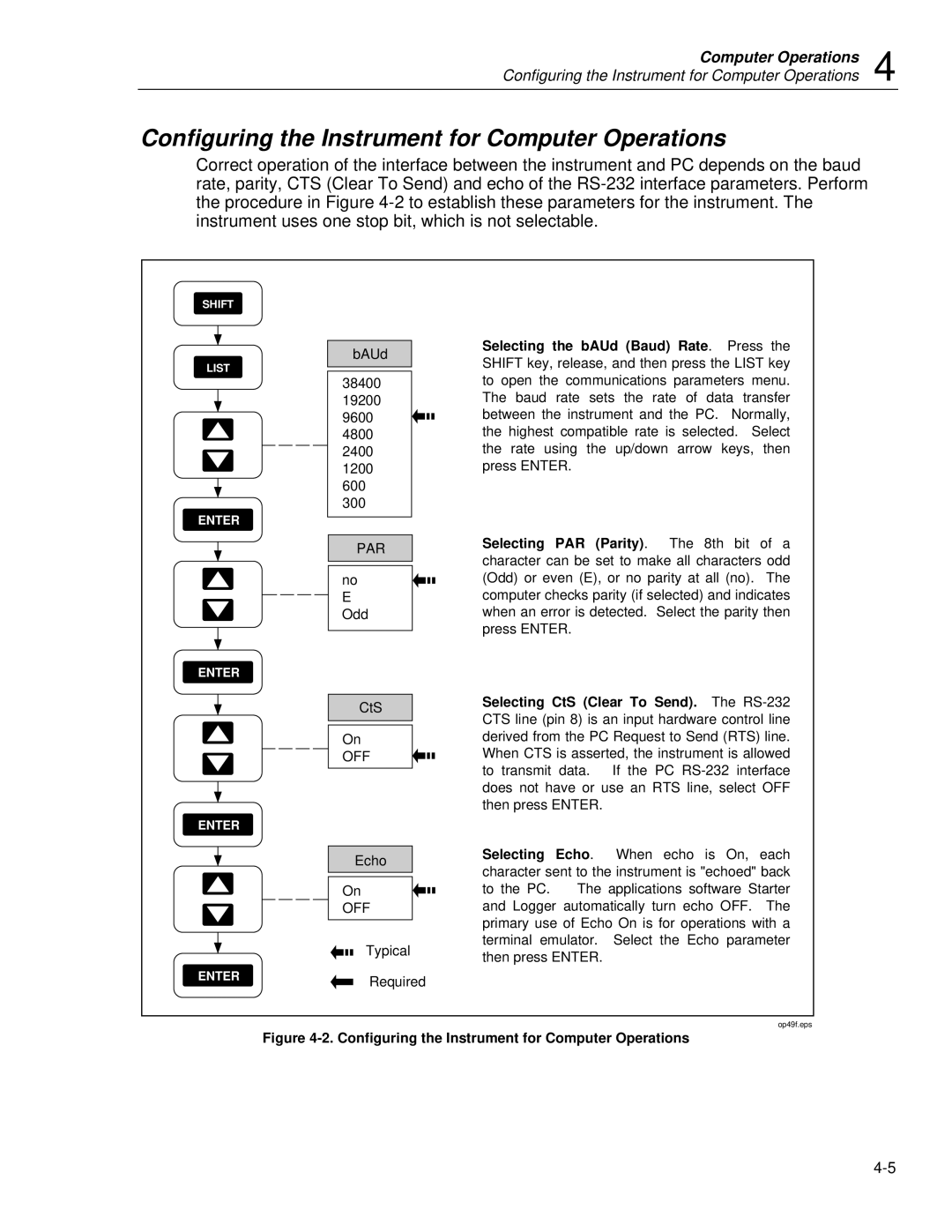
Configuring the Instrument for Computer Operations
Testing the Instrument/PC RS-232 Interface
Configuring the PC for Computer Operations
Rstfunc 0,VDC,4PRINTTYPE 0,0PRINT 1*TRG
2635A
Open COM1,9600,N,8,1,CS,CD for Random AS #1
Testing the RS-232 Interface Using Gwbasic
Print #1, Printtype 0,0PRINT INPUT$20, #1
Testing the RS-232 Interface Using Qbasic
IDN?
How the Instrument Processes Input
Computer Interface Commands and Operation
Input Terminators
Sending Numeric Values to the Instrument
Input String Examples
How the Instrument Processes Output
Instrument Event Register IER
Status Registers
Overview of Status and Event Data Registers
Bit Name
Standard Event Status Register ESR
Instrument Event Register IER Description
Bit Event Status Register ESR Name Description
Status Byte Register STB
Xmodem File Transfers
Computer Interface Command Set
IEB
MAV ESB
Echo
Command and Query Summary
DIOLEVELS? Dolevel
Func FUNC? RTDR0 RTDR0? RANGE?
MAX? MIN? NEXT?
Rate RATE?
MON MONCHAN? MONVAL?
Scalemb SCALEMB?
Lock LOCK? Locs Lwls Rems Rwls
Tempconfig TEMPCONFIG?
Format FORMAT?
Reviewclr
Date Time TIMEDATE?
IDN? TST?
Total TOTAL? Totaldbnc TOTALDBNC?
Trigger TRIGGER?
Cntlc CLS ESE ESE? ESR?
Command and Query Reference
Field Description
IDN?
OPC OPC? RST SRE SRE?
TST? WAI
TRG
ALARMS?
Alarmassoc
Alarmassocclr
ALARMASSOC?
ALARMDOLEVELS?
Alarmdolevel
ALARMLIMIT? CLS Date
Alarmlimit
LO OFF
DIR
DIOLEVELS? Digital I/O State Query
Echo ESE ESE? ESR? FILEERROR? Fileload
FILEOPEN? Fileremove
FILESPACE? Filestore
Configuration File Tag
Measurement Units String
Format
MX+B
VDC
Range Voltage Ohms Frequency
Func
IEE? IER?
FUNC? IDN? IEE
Intvl INTVL? LAST?
Lock
LOCK? Locs LOG? LOGGED?
Logmode LOGMODE? Lwls
LOGBIN? Logclr LOGCLR1 LOGCOUNT?
MAX? MCARD?
BIT Memory Card Battery Status
MAX?
MCARDSIZE?
Mcardformat
Disables monitoring
OPC OPC? Print
PRINT? Printtype
PRINTTYPE?
Rate RATE? Rems Reviewclr RST RTDR0
RTDR0? Rwls
Scalemb
SCALEMB? Scan
SCAN? SCANTIME? SRE SRE? STB? Tempconfig
Total
TEMPCONFIG?
TOTAL? Totaldbnc TOTALDBNC? TRG Trigger
Returns an integer representing the present trigger type
Sample Program Gwbasic 1
Sample Program Gwbasic 2
Sample Program Qbasic 1
Sample Program QBASIC2
Sample Program Qbasic 3
Sample Program QuickC 1of
Sample Program QuickC 2
Sample Program QuickC 3
Sample Program QuickC4
Sample Program QuickC5
Printer Operations
Op83f.eps
Summary of Printer Operations
Connecting the Instrument to a Printer
Printer
SERIAL-INPUT
PARALLEL-INPUT
Configuring the RS-232 Ports for Print Operations
Configuring for Printer Operations
Printing Measurement Data and Memory Card Directory
Problems?
Printing Measurement Results During Scanning
Printing Measurement Data and Memory Card Directory
Printing the Review Array
Printing the Review Array
Printing the Memory Card Directory
Printing the Directory of the Memory Card
2635A
Modem Operations
Configuring the Instrument for Modem Operations
Op84f.eps
Overall PC-to-Instrument Modem Connection
Summary of Modem Operations
Configuring the Instrument Modem for Modem Operations
Connecting the Modem to a PC for Modem Configuration
Modem Connection With PC DB-25 Connector
Modem Connection With PC DB-9 Connector
Connecting the Modem to an Instrument
Connecting the Modem to an Instrument
Enter
Configuring the Instrument for Modem Operations
Testing the RS-232/Modem Interface
Dedicated Alarm Output Test
Maintenance
Calibrator
Line Fuse
Introduction Cleaning
Error Power-Up Error Codes Description
Selftest Diagnostics and Error Codes
Performance Tests
Performance Tests
Instrument Type
Recommended Test Equipment Minimum Specification
Recommended Model
Instrument Type Recommended Model
Function
Accuracy Verification Test
Range
Input Level Frequency
Channel Integrity Test
Thermocouple Measurement Range Accuracy Test
Four-Terminal Resistance Test
Thermocouple Temperature Accuracy Test
Open Thermocouple Response Test
5700A
Hydra Input Module
UUT
RTD Temperature Accuracy Test Using Decade Resistance Source
RTD Temperature Accuracy Test
Temperature Simulated
RTD Temperature Accuracy Test Using DIN/IEC 751 RTD
Temperature Accuracy
Decade Resistance Source
Digital Output Test
Digital Input/Output Verification Tests
Digital Input Test
Dolevel 0,0 CR
Terminal Grounded
Totalizer Test
Digital Input Values
State of Digital Inputs
Totalizer Sensitivity Test
Dedicated Alarm Output Test
Maintenance
GND Source Input
Alarm Output
Module Sense
Hydra
External Trigger Input Test
Calibration
Variations in the Display
Service
Appendix Title
Appendices
Page
Accuracies at Ambient Temperatures Other than Specified
Specifications
Resolution
DC Voltage Measurements
Common Mode Rejection
Normal Mode Rejection
Accuracy
Input Impedance
Maximum Input
Appendices
Cross-Talk Rejection
Accuracy
Resolution
Type Temperature Days Year Slow Fast 0C to 60C
Temperature Measurements Thermocouples
2635A
Common Mode and Normal Mode Rejection
Temperature Measurements RTDs
Open Thermocouple Detect
RTD
Temperature Slow Fast
Wire Accuracy
AC Voltage Measurements
RTD Type
Resolution Slow Fast
Table A-10. AC Voltage Measurements Resolution Range
Minimum Input for Rated Accuracy
DC Component Error
Crest Factor Error
2635A Maximum Voltage Input VS. Frequency Input
Maximum Crest Factor
Resistance Measurements
Resolution and Accuracy
2635A Wire Accuracy
Frequency Measurements
Input Sensitivity
Table A-17. Typical Scanning Rate
Typical Scanning Rate
Totalizing Input
Maximum Autoranging Time
Digital Inputs
Input Voltages
Trigger Inputs
Minimum Pulse Width Maximum Frequency Specified Conditions
Maximum Latency
Environmental Specifications
Digital and Alarm Outputs
Real-Time Clock and Calendar
General
Power
Weight
2635A Voltage Ratings
Size
Crosstalk Considerations
AC Signal Cross Talk in a DC Voltage Channel
AC Signal Cross Talk into an Ohms Channel
AC Signal Cross Talk into an AC Voltage Channel
AC Signal Crosstalk into a Temperature Channel
AC Signal Cross Talk into a Frequency Channel
2635A
Decoding the Ascii String
Binary Upload of Logged Data
+--------+--------+--------+--------+
Figure C-1. Ascii String Decoding
Floating Point Conversion
Mmsb
Sign Bit
Mlsb Lmsb
Figure C-2. FloatingPoint Conversion
Example
Figure C-3. Example
Cables
RS-232 Cabling
Figure D-1. Summary of RS-232 Connections
RS-232 Cabling D
Figure D-3. Hydra DB-9 to PC DB-25 RS-232 Connection
RS41 Cable or Equal
Printer
Side Male Female
Connector
Side
2635A
Bit Binary-Coded-Decimal Table
Binary
Table E-1 -Bit Binary-Coded-Decimal
Memory Card File Formats
Setup File Format
Data File Format
Trigger
Memory Card File Formats
Unsigned char mdr unsigned char bdr float rtdr0
Appendices
2635A
Appendices
2635A
Effect of Internal Noise in AC Measurements
True RMS Measurements
Waveform Comparison True RMS VS Average Responding
Waveform RMS CAL Hydra Only
Component
Sine
PK-PK
Scan Rate
Temperature Units
RS-232-C Communication
Output
Hydra Memory Card Record
Index
2635A
Index
2635A