CHAPTER 5 CPU SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
5.2Special Instructions
In the
•JMP @A
•MOVW A, PC
•MULU A
•DIVU A
•XCHW A, PC
•CALLV #k
■JMP @A
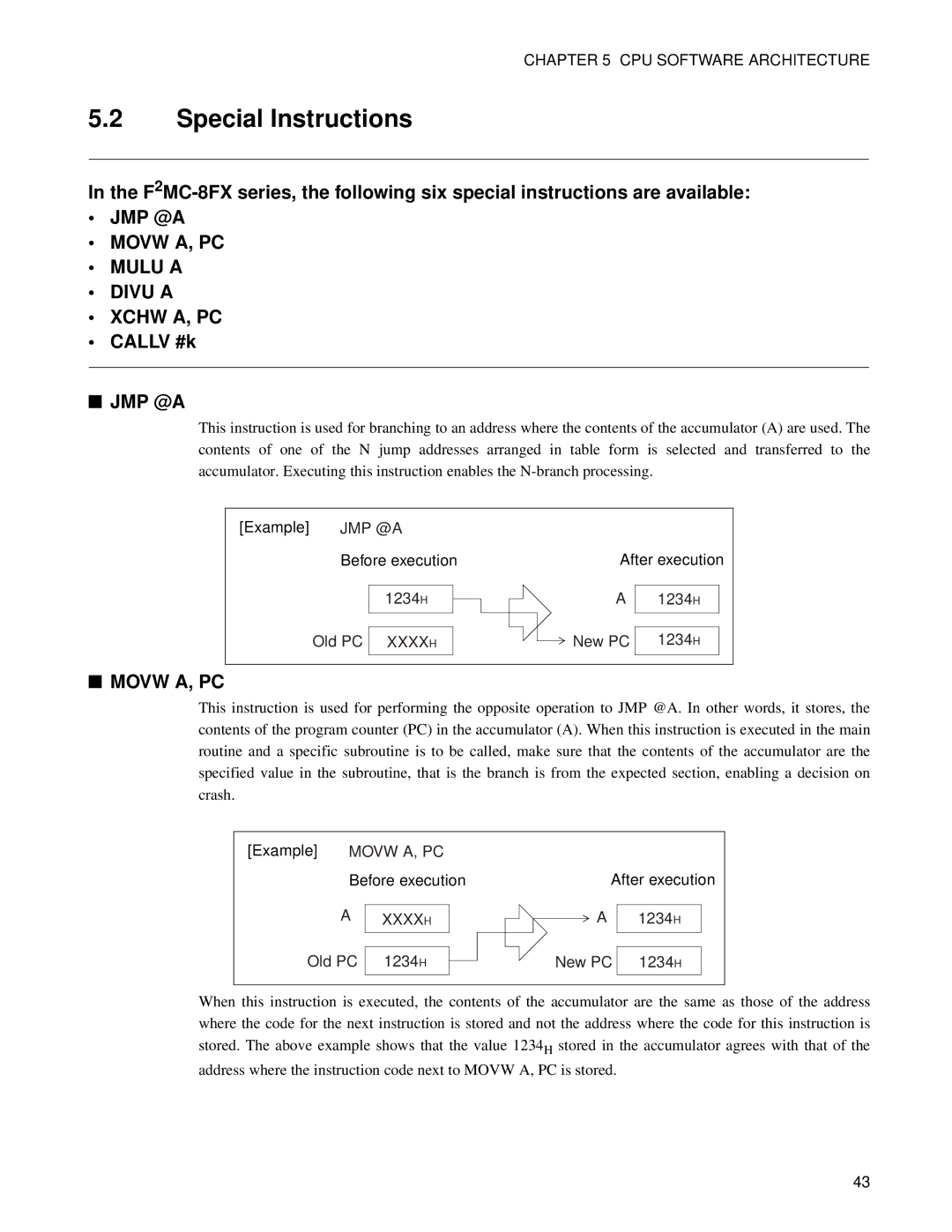
This instruction is used for branching to an address where the contents of the accumulator (A) are used. The contents of one of the N jump addresses arranged in table form is selected and transferred to the accumulator. Executing this instruction enables the
[Example] JMP @A Before execution
1234H
Old PC XXXXH
■MOVW A, PC
After execution
A | 1234H |
|
|
|
|
New PC | 1234H |
|
|
This instruction is used for performing the opposite operation to JMP @A. In other words, it stores, the contents of the program counter (PC) in the accumulator (A). When this instruction is executed in the main routine and a specific subroutine is to be called, make sure that the contents of the accumulator are the specified value in the subroutine, that is the branch is from the expected section, enabling a decision on crash.
[Example] MOVW A, PC Before execution
A XXXXH
After execution

 A 1234H
A 1234H
Old PC
1234H
New PC
1234H
When this instruction is executed, the contents of the accumulator are the same as those of the address where the code for the next instruction is stored and not the address where the code for this instruction is stored. The above example shows that the value 1234H stored in the accumulator agrees with that of the address where the instruction code next to MOVW A, PC is stored.
43