CHAPTER 5 CPU SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
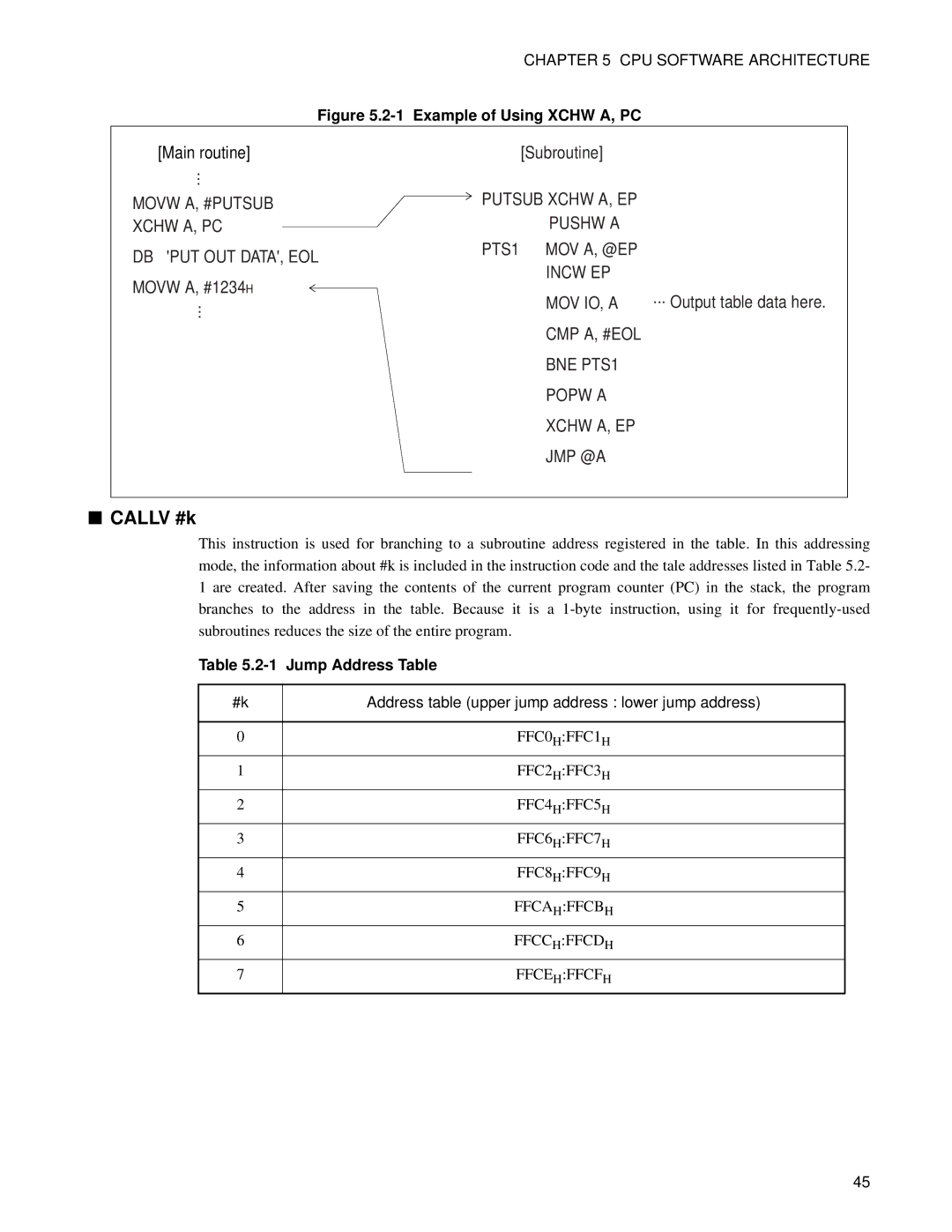
Figure 5.2-1 Example of Using XCHW A, PC
[Main routine] ... MOVW A, #PUTSUB XCHW A, PC
DB 'PUT OUT DATA', EOL
MOVW A, #1234H
...
[Subroutine] |
|
PUTSUB XCHW A, EP |
|
PUSHW A |
|
PTS1 MOV A, @EP |
|
INCW EP |
|
MOV IO, A | ... Output table data here. |
CMP A, #EOL |
|
BNE PTS1 |
|
POPW A |
|
XCHW A, EP |
|
JMP @A |
|
■CALLV #k
This instruction is used for branching to a subroutine address registered in the table. In this addressing mode, the information about #k is included in the instruction code and the tale addresses listed in Table 5.2- 1 are created. After saving the contents of the current program counter (PC) in the stack, the program branches to the address in the table. Because it is a
Table 5.2-1 Jump Address Table
#k | Address table (upper jump address : lower jump address) |
|
|
0 | FFC0H:FFC1H |
|
|
1 | FFC2H:FFC3H |
|
|
2 | FFC4H:FFC5H |
|
|
3 | FFC6H:FFC7H |
|
|
4 | FFC8H:FFC9H |
|
|
5 | FFCAH:FFCBH |
|
|
6 | FFCCH:FFCDH |
|
|
7 | FFCEH:FFCFH |
|
|
45