5 |
Configurable Faults
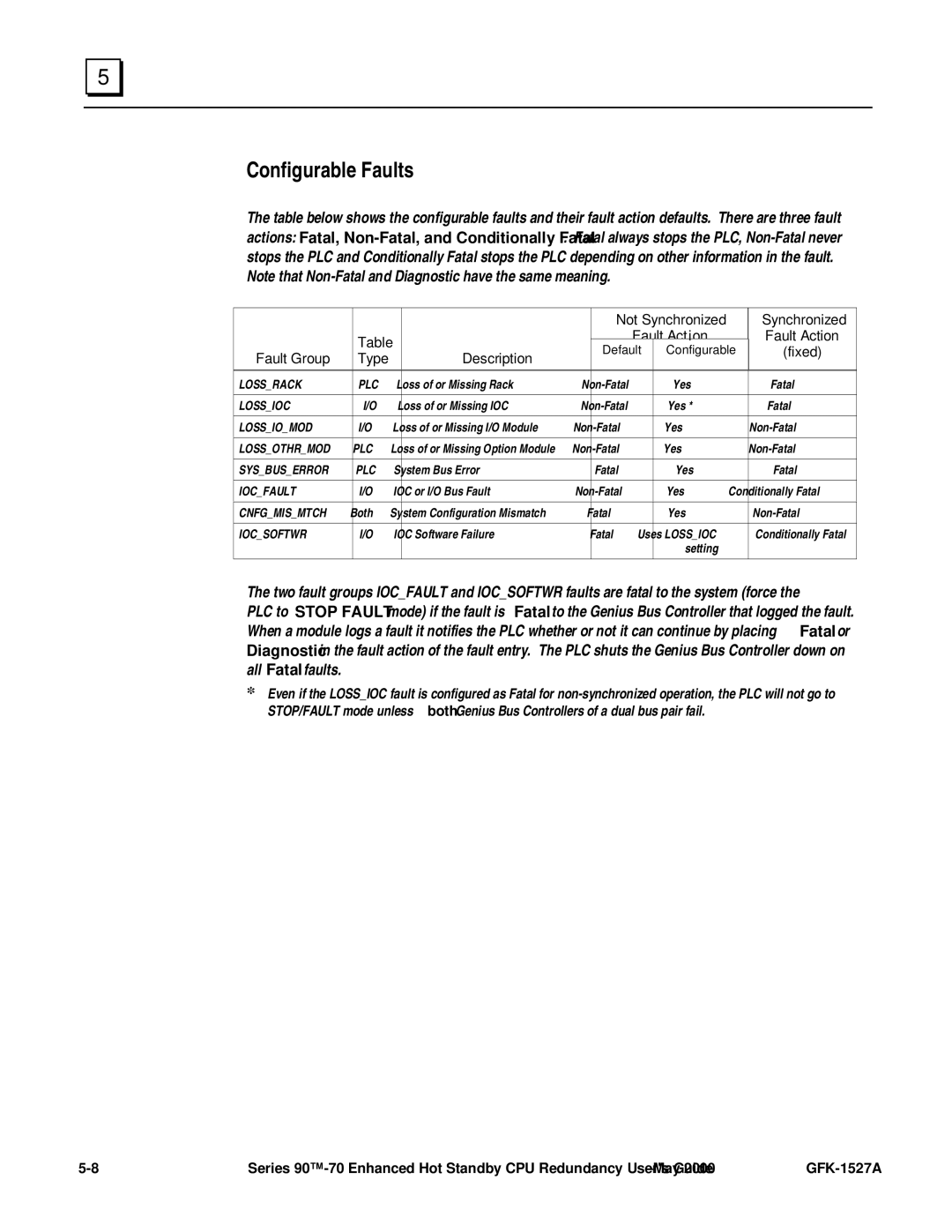
The table below shows the configurable faults and their fault action defaults. There are three fault actions: Fatal,
|
|
| Not Synchronized | Synchronized | ||
| Table |
| Fault Action | Fault Action | ||
|
| |||||
|
|
|
| |||
|
| Default | Configurable | (fixed) | ||
Fault Group | Type | Description | ||||
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LOSS_RACK | PLC | Loss of or Missing Rack | Yes | Fatal | ||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LOSS_IOC | I/O | Loss of or Missing IOC | Yes * | Fatal | ||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LOSS_IO_MOD | I/O | Loss of or Missing I/O Module | Yes | |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LOSS_OTHR_MOD | PLC | Loss of or Missing Option Module | Yes | |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
SYS_BUS_ERROR | PLC | System Bus Error | Fatal | Yes | Fatal | |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
IOC_FAULT | I/O | IOC or I/O Bus Fault | Yes | Conditionally Fatal | ||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
CNFG_MIS_MTCH | Both | System Configuration Mismatch | Fatal | Yes | ||
|
|
|
|
|
| |
IOC_SOFTWR | I/O | IOC Software Failure | Fatal | Uses LOSS_IOC | Conditionally Fatal | |
|
|
|
| setting |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
The two fault groups IOC_FAULT and IOC_SOFTWR faults are fatal to the system (force the PLC to STOP FAULT mode) if the fault is Fatal to the Genius Bus Controller that logged the fault. When a module logs a fault it notifies the PLC whether or not it can continue by placing Fatal or Diagnostic in the fault action of the fault entry. The PLC shuts the Genius Bus Controller down on all Fatal faults.
*Even if the LOSS_IOC fault is configured as Fatal for
Series |