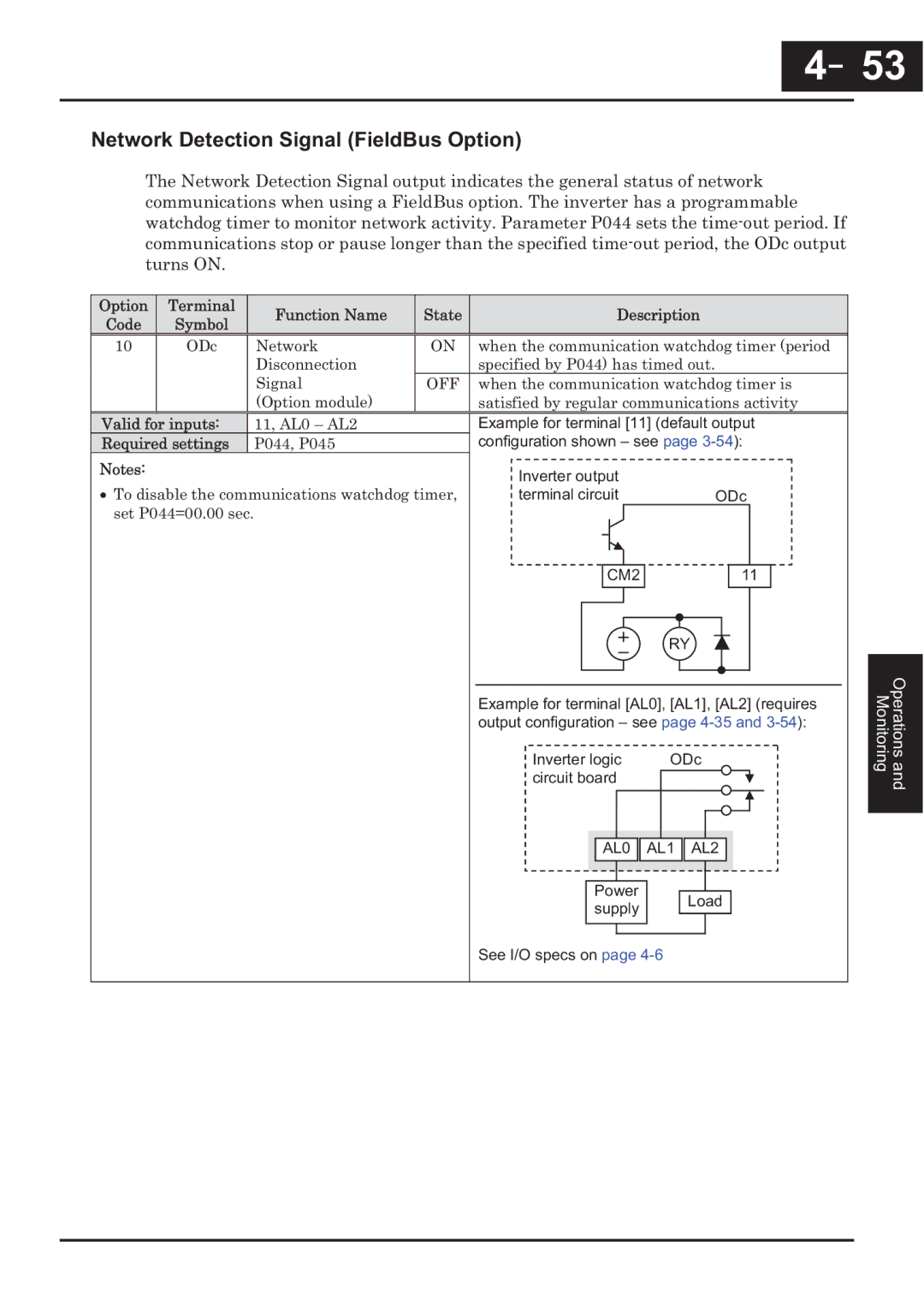
CP-X200 specifications
The Hitachi CP-X200 is a versatile and robust projector designed to cater to the needs of educational and business environments. It combines affordability with high-quality performance, making it an attractive option for various presentations and multimedia applications.At the heart of the CP-X200 is its high brightness capability, with a lumen output of 3,000 ANSI lumens. This feature enables the projector to deliver clear and vibrant images even in well-lit rooms. The resolution of XGA (1024 x 768 pixels) ensures that text and graphics are sharp, making it suitable for everything from classroom lectures to corporate presentations.
One of the standout characteristics of the Hitachi CP-X200 is its advanced lamp technology. The projector uses a long-lasting lamp that can provide up to 5,000 hours of usage in standard mode, allowing for extended intervals between lamp replacements. Additionally, the ECO mode can further enhance the lamp life, extending its longevity while reducing energy consumption.
The CP-X200 is equipped with a variety of connectivity options, including HDMI, VGA, and composite inputs, allowing users to easily connect it to various devices such as laptops, DVD players, and other multimedia systems. The inclusion of USB and RS-232 interfaces ensures compatibility with different control systems, making it a flexible choice for diverse setups.
Another significant feature is the projector's built-in 10-watt speaker, which provides decent audio output, eliminating the need for external speakers in smaller venues. The speaker system enhances presentations, ensuring that audio and visuals are cohesive, promoting better audience engagement.
Portability is another key aspect of the Hitachi CP-X200, which weighs just around 3.5 kg (approximately 7.7 lbs), allowing for easy transport between locations. Its compact design makes it suitable for both fixed installations and mobile use, catering to professionals who require a projector that adapts to various environments.
The user-friendly interface and robust remote control enhance the projector's operability, providing easy access to essential functions. Additionally, features such as auto keystone correction adjust the image to maintain consistent quality even when the projector is not perfectly aligned with the screen.
In summary, the Hitachi CP-X200 is a feature-rich projector that embodies reliability, performance, and ease of use. Its combination of high brightness, various connectivity options, long lamp life, portability, and integrated audio makes it an excellent choice for education and business professionals seeking a dependable presentation solution.