C H A P T E R 2 | Using the Intel® NetStructure™ 470T and 470F Switches |
Flow Control
During heavy network activity, the switch’s port buffers can receive too much traffic and fill up faster than the switch can send the information. In cases like this, the switch tells the transmitting device to wait until the information in the buffer can be sent. This traffic control mechanism is called flow control.
The method of flow control depends on whether the port is set to
•If a port operates at
•If the port operates at
You can enable or disable flow control for each port on the 470 switch.
Broadcast Storm Control
You can use broadcast storm control to control the amount of broadcast traffic serviced by the switch. You can prevent broadcasts from taking an excessive amount of network resources and degrading network performance.
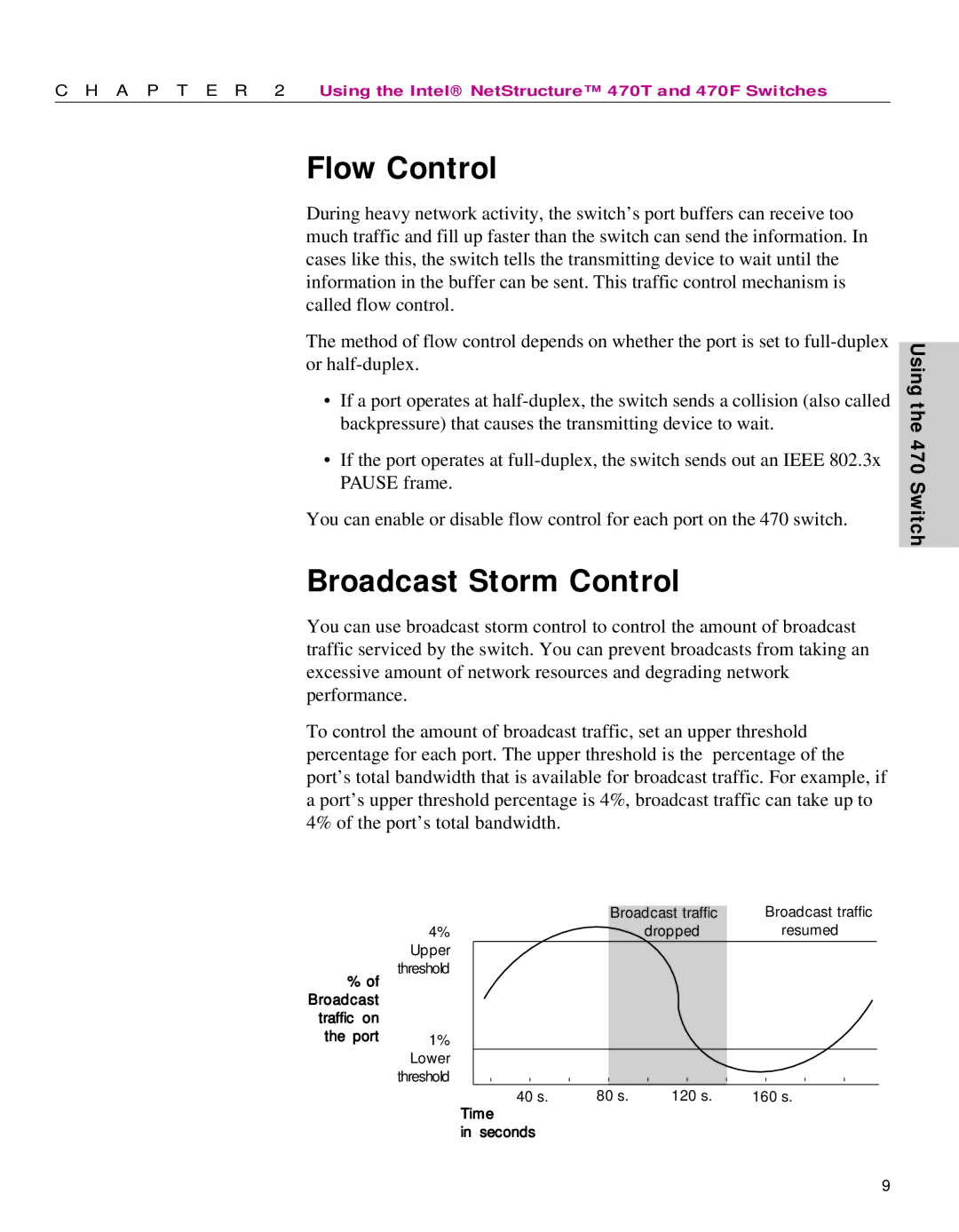
To control the amount of broadcast traffic, set an upper threshold percentage for each port. The upper threshold is the percentage of the port’s total bandwidth that is available for broadcast traffic. For example, if a port’s upper threshold percentage is 4%, broadcast traffic can take up to 4% of the port’s total bandwidth.
Using the 470 Switch
| Broadcast traffic | Broadcast traffic |
4% | dropped | resumed |
Upper |
|
|
threshold |
|
|
%of Broadcast traffic on
the port | 1% |
| Lower |
| threshold |
40 s. | 80 s. | 120 s. | 160 s. |
Time
in seconds
9