C H A P T E R 2 | Using the Intel® NetStructure™ 470T and 470F Switches |
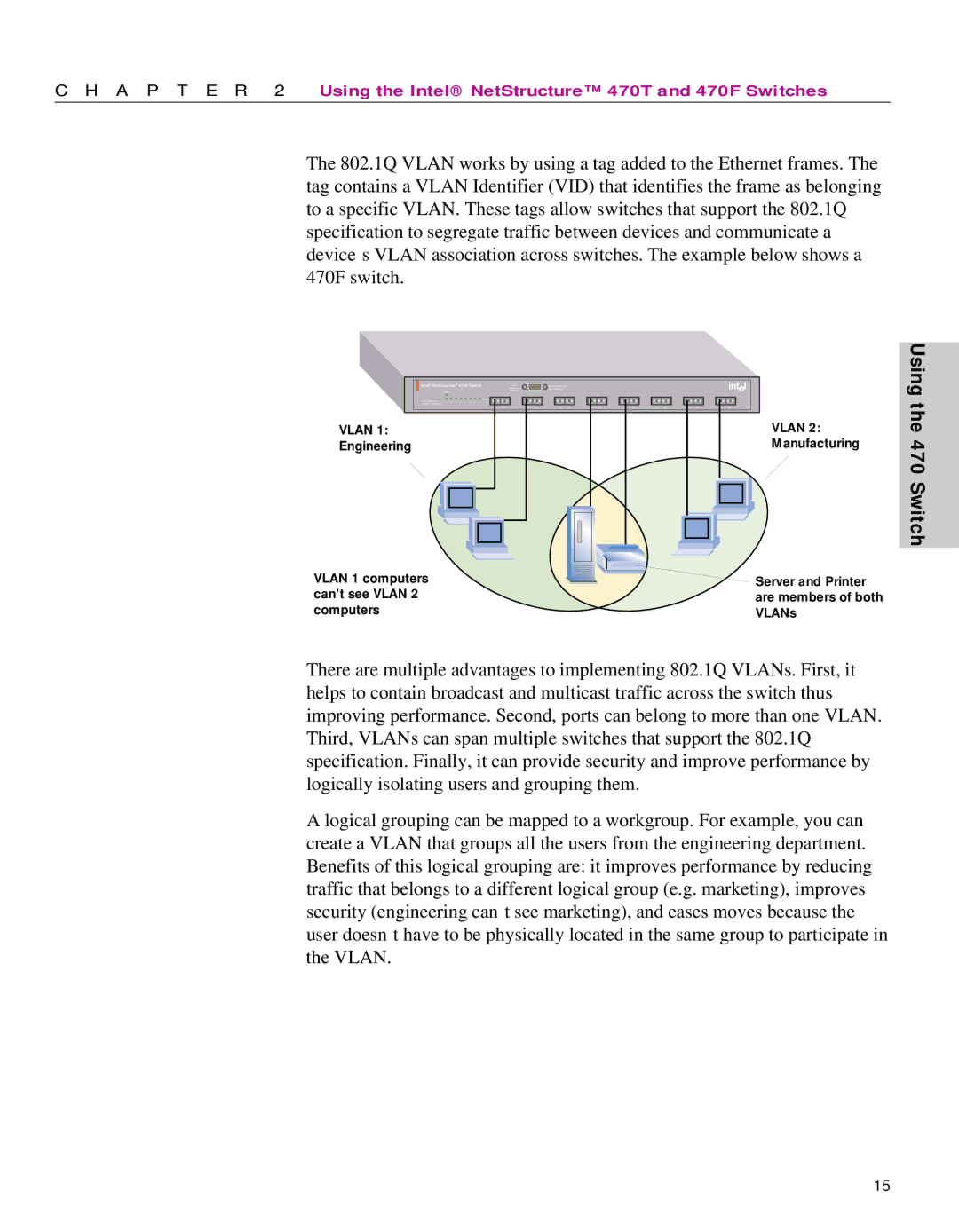
The 802.1Q VLAN works by using a tag added to the Ethernet frames. The tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that identifies the frame as belonging to a specific VLAN. These tags allow switches that support the 802.1Q specification to segregate traffic between devices and communicate a device’s VLAN association across switches. The example below shows a 470F switch.
Intel® NetStructure™ 470F Switch | Local | Console: |
| Management | Flow Ctrl=None |
Status | (EIA 232) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Link\Act |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX | TX | RX |
VLAN 1: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VLAN 2: |
Engineering |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Manufacturing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLAN 1 computers |
| Server and Printer |
| ||
| ||
can't see VLAN 2 |
| are members of both |
computers |
| VLANs |
Using the 470 Switch
There are multiple advantages to implementing 802.1Q VLANs. First, it helps to contain broadcast and multicast traffic across the switch thus improving performance. Second, ports can belong to more than one VLAN. Third, VLANs can span multiple switches that support the 802.1Q specification. Finally, it can provide security and improve performance by logically isolating users and grouping them.
A logical grouping can be mapped to a workgroup. For example, you can create a VLAN that groups all the users from the engineering department. Benefits of this logical grouping are: it improves performance by reducing traffic that belongs to a different logical group (e.g. marketing), improves security (engineering can’t see marketing), and eases moves because the user doesn’t have to be physically located in the same group to participate in the VLAN.
15