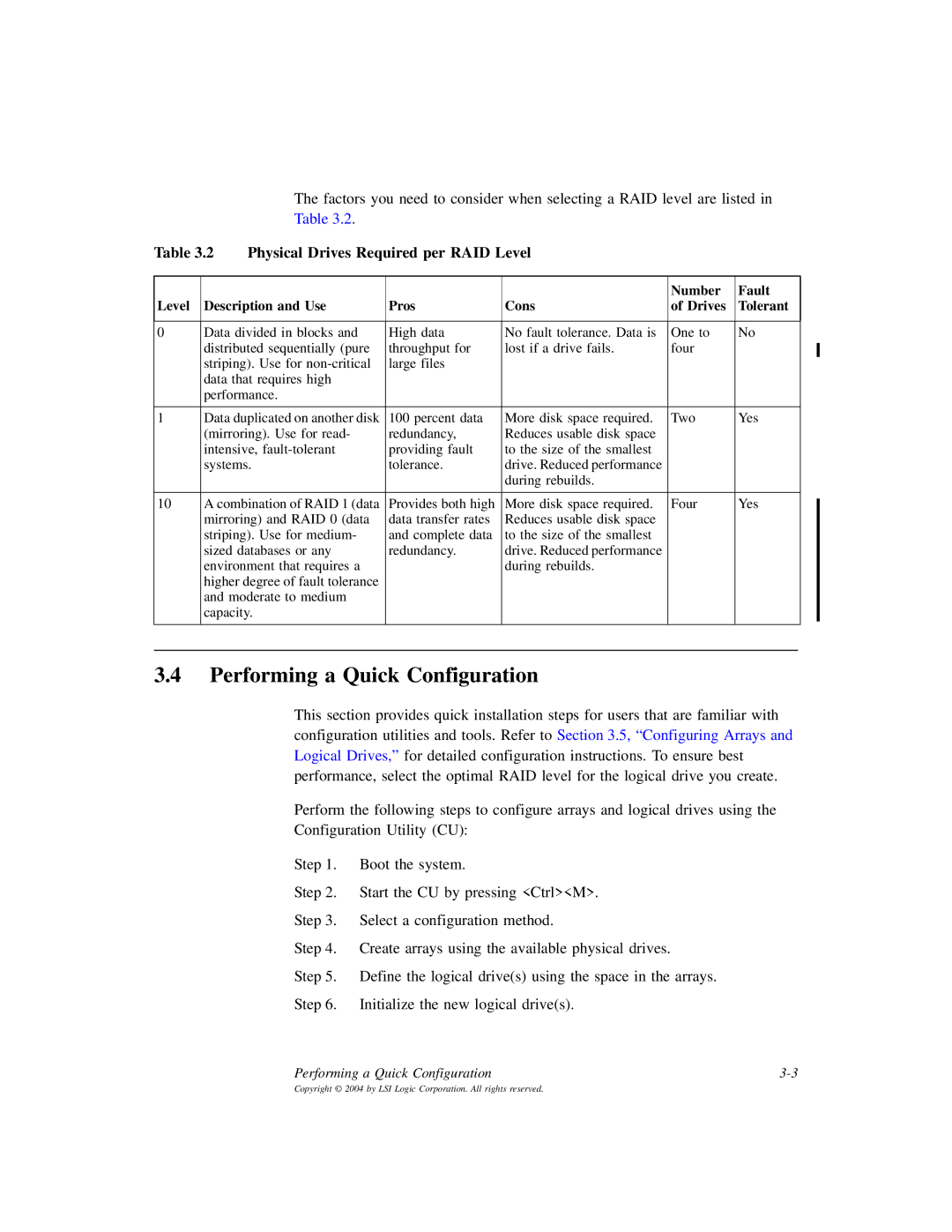
The factors you need to consider when selecting a RAID level are listed in Table 3.2.
Table 3.2 Physical Drives Required per RAID Level
Level Description and Use
Pros
Cons
Number of Drives
Fault Tolerant
0 | Data divided in blocks and | High data | No fault tolerance. Data is | One to | No |
| distributed sequentially (pure | throughput for | lost if a drive fails. | four |
|
| striping). Use for | large files |
|
|
|
| data that requires high |
|
|
|
|
| performance. |
|
|
|
|
1 | Data duplicated on another disk | 100 percent data | More disk space required. | Two | Yes |
| (mirroring). Use for read- | redundancy, | Reduces usable disk space |
|
|
| intensive, | providing fault | to the size of the smallest |
|
|
| systems. | tolerance. | drive. Reduced performance |
|
|
|
|
| during rebuilds. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 | A combination of RAID 1 (data | Provides both high | More disk space required. | Four | Yes |
| mirroring) and RAID 0 (data | data transfer rates | Reduces usable disk space |
|
|
| striping). Use for medium- | and complete data | to the size of the smallest |
|
|
| sized databases or any | redundancy. | drive. Reduced performance |
|
|
| environment that requires a |
| during rebuilds. |
|
|
| higher degree of fault tolerance |
|
|
|
|
| and moderate to medium |
|
|
|
|
| capacity. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.4Performing a Quick Configuration
This section provides quick installation steps for users that are familiar with configuration utilities and tools. Refer to Section 3.5, “Configuring Arrays and Logical Drives,” for detailed configuration instructions. To ensure best performance, select the optimal RAID level for the logical drive you create.
Perform the following steps to configure arrays and logical drives using the
Configuration Utility (CU):
Step 1. Boot the system.
Step 2. Start the CU by pressing <Ctrl><M>.
Step 3. Select a configuration method.
Step 4. Create arrays using the available physical drives.
Step 5. Define the logical drive(s) using the space in the arrays.
Step 6. Initialize the new logical drive(s).
Performing a Quick Configuration |