Wheaton Road 1012 E. Boal Avenue
Paradise Datacom LLC
Table of Contents
Change, Tx/Rx, Mod/Demod, Scrambler Menu
Change, Tx/Rx, Mod/Demod, REED-SOLOMON Menu
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Define IDR Menu
100
Page
Page
Page
Safety
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility and Safety Notices
EMC
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Environmental
Installation
Overview
Introduction
Requires Drop/Insert feature standard on P300 IBS and above
P300 Series Features
Feature Means h/w option
Feature Summary
Fault and a deferred alarm
Feature Highlight
High Date Rate Feature
Wideband if Feature
IBS/SMS Feature
Drop/Insert Feature
Prbs tester feature
P300 / P310 -IDR Additional Features IDR Option
Extended D/I Feature
P300 / P310 -TCM Additional Features
`Custom Features` Feature
Turbo Product Code Forward Error Correction TPC FEC
Description
Fault Philosophy
Operation
Electrical Description
P300 Modem front panel view
Front Panel Features
Keyboard
Normal operation there should be three Green LEDsshowing
Rating
Rear Panel Description
Rx if input
Async ESC connector
Tx if output
Terrestrial Interface Connectors
Services
Overhead Pinout details are provided in Appendix B
Standby LED
To FEC/Modulator FromFEC/Demodulator
Block Diagram
Match
Common Main Specifications
Summary of Specifications
OutputOutput FrequencyPhase NoiseStability
Channel Spacing Phase and Amplitude
Scrambling
Filter Implementation
8PSK/TCM
Demodulator Specifications
Clocking and Buffering
Framing & Deframing
Intelsat Reed Solomon Codec & Custom Features
Extended Drop/ Insert Feature
Drop /Insert Feature
Async ESC Feature & Aux Data Channel
IDR Option
Monitor/AGC Option
Prbs Tester Feature
Traffic Log
Common Specifications
Auto Uplink Power Control Aupc
Redundancy Features
Configuration Memories
Weight
Controller
Safety
Power Supply
Supporting Products
EMC
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
8PSK
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
Installation and Configuration
Introduction
Menu System
To Completely Setup Initially
Menu Structure Diagrams
Menu Structure Sheet 1 / 7 Main Status, Change
Full Menu Structure Sheet 2 / 7 Main Monitor, Info
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
Full Menu Structure Sheet 5 / 7 Change, Tx
Full Menu Structure Sheet 6 / 6 Change, Rx
Full Menu Structure Sheet 7 / 7 Change, BUC/LNB
Status Screen Display
Status Display no faults
Carr Disabled
Configuration Summary
Carr Fault
Traffic Summary Screen
Unit Fault Tx if synth failure Tx carrier muted
Detailed Receive Traffic Status
Detailed Demodulator Status
Detailed Transmit Traffic Status
Setup 1Initial Config 2Check Memories 3Store 4Recall 5Erase
Setup Initial Configuration Menu
CHANGE, TX Menu
Tx 1Service 2Baseband 3Clocking 4Modulator 5ESC/Aux/BA
Closed Network mode ? =No ESC normal 2 Plus ESC min o/h
Change, Tx/Rx, Service, Closed Network
No ESC
Plus ESC
Normal
Change, Tx/Rx, Service, Closed Net, Plus ESC, BA Menu
Same async ESC rate
Tx BB ? 1=Continuous data 2=Drop Mux 3=Other function
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband Menu
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Continuous Menu
Select bearer ? =G.732 2=T1-D4 3=T1-ESF
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, DROP/INSERT Menu
Drop TS 1, 3-5, 17-15 Toggle ??-?? YES Help
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Drop/Insert, Timeslot Menu
Leave
Dropped TS ? =Leave 2=Replace with idle code
Replace
=Normal ignore 2=Transfer via sat o/h
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Drop/Insert, RBS Menu
T1 RBS over satellite ? =Normal or no RBS 2=Maintain RBS
Normal Maintain
=Normal maintain 2=Don’t care
Dont Care
Dont
TS identity over satellite ? =Maintain 2=Don’t care Normal
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Other Menu
Audio
Change, Tx, Clocking Menu
Tx clock mode ? =Tx Clock In 2=Internal 3=Rx ref=Sat
TX Clock
Internal
Clock
Change, Tx/Rx, Modulator, Modulation Menu Set modulation ?
Change, Tx/Rx, Mod/Demod, if Frequency Menu
=BPSK 2=QPSK 3=OQPSK 4=8PSK
None, Viterbi or Sequential at rate ½, ¾, or
Is available
Offset Qpsk Oqpsk Primer
For Turbo FEC the FEC rate selection screen is as follows
Screen Description Exact Delay Code rate Bits
Modulation Schemes from
V3.57 V3.40
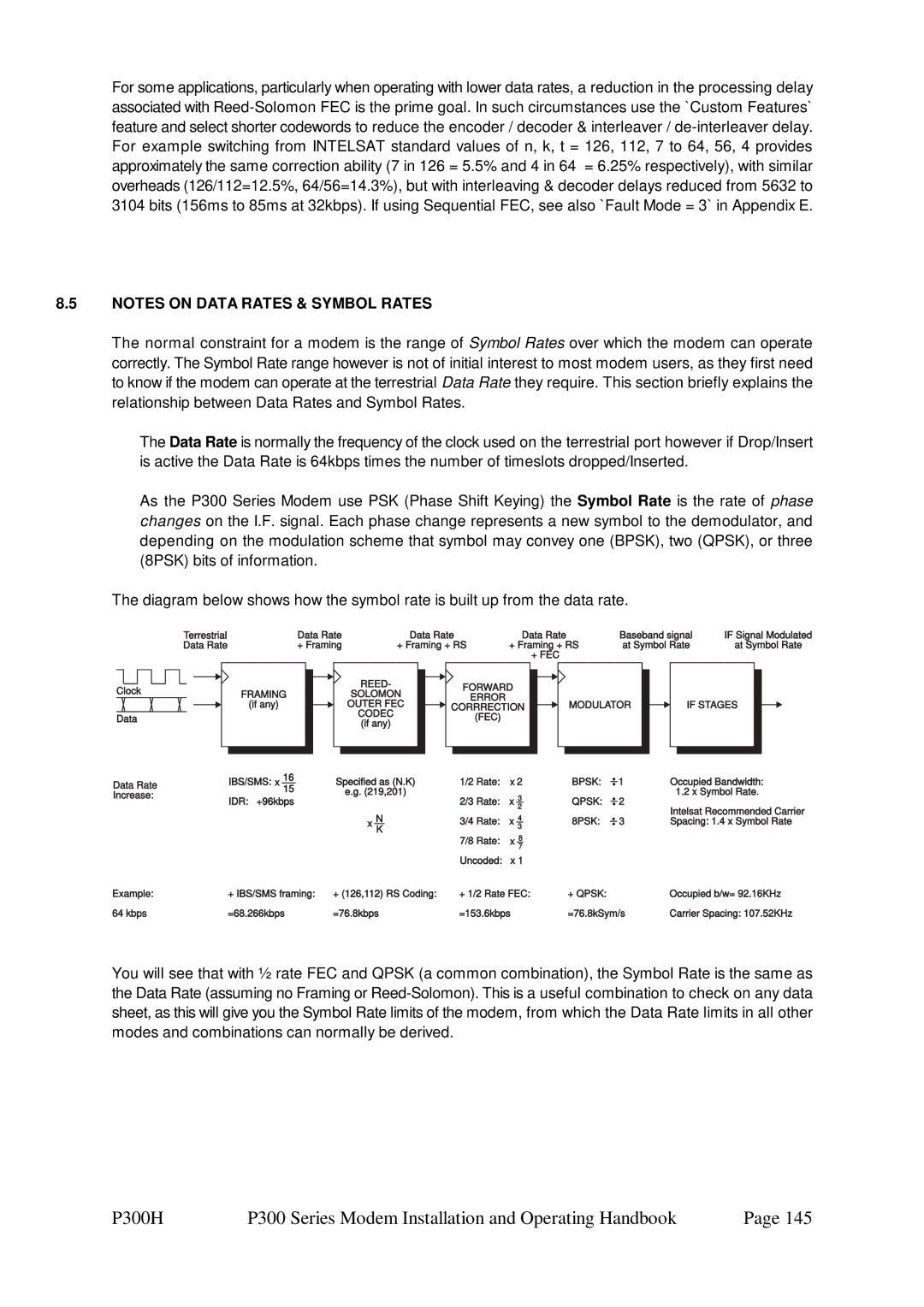
Introduction to REED-SOLOMON
Change, Tx/Rx, Mod/Demod, REED-SOLOMON Menu
Intelsat
Tx RS outer codec ? =Off 2=INTELSAT n,k,t & depth 3=Other
Other
Non standard equipment which leads onto the following menus
Performance
Toggle Scramblers =IBS Off 2=RS N/A 3=V.35 On 4=Turbo N/A
Change, Tx/Rx, Mod/Demod, Scrambler-Custom Menu
Change, Tx, Modulator, Power Level Menu
Power Break Mute
Set Tx Power -15.3dBm Enter value ??.? YES, or to change
RTS Controlled
Change, Tx, Modulator, Aupc Menu
Change, Tx, Modulator, Aupc Software =V2.12
MON Dist
Change, Tx, Modulator, Aupc Mode Menu Modes are as follows
Monitoring and logging of distant performance
Self MON
Change, Tx, Modulator, AUPC, Tolerance Menu
Nominal
Freeze
Maximum
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/AUX/BA Menu
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Define IDR Menu
IDR Mode ESC & AUX Port Definitions
IDR 8k ESC ? =Off 2=Sync 3=Async
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Define IBS Menu
IBS Mode ESC & AUX Port Definitions
ESC Port ? =Off 2High Rate async channel
High Rate Async
Custom
Sync Aux circuit o/h usage ? =Maximum 2Custom
ALL Avail
Use 1=TS16=XXX 2=TS32b5&6=XXX YES =TS32b7&8=XXX 4=TS48=XXX
Custom IBS Overhead Allocation
Use 1=TS0b1=XXX 2=TS32b1=XXX =TS32b3=XXX 4=TS32b4=XXX
Baud Rate
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Async ESC Menu
Format
SET AS M&C
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Config Async, SET AS REM M&C
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Config Async, Baud Rate Menu
Local
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Interfaces Menu
Remote
Aux Interface
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Audio Levels89Menu
Eeee
Change, Tx/Rx, ESC/Aux/BA, Backward Alarms Menu
Aeee
Aooo
Change, Rx Menu Rx not set to follow Tx
CHANGE, RX Menu
Change, Rx, Baseband Menu
Change, Rx, Service Menu
Bearer Routing
Insert bearer ? =Loop Terr 2=Generate internally
Change, Rx, Baseband, Insert Mux, Partial, Data Select Menu
Sat TS 1-3 Toggle??-?? YES
Change, Rx, Buffer / Clocking, Station Clock Menu
Change, Rx, Buffer / Clocking Menu
Station clock connection ? 1=None 2Via BNC 3RS422
Station clock frequency 0kHz 10MHz ????? YES
Normal non-Insert Mux operation
Change, Rx, Buffer / Clocking, RX Clock Menu
Satellite
TX CLK
Station
Reference as backup in order to maintain the Rx traffic
Same rate
DCE CLK
Buffer size end-end 16ms 99ms ??ms YES
Change, Rx, Buffer / Clocking, Buffer Size Menu
Rx=Tx Active
Change, Rx, DEMOD’ Menu
Change, Rx, Demod’, if Frequency Menu
Change, Rx, Demod’, Modulation Menu
Oqpsk
BPSK, Qpsk & 8PSK
Exactly on frequency
Change, Rx, ESC/AUX/BA Menu
Change, Rx, Demod’ Aupc Menu
Change, Rx, RX=TX Menu
Set Rx=Tx, so most Rx parameters track Tx ? =Off 2=On
CHANGE, TERR-INTFC Menu
Terr-Interface Nothing to configure With card fitted YES
Terr interface 1Electrical 2Control Lines 3Card specific
Change, Terr-intfc, Electrical
Set T1 line length ?ft =133 2=266 3=399 4=533 5=655
Set G.703 line code ? 1=AMI 2=HDB3 Normal
Line RTS Tx input signal valid ? =Ignore 2=Active
Interface control lines? =Ignore all 2Active-configure
Change, Terr-intfc, Control Lines
Line DTR DTE Ready In ? =Ignore 2=Active
CHANGE, REM-M&C Menu
Rem M&C philosophy ? =Takeaway 2Giveaway+M&C Timeout
Local Control Take Away / Give Away Selection
Takeaway
Interface
Protocol
Address
Change, User-Opt, Thresholds Menu
CHANGE, USER-OPT Menu
User BER
Buffer Slip
Default Action
Enabled BER Action
Backalarm
Buffer Autocentre
Change, User-Opt, Operation, Terrestrial Menu
Default Auto
Bearer CRC
Bits
FEC
FAW
Prbs
IBS MF Period
Change, User-Opt, Operation, TERR/SAT Menu
Back ALM MAP
Buffer MF Slip
Spoof
Change, User-Opt, Display Menu Options are
Upgrade Messages
Status Screen
Change TIME/DATE Menu
Now 112935 on 12/06/97 OK yes Time adjust, 2 Date Adjust
BUC/LNB 1Tx/BUC 2Rx/LNB 3Tune Ref
CHANGE, BUC/LNB Menu
BUC Type
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, BUC Type Menu
Lower Frequency Limit Upper Frequency Limit Frequency Shift
Tx/BUC 1DC SupplyOn 210M RefOff 3Current Monitor2400 2800mA
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, DC & References Menu
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, SHF Power/Units Menu
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, SHF POWER/UNITS Menu
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, SHF Frequency Menu
Freq shift of upconverter13050 MHz 65535MHz ??.??? YES
Change, BUC/LNB, Tx/BUC, BUC Control Menu
1BUC On/OffOn 2BUC Attenuator7dB Power at BUC reads 32.7dBm
BUC
Description
Change, BUC/LNB, Rx/LNB, LNB Type Menu
Low Frequency Limit High Frequency Limit Frequency Shift
Change, BUC/LNB, Rx/LNB, SHF Frequencies Menu
Change, BUC/LNB, Rx/LNB, DC & References Menu
Freq shift of downconverter13050 MHz 65535MHz ??.??? YES
Tune Reference50% to nudge
Change, BUC/LNB, Tune Ref Menu
Monitor Menu
Monitor, Carrier IDs Menu
Monitor, Carrier IDs Menu
Monitor, Distant Eb/No & BER Menu
Distant end Eb/No=9.7dB Distant end final BER=1.3E-7
BUC Type Std Ku Modem/BUC Mode Terminal
Distant Eb/No9.7dB Target10.±0.5dB Delta power+1.5dB
Monitor, Aupc Menu
Limits +3.5 -1.0dB Slew10dB/min Comms lost actionNominal
Info Menu
BUC Type Std Ku Software ver 2 Power Class 2W = +33dBm
LOG Menu
Buffer %
Aupc Delta Power
Bert BER
TX Terr BER
Test 1Loopbacks Off 2RF & FEC Off PSU/Temp 4Int Bert ESC
Test Menu
FEC L
Framer output is also looped
FRM L
Remote R
Data is not looped back to the remote site
RS Corrections
TX CW
Main, ESC, or Aux channel, restoring normal operation
ESC / AUX
Main
Closed Network
IBS/SMS
Custom Framing
IDR
ONE Minute
Test, Int BERT, Pattern Menu Bert Pattern 1211-12047 2215-1
Manual
Bert
Errors
Loss#
Time
Slip Count Reset
Setup Menu
Action Menu
Buffer Centre
Service 1User Parameters 2Factory parameters
Service Menu
Help Menu
Help 1Emergency Tx Carrier Off 2Menu operation 3Glossary
Traffic for a few seconds
Range
Custom Framing Menus
Menu Screens for Specialist Options
=IBS 2=IDR
Overhead Mode ? =Normal 2=Min o/h to provide set ESC
Backward Alarm? =Normal 2=No Backward Alarm facility
MIN O/H
LOW
Change, Tx/Rx, Service, Custom, IDR Menu
High
IDR o/h ? 1=96k2x16k-Audio+32k-BER =64k2x16k-Audio only
1XAUDIO64K
NORMAL96K
No AUDIO32K
16k Modes
IBS/SMS Operation with 2048KBPS Continuous Data
2048K IBS mode ? =Normal 6.7% overhead 2=G.732 0% overhead
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Continuous, 2048k G.732 Menu IBS
Channel Assoc Sig CAS in TS16 ? =Normal No CAS 2=CAS
TS order 0, 17-31, 16 Toggle ??-?? YES Help
Timeslot re-order option ? 1=Normal linear 2=Re-order
Custom IDR Operation with 2048KBPS Continuous Data
2048k IDR mode ? 1=Normal
Change, Tx/Rx, Baseband, Continuous, 2048k Menu IDR
Frame as per normal IDR operation
Doppler & Plesiochronous Buffering
Application Notes
Determining Clocking Schemes and Buffer Size
Bs = .002 + 172800 x Ms x Lc + Rc Seconds
Determining Buffer Size
Which the Tx data was dropped
Partial Insert and Multidestinational Working
Optimum n,k,t
Choosing Optimum Custom Values of RS N&K
+ FEC
Allocated to the ESC
Determining Exact Maximum ESC Baud Rates
Closed Network Plus ESC
TS32 MF
Closed Network Plus ESC via the Custom Service menu
ESC channel `delayed character mode` very technical
E1CAS 2048kbps G.732 with Channel Associated Signalling
E1CCS 2048kbps G.732 with common Channel Signalling
Cross Reference to SDM300 D/I & Framing Modes
E1IBS 2048kbps with no assumed G.732 frame format
T1ESF & T1ESFS 1544kbps Extended Super Frame S Special
Configure as follows
T1 & T1S 1544kbps D4 Framed S Special
T1IBS 1544kbps in the same bandwidth as Normal 1536kbps IBS
History
V.35 Scramblers
Other Derivatives
1x10-8error rate Hopeless Data Invert
1x10-8error rate Hopeless Data invert and 1x10-8error rate
Hopeless Linkabit Data invert and 1x10-8error rate
FDC Linkabit Pattern Dependent
Introduction
Introduction to Aupc Automatic Uplink Power Control
Eb/No
Limit only
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
Configuring Aupc for operation
Accurately you wish to try and maintain the Eb/No
Target
No slew rate limit
Derivation of Eb/No from C+N/N
Tutorial on CARRIER/NOISE & Eb/No Measurements Introduction
RS Code Rate
Summary
12.4 Eb/No Explanatory Diagram
Tables to Convert C+N/N to Eb/No
Adjust for Modulation FEC Rate RS Codec
For 1 Operation
Switching Philosophy
Theory
Manual changeovers
Detected failures
Practical 1 for 1 Implementation
Flash Software Update
Boot Code Operation
Banks
Other Boot Code Options
Appendix a Data Interface Information General
Data Circuit Towards Modem TX
P1440 in RS422 Mode
Local Loop Remote Loop
P1440 in V.35 Mode
141 140
RS232
Shield
P1440 in RS232 Mode
Switch/Link Settings
P1440 in G.703 Mode
Line Code / Line Length
Sw2 position
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
DCE Operation
P1440 in X.21 Mode
Clocking Important
113 103 105 104 109 102 101 19, 20 RS422 Ground Screen
DTE Operation
With older equipment
MIL-STD-188-114A Interface
P1451 Eurocom D/1 `D` & `G` Plus MULTI-STANDARD Interface
Eurocom D/1 interface `D` operation
Eurocom D/1 interface `G` operation
All links settings are
Links
Direction
Pin Signal Name
Name-RS485 SA Bus Paradise
Name RS232
P200 / P230 / P230DI P1300 / P1301
Interconnecting Devices Using RS485
Connector
Connector type 9 Pin `D male
For 1 Interface
Serial In/Out
Connector type 15 pin `D male
Alarms & AGC Connector
Alarms Connector
Prompt Traffic a Tx or Rx traffic fault exists
Async ESC Connector
Async ESC Connector
RX Constellation Monitor Port
Differential Station Clock
Async Port for ESC or AUX Channels
Serial Port for LOG Printing or Embedded M&C Update
Standard Lead
Connector type 50 pin `D female
ESC/AUX & Backward Alarms Connector
ESC Port
Pin Number Sync Async RS 485 / RS422 usage RS 232 usage
Pin Number Sync Async RS422 usage
Aux Port
Pin Number Description
Audio Ports
Menu Opt
Backward Alarms
P300 Series Modem Hardware
Appendix C Upgrade Information
Appendix C2 Feature Screens
Appendix C1 Modem Capabilities & Upgrades
Determining the Hardware Capability of a Modem
Hardware
Features in use by current config C E P - S - W X - Read
Features in USE
Features Temporary
Features Hardware
Features Test
Letter Description of Feature
Alphabetic Feature List
Appendix C5 Upgrade Available
Appendix C3 Features on Demo Expire Soon
Appendix C6 Features not Available
Do not Ignore this Message
Summary
Appendix D Remote M&C Remote M&C Protocol
Character Format / Baud Rate
RS 485 `A` Line
Paradise / FDC
Message Structure
Fixed character 02H
`Body`, up to and including the asterisk
Fixed character 06H or 15H
SA-bus
Checksum As Master to Slave
Message Categories
List of All Remote M&C Messages
First Direction Avail
Build Name Filename
Relay Mode Setting
Appendix E Customer Specific Features
Cable & Wireless Alarms Summarise
Tx Carrier On/Off indication Software =V2.12
Default normal fault detection
Fault Mode Setting
Severely Degraded Phase noise mode
Max Sequential decoder gain
Disable the Upper Temperature Limit
Comstream Sequential Mode Software =V2.12
Fine AGC voltage Rx Signal level
Coarse AGC voltage Rx Signal level, default
Uncommitted DAC Output Control
Rx Eb/No Level
Distant end Eb/No Software versions =2.12
Aupc Delta Power Software versions =2.12
Standard Features specified in IBS/SMS definitions
IBS/SMS Service Features
Additional Features Paradise products
Appendix F Framing and DROP/INSERT Overview IBS/SMS Framing
TS32 Multiframe
Backward Alarm
Synchronous IBS Scrambler
Low Rate ESC Channel
P300H P300 Series Modem Installation and Operating Handbook
Common Channel Signalling CCS
Signalling Systems Introduction CCS, CAS & RBS
Channel Associated Signalling
Robbed Bit Signalling RBS
CAS Multiframe Summary
CAS Multiframe
32+ CAS =
Standard Features specified in IDR definitions
IDR Service Features
IDR Framing
Appendix G Fault Messages and Action Table
P300H P300 Series Installation and Operating Handbook
Relays To Terr To Sat Other
Text on Display Description / Cause / Notes
CM, TF
Relays To Terr To Sat
To try and maintain the set flange power
Rx Traffic Faults Rx OK LED Off and Rx Traffic prompt relay
TA,TC
To Sat Other
An open or short circuit
P300H P300 Series Installation and Operating Handbook
P300H P300 Series Installation and Operating Handbook
Actions Relays
P300H P300 Series Installation and Operating Handbook

![]() 1
1![]() 2
2![]() 3
3