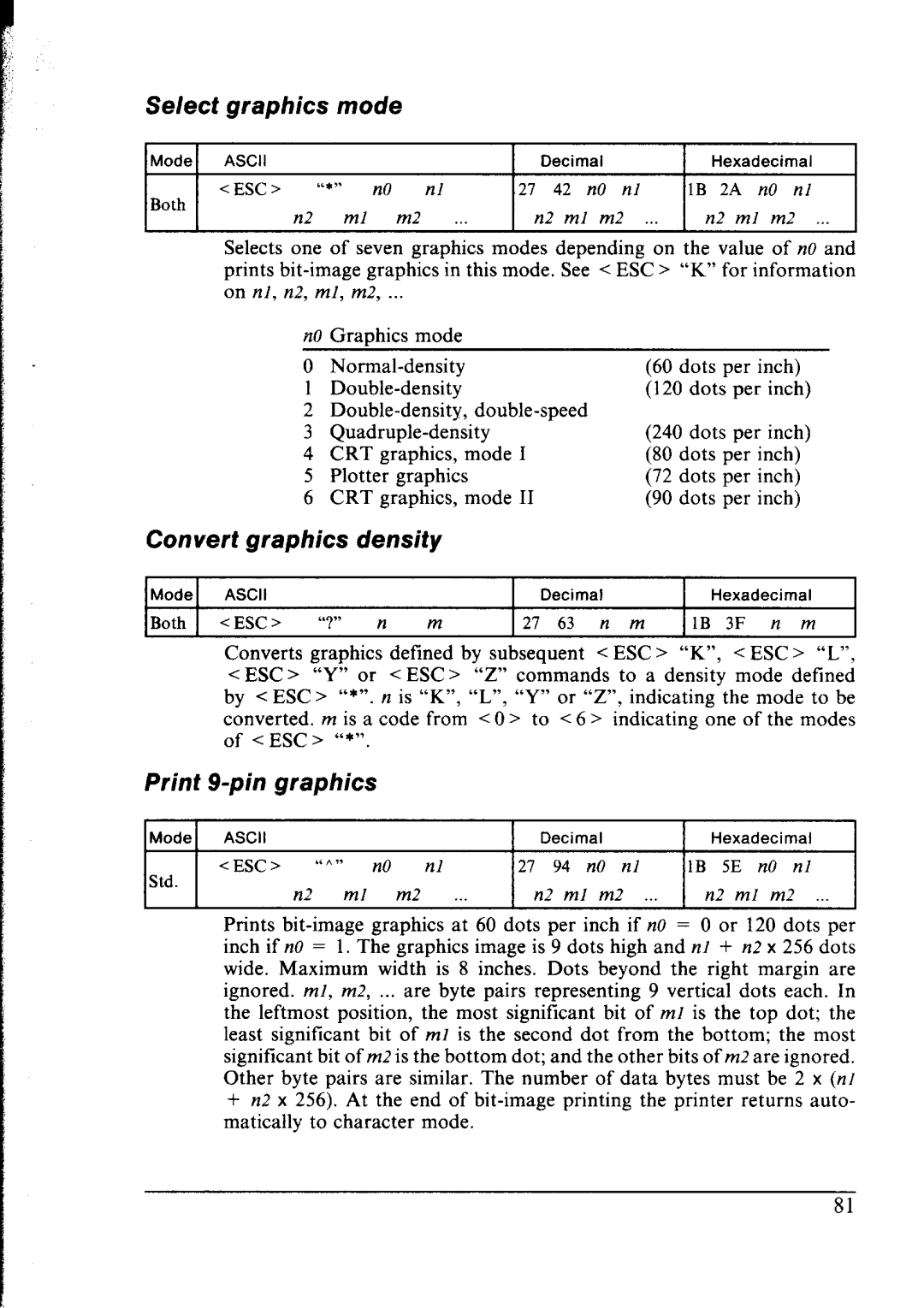
Select | graphics | mode |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Mode | ASCII |
|
| Decimal | Hexadecimal | ||||
Both | <ESC> | “*” n0 | nl | 21 | 42 | n0 nl | 1B 2A | n0 nl | |
n2 | ml | m2 | n2 | ml | m2 | n2 ml | m2 . | ||
| |||||||||
Selects one of seven graphics modes depending on the value of n0 and prints
on nl, n2, ml, m2, ..
n0 | Graphics mode |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
0 |
|
| (60 | dots | per | inch) | ||
1 |
|
| (120 | dots | per | inch) | ||
2 |
|
|
|
| ||||
3 |
|
| (240 | dots | per | inch) | ||
4 | CRT | graphics, | mode | I | (80 | dots | per | inch) |
5 | Plotter | graphics |
|
| (72 | dots | per | inch) |
6 | CRT | graphics, | mode | II | (90 | dots | per | inch) |
Convert | graphics | density |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Mode | ASCII |
|
|
|
|
|
| Decimal |
| Hexadecimal |
|
| ||||||
Both | <ESC> | “7,’ | n | m |
|
| 21 | 63 | n | m | 1B | 3F | n |
| m |
| ||
. |
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| Converts | graphics | defined by subsequent | < ESC > “K”, < ESC > “L”, | ||||||||||||||
| <ESC> | “Y” or | < ESC> | “Z” commands | to | a density | mode | defined | ||||||||||
| by | <ESC> |
| “*rr, | n is “K”, | “L”, | “Y” | or | “Z”, | indicating | the mode | to | be | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| converted. | m is a code | from | < 0 > | to | < 6 > indicating one of | the | modes | ||||||||||
| of | <ESC> |
| “*“. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Print |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Mode | ASCII |
|
|
|
|
|
| Decimal |
| Hexadecimal |
|
| ||||||
Std. | <ESC> | I“” |
| n0 | nl |
| 27 | 94 | n0 | nl | 1B | 5E | n0 | nl |
| |||
| n2 | ml | m2 |
|
|
| n2 | ml | m2 | n2 ml | m2 | ___ | ||||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Prints | |||||||||||||||||
| inch if n0 = 1. The graphics image is 9 dots high and nl + n2 x 256 dots | |||||||||||||||||
| wide. Maximum width is 8 inches. Dots beyond the right margin are | |||||||||||||||||
| ignored. ml, | m2, | ... are | byte | pairs | representing |
| 9 vertical | dots | each. | In | |||||||
the leftmost position, the most significant bit of ml is the top dot; the least significant bit of ml is the second dot from the bottom; the most significant bit of m2 is the bottom dot; and the other bits of m2 are ignored.
Other byte pairs are similar. The number of data bytes must be 2 x (nl
+n2 x 256). At the end of
81