5 Troubleshooting (continued)
5.2Troubleshooting Flow Charts (continued)
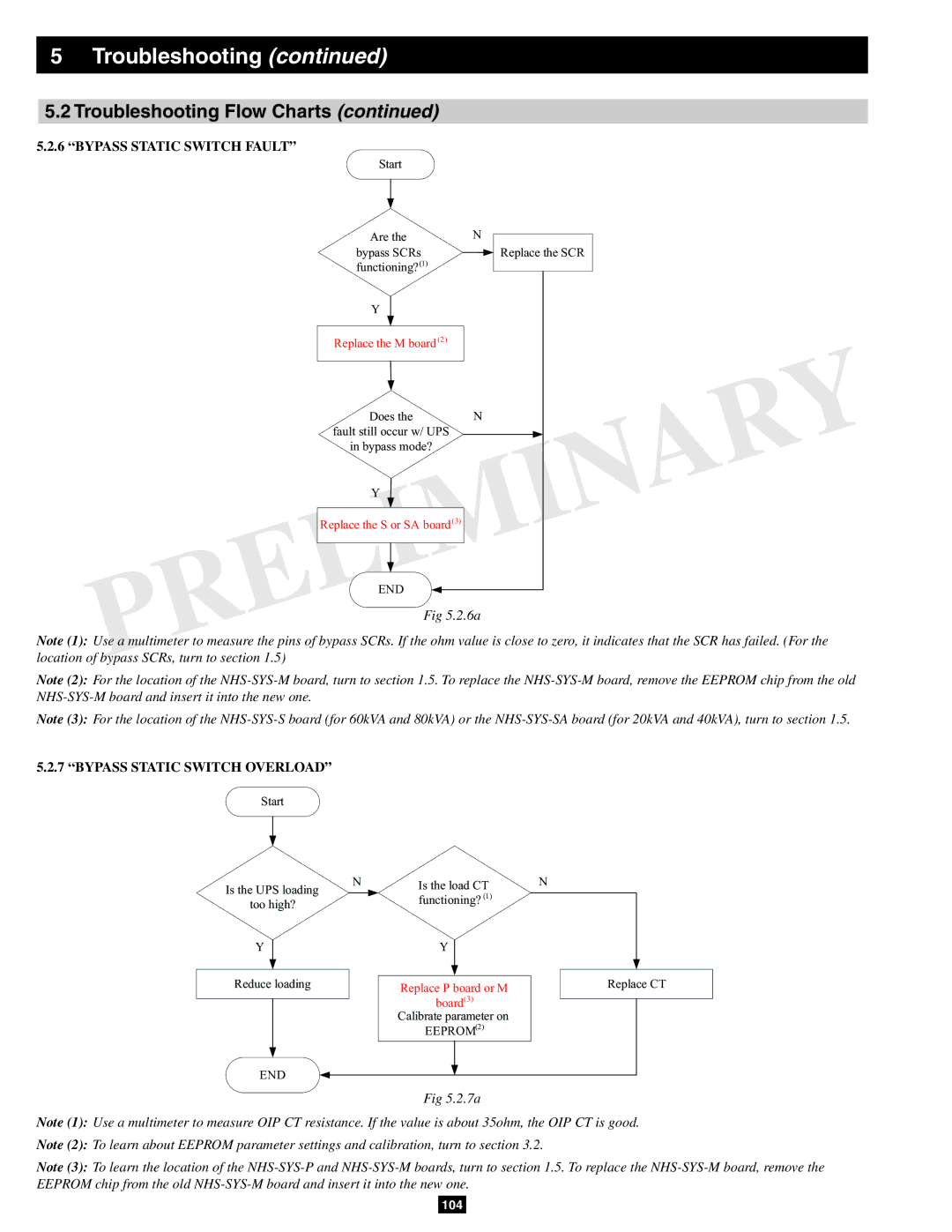
5.2.6“BYPASS STATIC SWITCH FAULT”
Start
Are the
bypass SCRs functioning?(1)
Y
Replace the M board (2)
Does the
fault still occur w/ UPS
in bypass mode?
Y
Replace the S or SA board(3)
END
N
![]() Replace the SCR
Replace the SCR
N
Fig 5.2.6a
Note (1): Use a multimeter to measure the pins of bypass SCRs. If the ohm value is close to zero, it indicates that the SCR has failed. (For the location of bypass SCRs, turn to section 1.5)
Note (2): For the location of the
Note (3): For the location of the
5.2.7“BYPASS STATIC SWITCH OVERLOAD”
Start
Is the UPS loading too high?
Y
Reduce loading
N
Is the load CT | N |
functioning? (1) |
|
Y
Replace P board or M
board(3) Calibrate parameter on
EEPROM(2)
Replace CT
END
Fig 5.2.7a
Note (1): Use a multimeter to measure OIP CT resistance. If the value is about 35ohm, the OIP CT is good.
Note (2): To learn about EEPROM parameter settings and calibration, turn to section 3.2.
Note (3): To learn the location of the
104