DAB (Digital Audio Broadcasting)
About DAB
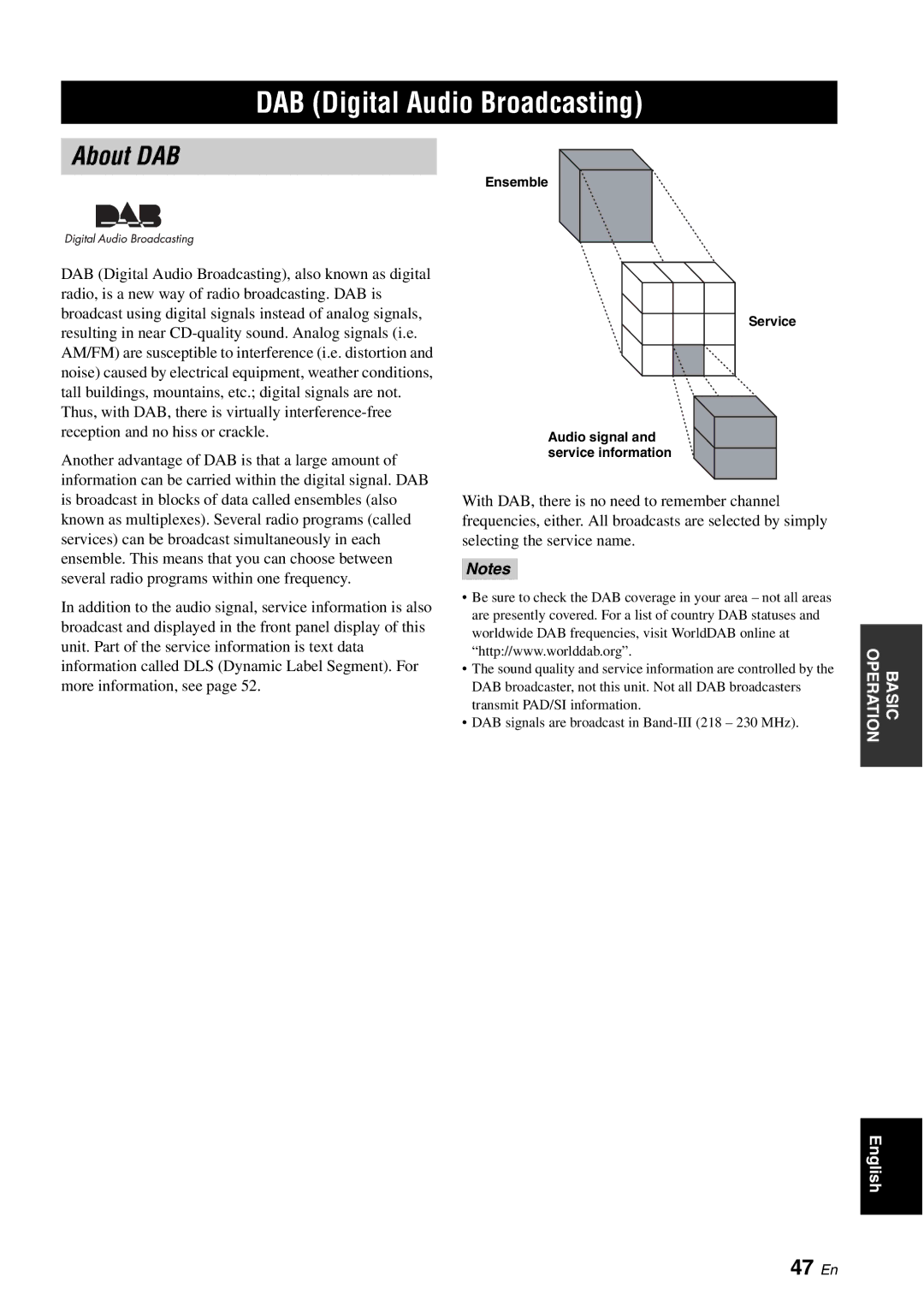
Ensemble
DAB (Digital Audio Broadcasting), also known as digital radio, is a new way of radio broadcasting. DAB is broadcast using digital signals instead of analog signals, resulting in near
Another advantage of DAB is that a large amount of information can be carried within the digital signal. DAB is broadcast in blocks of data called ensembles (also known as multiplexes). Several radio programs (called services) can be broadcast simultaneously in each ensemble. This means that you can choose between several radio programs within one frequency.
In addition to the audio signal, service information is also broadcast and displayed in the front panel display of this unit. Part of the service information is text data information called DLS (Dynamic Label Segment). For more information, see page 52.
Service
Audio signal and service information
With DAB, there is no need to remember channel frequencies, either. All broadcasts are selected by simply selecting the service name.
Notes
•Be sure to check the DAB coverage in your area – not all areas are presently covered. For a list of country DAB statuses and worldwide DAB frequencies, visit WorldDAB online at “http://www.worlddab.org”.
•The sound quality and service information are controlled by the DAB broadcaster, not this unit. Not all DAB broadcasters transmit PAD/SI information.
•DAB signals are broadcast in
OPERATION | BASIC |
|
|
English