Understanding RAID Levels and Concepts
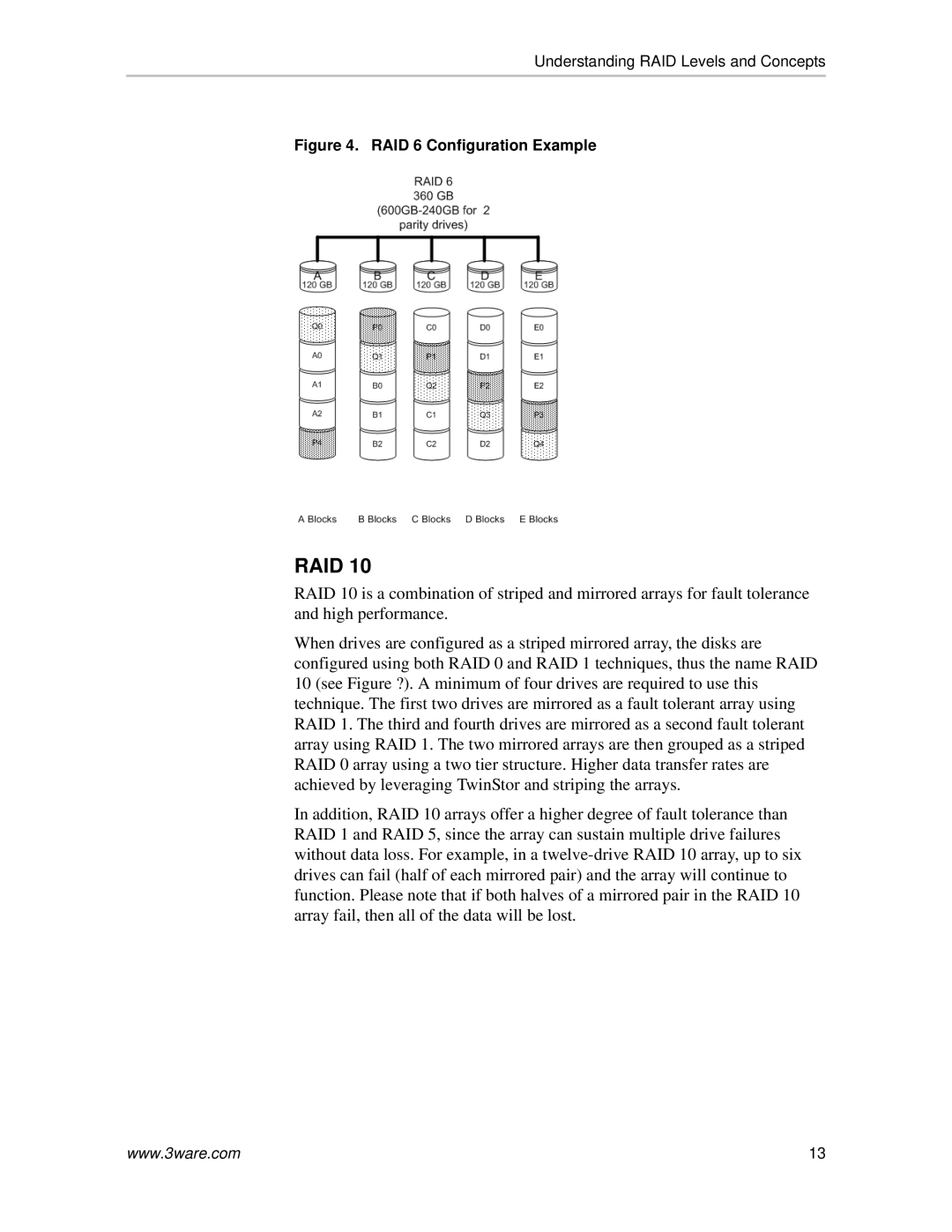
Figure 4. RAID 6 Configuration Example
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a combination of striped and mirrored arrays for fault tolerance and high performance.
When drives are configured as a striped mirrored array, the disks are configured using both RAID 0 and RAID 1 techniques, thus the name RAID 10 (see Figure ?). A minimum of four drives are required to use this technique. The first two drives are mirrored as a fault tolerant array using RAID 1. The third and fourth drives are mirrored as a second fault tolerant array using RAID 1. The two mirrored arrays are then grouped as a striped RAID 0 array using a two tier structure. Higher data transfer rates are achieved by leveraging TwinStor and striping the arrays.
In addition, RAID 10 arrays offer a higher degree of fault tolerance than RAID 1 and RAID 5, since the array can sustain multiple drive failures without data loss. For example, in a
www.3ware.com | 13 |