64 |
| The Unit Connectors | AXIS 2120 User’s Manual |
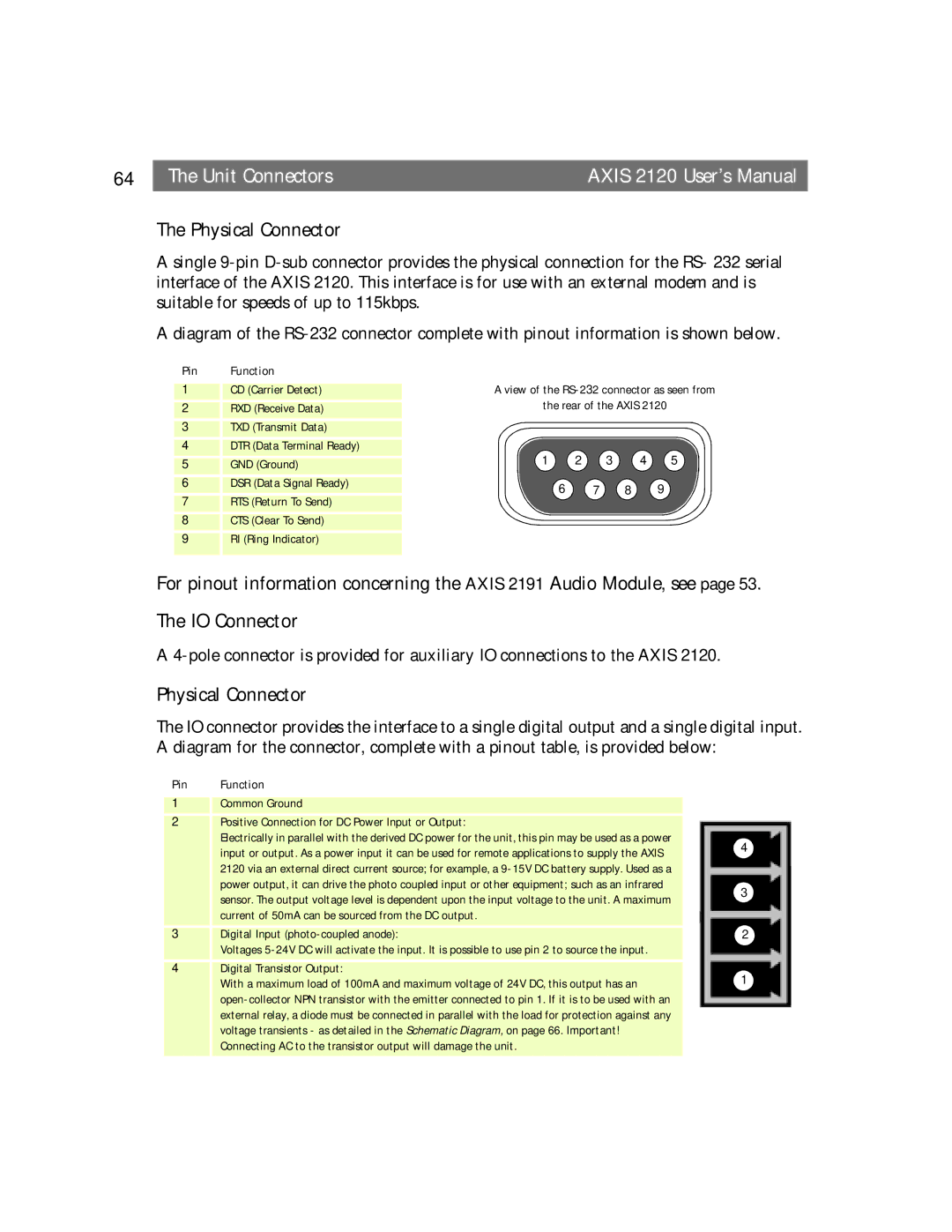
The Physical Connector
A single
A diagram of the
Pin | Function |
|
|
|
|
|
1 | CD (Carrier Detect) | A view of the | ||||
2 | RXD (Receive Data) | the rear of the AXIS 2120 |
| |||
3 | TXD (Transmit Data) |
|
|
|
|
|
4 | DTR (Data Terminal Ready) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
5 | GND (Ground) | |||||
6 | DSR (Data Signal Ready) | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|
7 | RTS (Return To Send) |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| ||
8 | CTS (Clear To Send) |
|
|
|
|
|
9 | RI (Ring Indicator) |
|
|
|
|
|
For pinout information concerning the AXIS 2191 Audio Module, see page 53.
The IO Connector
A
Physical Connector
The IO connector provides the interface to a single digital output and a single digital input. A diagram for the connector, complete with a pinout table, is provided below:
Pin | Function |
|
|
|
|
1 | Common Ground |
|
2 | Positive Connection for DC Power Input or Output: |
|
| Electrically in parallel with the derived DC power for the unit, this pin may be used as a power | 4 |
| input or output. As a power input it can be used for remote applications to supply the AXIS | |
|
| |
| 2120 via an external direct current source; for example, a |
|
| power output, it can drive the photo coupled input or other equipment; such as an infrared | 3 |
| sensor. The output voltage level is dependent upon the input voltage to the unit. A maximum | |
|
| |
| current of 50mA can be sourced from the DC output. |
|
3 | Digital Input | 2 |
| Voltages |
|
|
|
|
4 | Digital Transistor Output: | 1 |
| With a maximum load of 100mA and maximum voltage of 24V DC, this output has an | |
|
| |
| external relay, a diode must be connected in parallel with the load for protection against any |
|
| voltage transients - as detailed in the Schematic Diagram, on page 66. Important! |
|
| Connecting AC to the transistor output will damage the unit. |
|
|
|
|