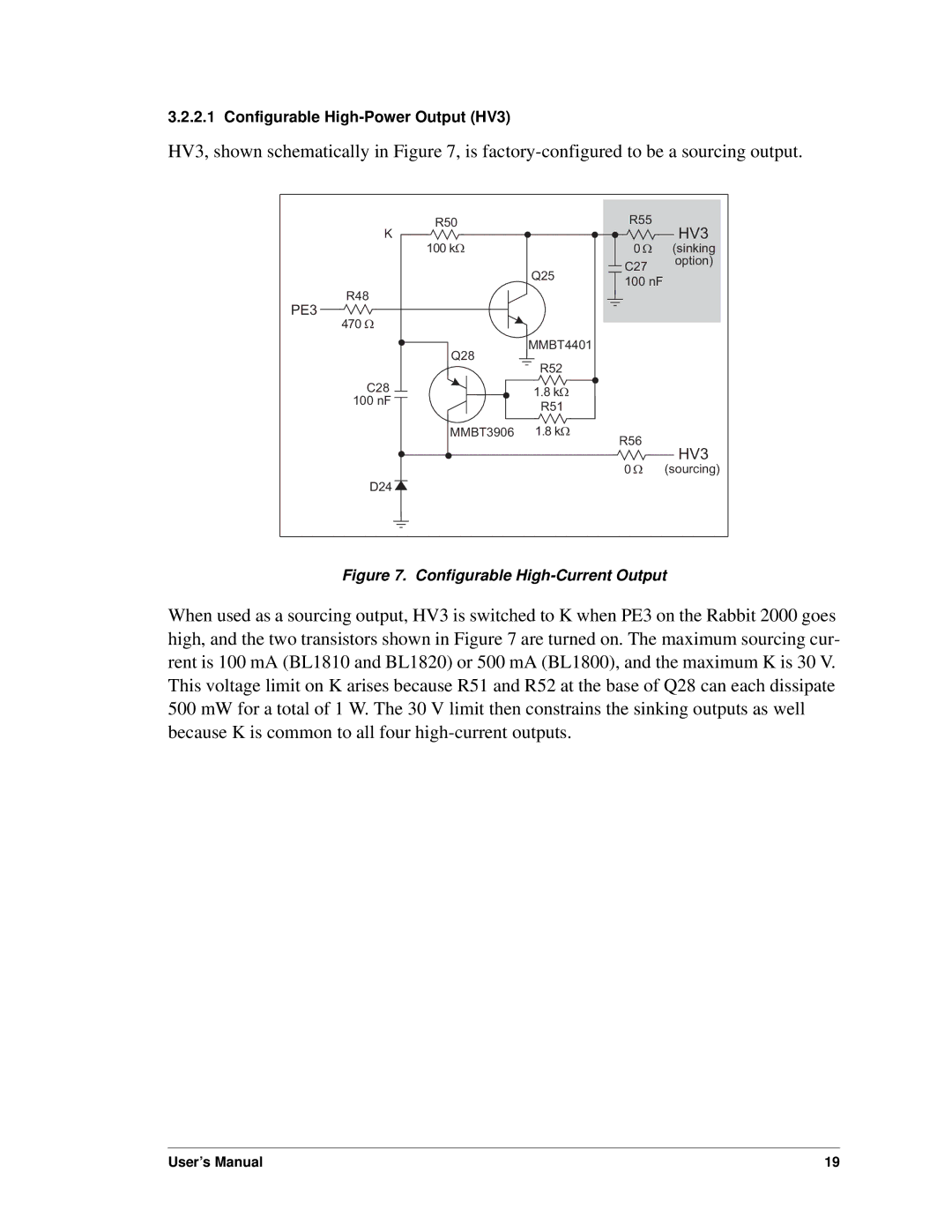
3.2.2.1 Configurable
HV3, shown schematically in Figure 7, is
R50 |
| R55 | HV3 |
K |
|
| |
100 kW |
| 0 W | (sinking |
|
| C27 | option) |
| Q25 |
| |
| 100 nF |
| |
R48 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
PE3 |
|
|
|
470 W |
|
|
|
Q28 | MMBT4401 |
|
|
R52 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
C28 | 1.8 kW |
|
|
100 nF |
|
| |
R51 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
MMBT3906 | 1.8 kW | R56 |
|
|
| HV3 | |
|
|
| |
|
| 0 W | (sourcing) |
D24 |
|
|
|
Figure 7. Configurable High-Current Output
When used as a sourcing output, HV3 is switched to K when PE3 on the Rabbit 2000 goes high, and the two transistors shown in Figure 7 are turned on. The maximum sourcing cur- rent is 100 mA (BL1810 and BL1820) or 500 mA (BL1800), and the maximum K is 30 V. This voltage limit on K arises because R51 and R52 at the base of Q28 can each dissipate 500 mW for a total of 1 W. The 30 V limit then constrains the sinking outputs as well because K is common to all four
User’s Manual | 19 |