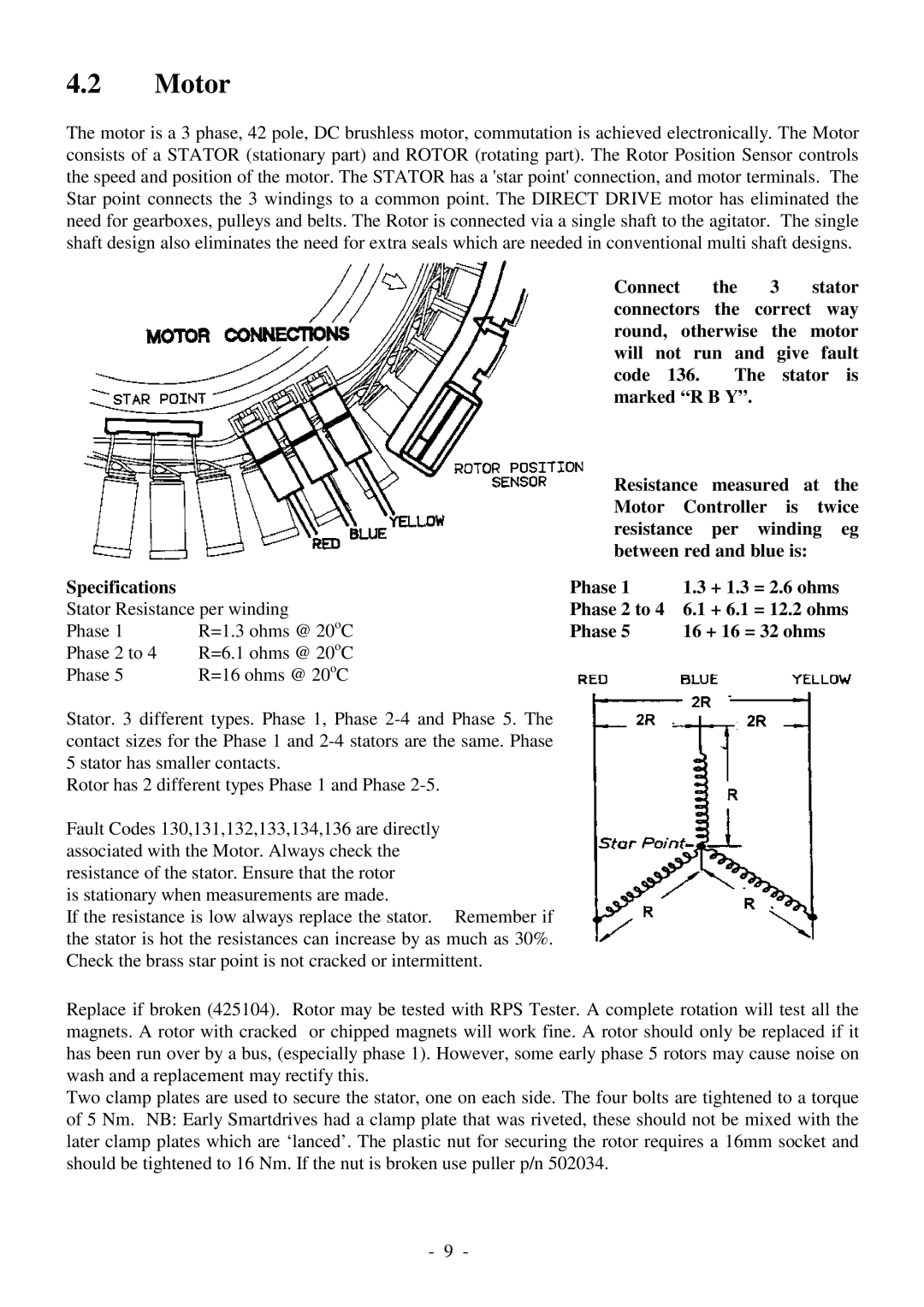
4.2Motor
The motor is a 3 phase, 42 pole, DC brushless motor, commutation is achieved electronically. The Motor consists of a STATOR (stationary part) and ROTOR (rotating part). The Rotor Position Sensor controls the speed and position of the motor. The STATOR has a 'star point' connection, and motor terminals. The Star point connects the 3 windings to a common point. The DIRECT DRIVE motor has eliminated the need for gearboxes, pulleys and belts. The Rotor is connected via a single shaft to the agitator. The single shaft design also eliminates the need for extra seals which are needed in conventional multi shaft designs.
Specifications
Stator Resistance per winding
Phase 1 | R=1.3 ohms @ 20oC |
Phase 2 to 4 | R=6.1 ohms @ 20oC |
Phase 5 | R=16 ohms @ 20oC |
Stator. 3 different types. Phase 1, Phase
Rotor has 2 different types Phase 1 and Phase
Fault Codes 130,131,132,133,134,136 are directly associated with the Motor. Always check the resistance of the stator. Ensure that the rotor
is stationary when measurements are made.
If the resistance is low always replace the stator. Remember if the stator is hot the resistances can increase by as much as 30%. Check the brass star point is not cracked or intermittent.
Connect the 3 stator connectors the correct way round, otherwise the motor will not run and give fault code 136. The stator is marked “R B Y”.
Resistance measured at the Motor Controller is twice resistance per winding eg between red and blue is:
Phase 1 1.3 + 1.3 = 2.6 ohms Phase 2 to 4 6.1 + 6.1 = 12.2 ohms
Phase 5 16 + 16 = 32 ohms
Replace if broken (425104). Rotor may be tested with RPS Tester. A complete rotation will test all the magnets. A rotor with cracked or chipped magnets will work fine. A rotor should only be replaced if it has been run over by a bus, (especially phase 1). However, some early phase 5 rotors may cause noise on wash and a replacement may rectify this.
Two clamp plates are used to secure the stator, one on each side. The four bolts are tightened to a torque of 5 Nm. NB: Early Smartdrives had a clamp plate that was riveted, these should not be mixed with the later clamp plates which are ‘lanced’. The plastic nut for securing the rotor requires a 16mm socket and should be tightened to 16 Nm. If the nut is broken use puller p/n 502034.
- 9 -