Thermal Solution
5.0Thermal Solution Requirements
5.1Characterizing the Thermal Solution Requirement
The idea of a “thermal characterization parameter” Ψ (the Greek letter psi), is a convenient way to characterize the performance needed for the thermal solution and to compare thermal solutions in identical situations (i.e., heating source, local ambient conditions, etc.). The thermal characterization parameter is calculated using total package power, whereas actual thermal resistance, θ (theta), is calculated using actual power dissipated between two points. Measuring actual power dissipated into the heat sink is difficult, since some of the power is dissipated via heat transfer into the package and board.
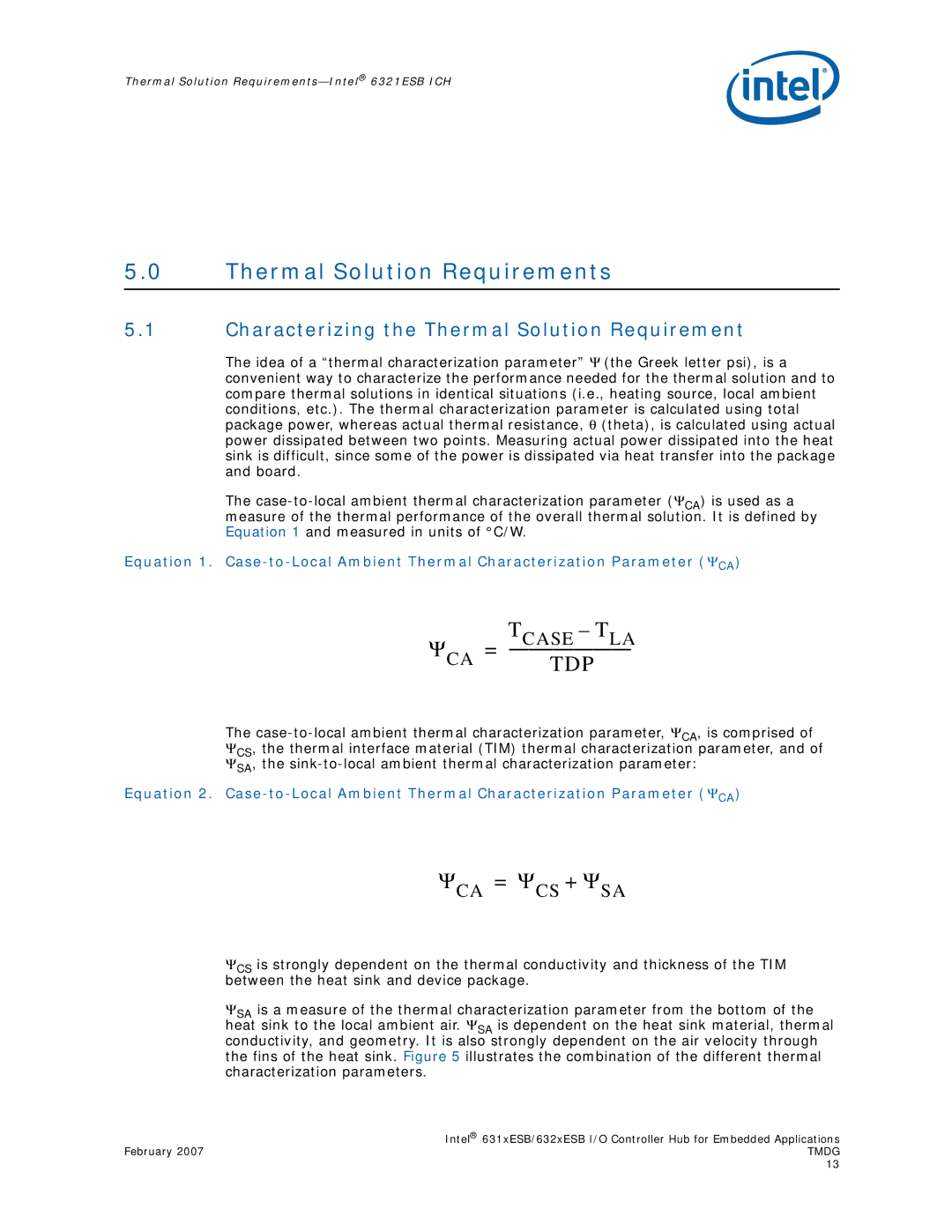
The
Equation 1.
ΨCA = | TCASE – TLA |
The
Equation 2.
ΨCA = ΨCS + ΨSA
ΨCS is strongly dependent on the thermal conductivity and thickness of the TIM between the heat sink and device package.
ΨSA is a measure of the thermal characterization parameter from the bottom of the heat sink to the local ambient air. ΨSA is dependent on the heat sink material, thermal conductivity, and geometry. It is also strongly dependent on the air velocity through the fins of the heat sink. Figure 5 illustrates the combination of the different thermal characterization parameters.
Intel® 631xESB/632xESB I/O Controller Hub for Embedded Applications
February 2007TMDG 13