THEORY OF OPERATION
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
DC GENERATOR MACHINES
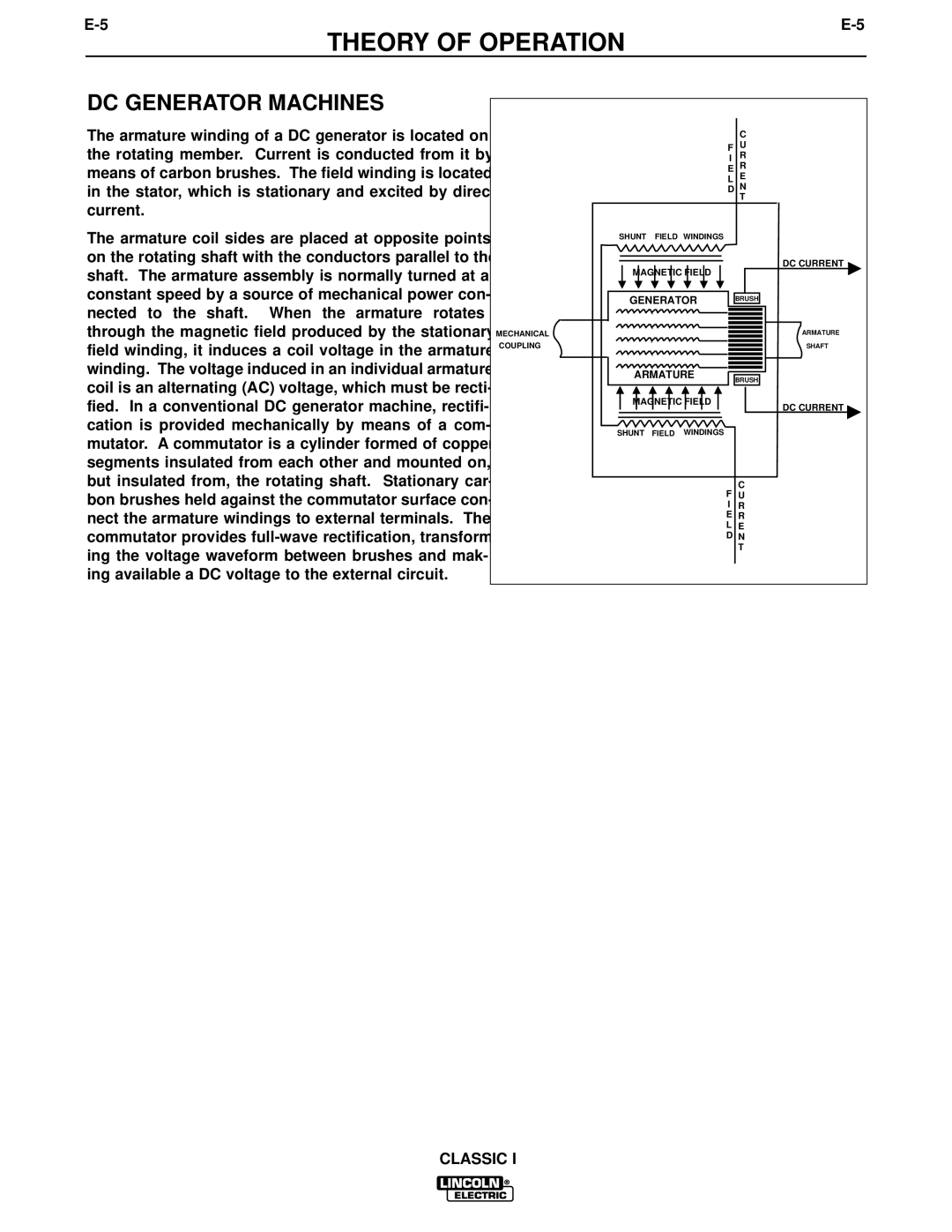
The armature winding of a DC generator is located on the rotating member. Current is conducted from it by means of carbon brushes. The field winding is located in the stator, which is stationary and excited by direct current.
The armature coil sides are placed at opposite points on the rotating shaft with the conductors parallel to the shaft. The armature assembly is normally turned at a constant speed by a source of mechanical power con- nected to the shaft. When the armature rotates through the magnetic field produced by the stationary field winding, it induces a coil voltage in the armature winding. The voltage induced in an individual armature coil is an alternating (AC) voltage, which must be recti- fied. In a conventional DC generator machine, rectifi- cation is provided mechanically by means of a com- mutator. A commutator is a cylinder formed of copper segments insulated from each other and mounted on, but insulated from, the rotating shaft. Stationary car- bon brushes held against the commutator surface con- nect the armature windings to external terminals. The commutator provides
|
| C |
| F | U |
| I | R |
| E R | |
| L | E |
| D N | |
|
| T |
SHUNT FIELD | WINDINGS |
|
MAGNETIC FIELD | DC CURRENT | |
| ||
GENERATOR | BRUSH | |
| ||
MECHANICAL |
| ARMATURE |
COUPLING |
| SHAFT |
ARMATURE | BRUSH | |
|
| |
MAGNETIC FIELD | DC CURRENT | |
|
| |
SHUNT FIELD | WINDINGS |
|
| F | C |
| U | |
| I | R |
| E R | |
| L | E |
| D N | |
|
| T |
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC