Troubleshooting Guide
IP88S36-T001-000
November, 2009 1st Edition IP88S36-T001-000
Copyright c 2009, NEC Corporation, All rights reserved
Correction of this manual
Introduction
Applicable product
Intended users
IP8800/S3600, IP8800/S2400
Troubleshooting Guide IP88S36-T001
Operation Commands, Vol.1 IP88S63-S006
IP8800/S6700, IP8800/S6600, IP8800/S6300
III
Introduction
Conventions abbreviations
BGP4+
CIR
MIP
Conventions kB, MB, GB, and TB
Page
Contents
Layer 2 Network Communication Failure
Layer 2 Authentication Communication Failure
Network Interface Communication Failure
IPv4 Network Communication Failure
Communication Failure on High-reliability Function 103
Problems on Power Saving Feature 123
When Resource Shortage Occurs in Shared Memory 135
Snmp Communication Failure 110
Writing to MC 152
Transferring Files for Maintenance Information 144
Testing Line 154
Restarting the System 160
Operations and actions
Safety guide for the IP8800/S6700 series
Symbols
Be careful in operation
Do not remove the device cover
Do not use power not specified
Do not place the device in an unstable location
Do not put foreign matters in the device
Grounding is required
Do not touch the potential tap
Handle the power cable with caution
Do not plug too many leads into a single outlet
Keep air dusters away from fire
Do not block the intake and/or exhaust port
Do not install the device in a humid or dusty environment
Do not stack the devices
Before carrying the device, remove the cables
Do not touch the inside of the device
Do not roughly handle the power cable
Do not drop an optional component
Be careful of laser beams
Lithium battery
Cleaning
An SFP-T has the following label attached
Handle a memory card with care
Do not attach a label or the like to the transceivers
Attach an option component with care
Do not bring a TV or radio close to the device
Handle the optical connector with care
Maintenance and cleaning
Use air dusters with care
Page
Safety Guide IP8800/S6600
Safety guide for the IP8800/S6600 series
Safety Guide IP8800/S6600
IP8800/S6604 45 kg/100 lb Or more IP8800/S6608 64 kg/142 lb
Xix
Model Mass Number of people
Label below is attached to the device
Keep air dusters away from fire
Model Items
Use support brackets only for IP8800/S6604
Use support brackets with care
IP8800/S6604
Do not block the intake and/or exhaust port
Do not roughly handle the power cable
Lithium battery
Handle a memory card with care
Attach an option component with care
Do not bring a TV or radio close to the device
Safety Guide IP8800/S6300
Safety guide for the IP8800/S6300 series
Safety Guide IP8800/S6300
Grounding is required
IP8800/S6304 45kg/100 lb Or more IP8800/S6308 64kg/142 lb
Keep air dusters away from fire
Use support brackets only for IP8800/S6304
IP8800/S6304
Do not block the intake and/or exhaust port
Do not roughly handle the power cable
Lithium battery
Handle a memory card with care
Damaged by the static electricity
Do not bring a TV or radio close to the device
Safety guide for the IP8800/S3600 and IP8800/S2400 series
Operations and Handling
Device in Trouble Action to Be Taken
Safety Guide IP8800/S3600 IP8800/S2400
Do not put foreign materials in the device
Do not use power not specified
Do not use the cable with the protection cap detached
Do not use too many plugs at a single outlet
Do not block the intake/exhaust port
Precaution on carrying the device
Xlvi
Be careful of the laser beams
Do not ride, recline, or place a heavy loading on the device
Do not bring a TV or radio close to the device
Before installing or Uninstalling
Handle a memory card and a dummy memory card with care
Discarding the device
Page
Overview
Failure Analysis Overview
Overview
Name Type Status Description
LED Indications, Switches, and Connectors
System and Partial Failure Analysis Overview
Overview Name Type Status Description
Connecting operation terminal
Failure Analysis for IP8800/S3600 and IP8800/S2400
Name Type Function Description
Lit in green Power on OFF Power OFF or power failure
Connector Memory card slot
LED Green
Sent/received
Overview Name Type Function Description
Orange 100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port
Blocked
Subitem Reference
Functional Failure Analysis Overview
Functional Failure Status and Reference
Overview Subitem Reference
Active BSU Switchover Is Disabled
Time Synchronization by NTP Is Disabled
Active System Switchover Is Disabled
Schedule Is Disabled IP8800/S6700
Page
Troubleshooting System Failures
Troubleshooting System Failures
Troubleshooting Procedure on System Failures
Troubleshooting System Failures
Failure Action
Power Failure Check Items
Troubleshooting System Failures Action
Replacement Method of Optional Components
Troubleshooting for IP8800/S3600 and IP8800/ S2400
Follow the steps in -4 Isolating Power Supply Failure
Failures on External Power Unit to isolate the failure
Isolating Power Supply Failure
Power failure according to -4 Isolating Power Supply
Isolating Failures on External Power Unit Main Body
Isolating Failures on External Power Unit
Isolating Failures on External Power Unit
Isolating Failures on Power Module
Replacement Method of System and Optional Components
Troubleshooting Functional Failures in Operation
Troubleshooting Functional Failures in Operation
Forgot the System Administrator Password
Problems on Login Password
Forgot the Login User Password
Problems and Actions When MC not found is displayed
Problems on MC
MC not found is displayed when MC is accessed
Instruction in -1 Problems and Actions When MC
Unable to Input/Display from the Console Correctly
Problems on Operation Terminal
Problems and Actions When Connecting to Console
System and Partial Failure Analysis Overview
Symptom Action to Be Taken or Reference
Login from the Remote Operation Terminal Is Failed
Problems and Actions When Connecting to Modem
Disabled, check No or later
Login Authentication Using RADIUS/TACACS+ Is Disabled
Command Authorization Using RADIUS/TACACS+ Is Disabled
Some users remain in the login
Troubleshooting Functional Failures in Operation
Ethernet Port Cannot Be Connected
NIF Status Problem Action
Network Interface Communication Failure
Checking port status
Check and Action for Port Status
Port Status Problem Action
Checking statistical information
Checking BSU/PSP operation status
Communication Failure in Basic Switching Unit BSU/PSP
BSU Operation Problem Action Status
Check and Action for BSU/PSP Operation Status
Actions against Troubles on 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/ 1000BASE-T
Status, see 3.20 Problems on Redundant
Configuration of Basic Switching Unit BSU
Troubleshooting for Failed 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T
Troubleshooting Steps Problem Action
Actions against Troubles on 1000BASE-X
10 Failure Analysis Method for Troubles on 1000BASE-X
Actions against Troubles on 10GBASE-R
11 Failure Analysis Method for Troubles on 10GBASE-R
Communication Failure on Using PoE
Troubleshooting Steps and Command Action
Check the setting of failed link aggregation
Communication Failure on Using Link Aggregation
Function of the port by the power inline command
Allocations
Link aggregation group is Disabled and Down
Check the setting of failed port status using
CH Disabled
Tion, set the Duplex mode to Full
Checking Vlan status
Layer 2 Communication by Vlan Is Disabled
Layer 2 Network Communication Failure
Checking MAC address table
Take the action below according to the Type displayed
Flooding is executed if the MAC address is not displayed
Failures on Using Spanning Tree
Checking filtering/QoS
See 3.4 Network Interface Communication Failure
Failures on Using Ring Protocol
14 Spanning Tree Failure Analysis Method
15 Ring Protocol Failure Analysis Method
Replace the faulty Parts
Troubleshooting Steps Action Command
Analysis Flow
See the manual Configuration Guide
Command to check timer values for
Transmission delay is not considered
Spanning tree or Gsrp is used at Configurations Same time
Multicast Relay by Igmp snooping Is Disabled
Show system command
16 Troubleshooting on Multicast Relay
Has been set up appropriately for system operation
Multicast in the VLAN. IP8800/S3600
If a multicast router is connected, check mrouter-port
Group address
Multicast Relay by MLD snooping Is Disabled
Is it a relay within the same VLAN?
17 Troubleshooting on Multicast Relay
Check the following You want to use IPv6 multicast at
Using the show mld-snooping
Communication Is Disabled or Is Disconnected
IPv4 Network Communication Failure
Checking log
Route
Checking ARP resolution information with neighboring system
Checking interface status
Checking unicast routing information
Checking DHCP/BOOTP setting information
Checking filtering/QoS setting information
Checking option license OP-NPAR OP-NPAR
IP Addresses Cannot Be Assigned Using Dhcp Function
DHCP/BOOTP relay communication failure
Checking route information
Checking ARP resolution information with neighboring system
Checking the log and interface
Dhcp server communication trouble
Checking filtering/QoS setting information
Checking DHCP/BOOTP setting information
Associated with each log message
Checking configuration
Checking the log message and interface
DynamicDNS Cooperation in Dhcp Function Is Disabled
Checking layer 2 network
DNS update disabled Check the configuration
System
Checking route information
No Ospf Routing Information Exists
IPv4 Unicast Routing Communication Failure
No RIP Routing Information Exists
18 RIP Failure Analysis Method
20 BGP4 Failure Analysis Method
No BGP4 Routing Information Exists
No Routing Information Exist OP-NPAR
21 VRF Failure Analysis Method
Common check items
Communication on IPv4 PIM-SM Network Is Disabled
IPv4 Multicast Routing Communication Failure
22 Common Check Items
BSR check items
23 BSR Check Items
Rendezvous point router check items
Last-hop-router check items
24 Rendezvous Point Router Check Items
26 first-hop-router Check Items
Multicast Data Is Double-relayed on IPv4 PIM-SM Network
First-hop-router check items
28 Common Check Items
Communication on IPv4 PIM-SSM Network Is Disabled
27 Check Items When Double-relay Continues
Multicast Sender First-hop-router Last-hop-router Data
29 last-hop-router Check Items
Multicast Data Is Double-relayed on IPv4 PIM-SSM Network
30 first-hop-router Check Items
32 Check Items for VRF
31 Check Items When Double-relay Continues
5 IPv4 Multicast Communication Failure In VRF OP-NPAR
Is Double-relayed on IPv4 PIM-SSM Network
IPv6 Network Communication Failure
Checking unicast interface information
Checking NDP resolution information with neighboring system
Checking the log and interface
Configuration is not distributed
2 IPv6 Dhcp Troubleshooting
Checking RA setting information
Check the status of IPv6DHCP server
Checking the status of the IPv6 Dhcp server in this system
See the manuals Message Log Reference
Procedure to check configuration
Duplicate acquisition by the client
Condition Cause Binding Information Route Information
Checking client setting
Procedure for restoring from duplicate distribution
Deleting the file containing Duid information
Reconfiguring route information
If Duid of this system conflicts with other system
Reproducing the Duid
Checking the Duid
No OSPFv3 Routing Information Exists
10 IPv6 Unicast Routing Communication Failure
No RIPng Routing Information Exists
35 Failure Analysis of RIPng
37 BGP4+ Failure Analysis Method
Hop address resolution in BGP4+ exist Exists
No BGP4+ Routing Information Exists
Go to No.5 if no route exist
38 Common Check Items
Communication on IPv6 PIM-SM Network Is Disabled
11 IPv6 Multicast Routing Communication Failure
Relay target group address Rendezvous point setting
Neighboring router using the show ipv6 pim
Command with interface parameter specified
If the unicast route does not exist, see 3.10 IPv6 Unicast
40 Rendezvous Point Router Check Items
Multicast receiver Configuration to run MLD
39 BSR Check Items
41 last-hop-router Check Items
42 first-hop-router Check Items
43 Check Items When Double-relay Continues
Multicast Data Is Double-relayed on IPv6 PIM-SM Network
To the ports to which neighboring routers connect
Communication on IPv6 PIM-SSM Network Is Disabled
44 Common Check Items
45 last-hop-router Check Items
Group join function is running
Multicast Data Is Double-relayed on IPv6 PIM-SSM Network
46 first-hop-router Check Items
For MLD snooping
47 Check Items When Double-relay Continues
48 Ieee 802.1X Failure Analysis Method
Layer 2 Authentication Communication Failure
Communication Failure on Using Ieee
Authentication dynamic mode, go to No
Following cause. Check to see if there is any problem
Table setting failed
To see if authentication failed
Authentication dynamic. Match the Vlan ID set for
Command and check to see if dynamic
Assignment of Vlan authentication
Tunnel-Type for the Radius server to VLAN13
Communication Failure on Using Web Authentication
50 Failure Analysis Method for Web Authentication
IPv4 access list are set in the access list as well
Check to see authentication Ipv4 access list
Confirm that authentication IPv4 access list is applied
Port for authentication
When Web Server Is restarted Using
Authenticated
Command Soon After Suspended
Restarted. The Web server starts to perform authentication
Setting Information
51 Checking Web Authentication Configuration
Check Point Troubleshooting Steps
52 Web Authentication Failure Analysis Method
Failure Analysis Method for Web Authentication
Communication Failure on Using MAC Authentication
53 Failure Analysis Method for MAC Authentication
Authentication is displayed by the show To No.7
IPv4 access list is applied
Not applied to the port for authentication
Configuration command mac-authentication port
55 MAC Authentication Failure Analysis Method
Communication Failure on Using Authentication Vlan OP-VAA
54 Checking MAC Authentication Configuration
Failure Analysis Method for MAC Authentication
56 Authentication Vlan Failure Analysis Method
100
101
57 Checking Authentication Vlan Configuration
When Vlan Identification Table Resource Shortage Occurs
102
Communication Failure on High-reliability Function
Gsrp Communication Failures
60 Analysis Method for Gsrp Unknown Adjacency
104
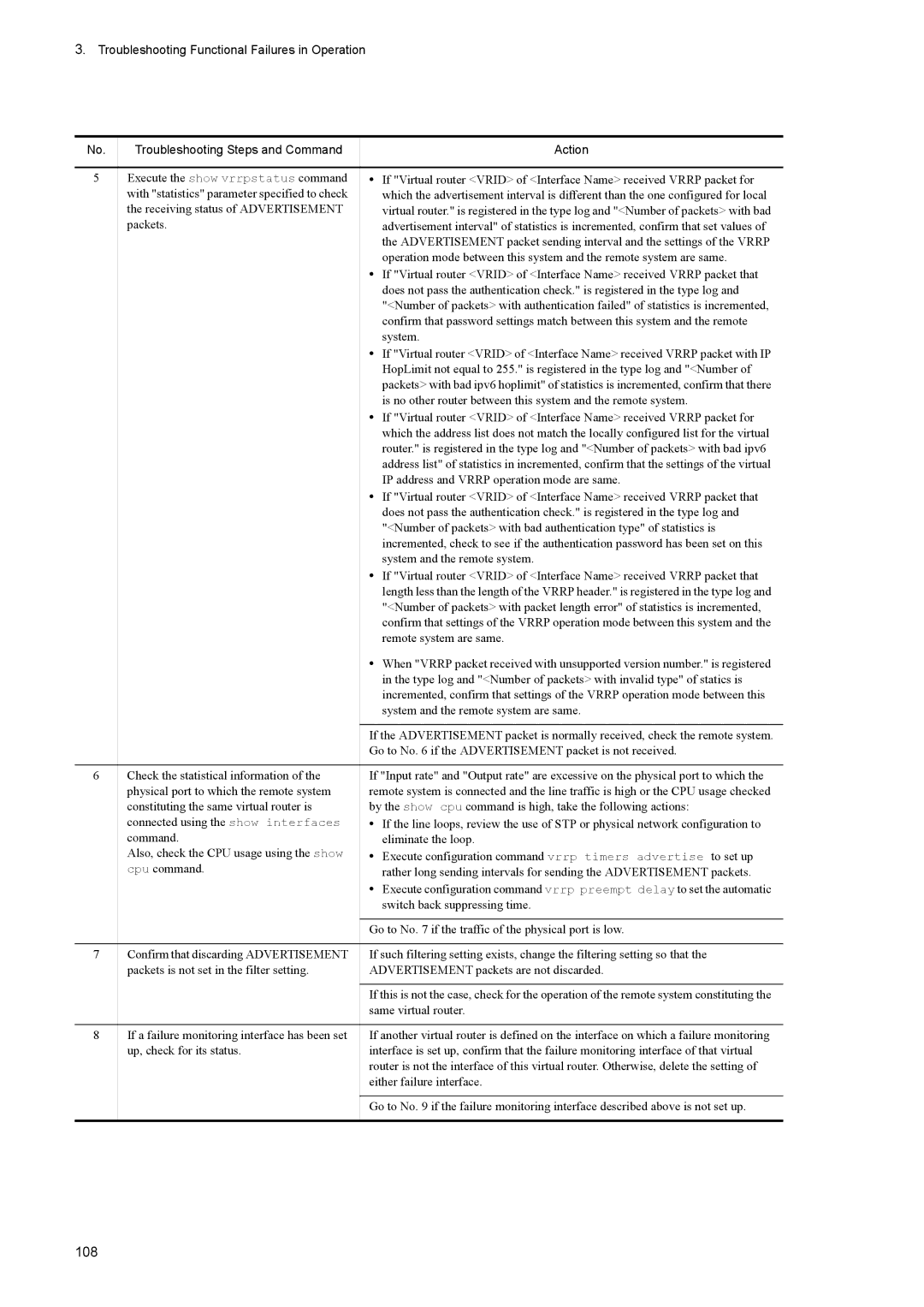
61 Vrrp Failure Analysis Method
105
106
62 Vrrp Failure Analysis Method
107
108
Set up, and the virtual router may operate. IP8800/S3600
109
Traps Cannot Be Received by Snmp Manager
Snmp Communication Failure
MIBs Cannot Be Obtained from Snmp Manager
111
SFlow Packets Do Not Reach Collector
Checking operation status by operation command
Checking configuration Checking failures etc
Checking route to the collector
Checking configuration
Collector information must be set correctly
114
Checking settings of collector
Checking NIF/port status
Checking presence/absence of the relay packet
Flow Sample Does Not Reach Collector
Counter Sample Does Not Reach Collector
Checking transmission interval of counter sample
Network Interface Communication Failure
63 Failure Analysis Method When Using Lldp Functions
64 Failure Analysis When Using Oadp Function
Otherwise, see 3.4 Network Interface Communication Failure
Checking Filtering/QoS Setting Information to check for it
117
Otherwise, see 3.5 Layer 2 Network Communication Failure
65 NTP Failure Analysis Method
Time Synchronization by NTP Is Disabled
NTP Communication Failure
Communication Failure on IEEE802.3ah/UDLD Function
Port Becomes Inactive Due to IEEE802.3ah/UDLD Function
Cause for Switchover Disabled Troubleshooting Steps
Active System Switchover Is Disabled
67 Problems and Actions When Switching Active System
Active BSU Switchover Is Disabled
68 Failure Analysis Method When BSU Switchover Disabled
122
Boards
Schedule error caused by
Problems on Power Saving Feature
Set to disabled, delete the entry that is
Display of Result Confirmation Cause Action
Disconnected
Neighboring system in 3.6.1 Communication Is Disabled or Is
Neighboring system in 3.9.1 Communication Is Disabled or Is
125
Checking packet discarding by filtering
Communication Failure Caused by Settings of Filtering/QoS
Checking Filtering/QoS Setting Information
IP8800/S3600 and IP8800/S2400
127
Page
IP8800/S6700 IP8800/S6600 IP8800/S6300
129
Operation Log Message for Checking Resource Usage
MAC Address Table Resource Shortage
Checking Resource Usage of MAC Address Table
Operation Log Message for Checking Resource Use Status
131
File Name Specified for get Log Message
132
Checking Vlan Identification Table Resource Usage
Entry to Be Cleared Step
Vlan setting.*1
Vlan Identification Table Entry Clear Method
Tag translation function
When Resource Shortage Occurs in Shared Memory
Checking Resource Usage of Shared Memory
Page
Collecting Failure Information
137
Collecting Failure Information
Collecting Failure Information
Available Information via ftp
File Name Specified for get Acquiring Basic Information
Collecting basic information
139
140
Collecting Failure Information Using dump Command IP8800
Collecting memory dump when communication failure occurs
After above log is displayed, execute next the dump command
141
142
143
Storage Location and File Name File Transfer
Transferring Files for Maintenance Information
Maintenance Information
145
Transferring Files Using ftp Command
Transferring dump files to the remote operation terminal
146
ETA
147
Transferring log information to a console
Transferring failure backup information files to a console
Transferring dump files to a console
148
IP8800/S6700 IP8800/S6600 IP8800/S6300
149
File Name Specified for Acquired Files
Files That Can Be Acquired Using ftp Command
150
10 Collecting Dump Files from the Remote Terminal
151
Writing File to MC Using Operation Terminal
Writing to MC
Line Test
153
Checking frame loopback within system
Testing Line
Ethernet Port
Line Test Type for Each Frame Loopback Point
Command IP8800/S6700 IP8800/S6600 IP8800/S6300
155
Checking frame loopback at a loop connector
156
157
Page
Restarting the System
159
Restarting the System
Restarting the System
Specifying when
161
Set the system to restart Or stop
Parameter to input Active Standby None
162
163
Collect Memory dump? Memorydump is Restart?
Dump Back to command input mode
164
Collecting memory
Appendix
165
Appendix a Contents of show tech-support Command Display
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
Table A-2 Details of Display Contents IP8800/S3600
IP8800/S3600
175
Log information during software
Update for Ver.11.1 and later
176
Information 2 for Ver.10.7 Earlier
177
178
179
180
181
Table A-3 Details of Display Contents IP8800/S2400
IP8800/S2400
182
183
Information on L2 loop detection For Ver.10.7 and later
184
Built-in WEB authentication DB For Ver.10.3 and later
Authenticated user account
MLD snooping group information
185
Page
Index
187
188
Index