72
2. RAID Levels
This section details the RAID levels which the disk array controller can support.
2-1. Characteristics of RAID Levels
The table below lists the characteristics of the RAID levels.
Level | Function | Redundancy | Characteristics |
RAID0 | Striping | No | Data read/write at the highest rate |
|
|
| Largest capacity |
|
|
| Capacity: (capacity of single HDD) × |
|
|
| (number of HDDs) |
RAID1 | Mirroring | Yes | Two HDDs required |
|
|
| Capacity: capacity of single HDD |
RAID5 | Striping of both data | Yes | Three or more HDDs required |
| and redundant data |
| Capacity: (capacity of single HDD) × |
|
|
| ((number of HDDs) - 1) |
RAID10 | Combination of striping | Yes | Four HDDs required |
| and mirroring |
| Capacity: (capacity of single HDD) × 2 |
2-2. RAID0
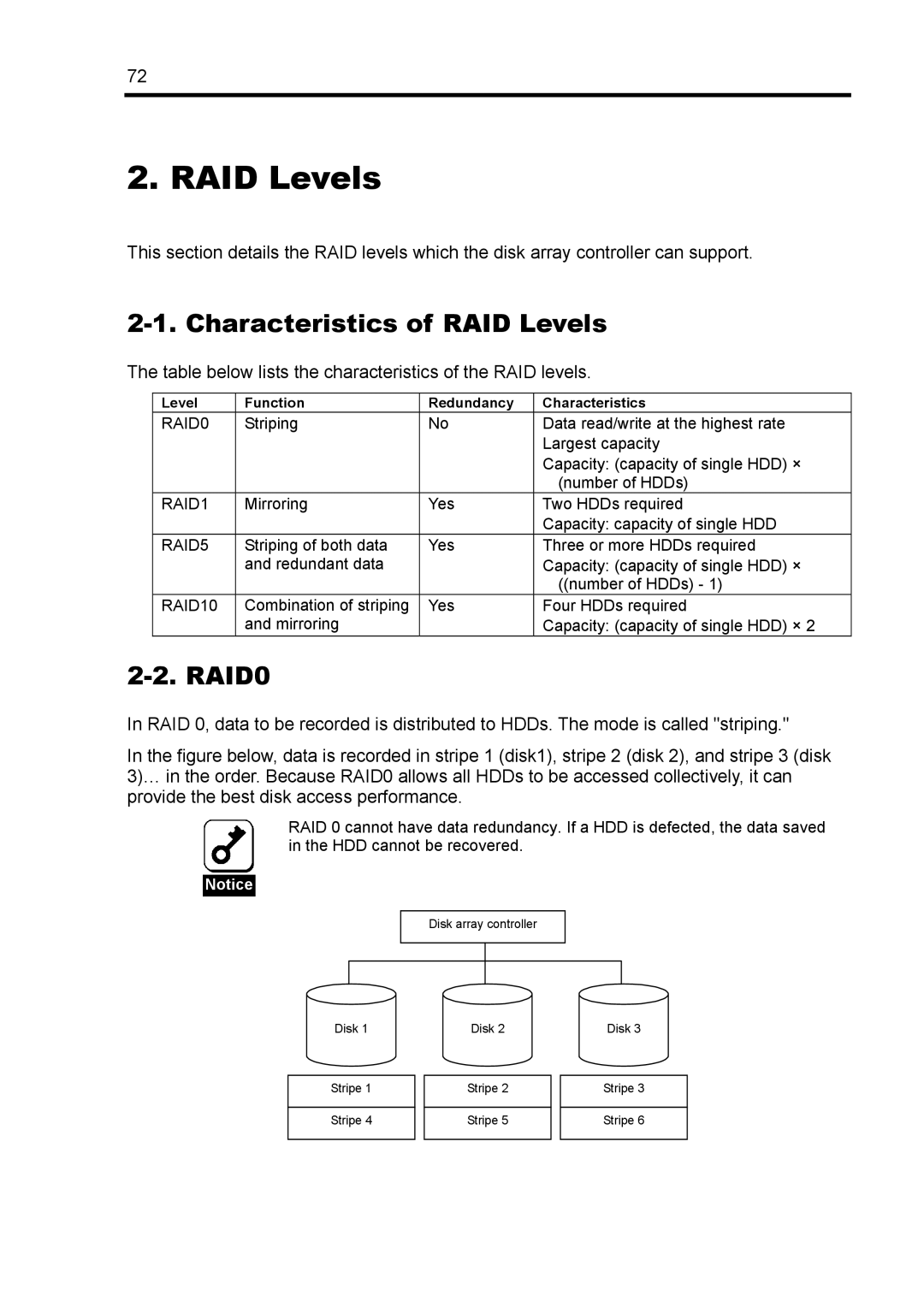
In RAID 0, data to be recorded is distributed to HDDs. The mode is called "striping."
In the figure below, data is recorded in stripe 1 (disk1), stripe 2 (disk 2), and stripe 3 (disk 3)… in the order. Because RAID0 allows all HDDs to be accessed collectively, it can provide the best disk access performance.
RAID 0 cannot have data redundancy. If a HDD is defected, the data saved in the HDD cannot be recovered.
Notice
Disk array controller
Disk 1
Stripe 1
Stripe 4
Disk 2
Stripe 2
Stripe 5
Disk 3
Stripe 3
Stripe 6